Your Location:Home >Products >OLED intermediates >Thiophenes >65016-55-9


Product Details
Chemical Properties
Colorless liquid
Uses
Conducting polymer precursor.
InChI:InChI=1/C14H24S/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-14-11-12-15-13-14/h11-13H,2-10H2,1H3
The isomers of 3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadienal, more commonly known together as citral, are two of the most notable natural compounds in the flavor and fragrance industry. However, both isomers are inherently unstable, limiting their potential use in various applications. To identify molecules in nature that can impart the fresh lemon character of citral while demonstrating stability under acidic and thermal conditions has been a major challenge and goal for the flavor and fragrance industry. In the study of fried chicken, several alkyl thiophenecarbaldehydes were identified by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and gas chromatography-olfactometry that provided a similar citral-like aroma. The potential mechanism of formation in fried chicken is discussed. Furthermore, in order to explore the organoleptic properties of this structural backbone, a total of 35 thiophenecarbaldehyde derivatives were synthesized or purchased for evaluation by odor and taste. Certain organoleptic trends were observed as the length of the alkyl or alkenyl chain increased or when the chain was moved to different positions on the thiophene backbone. The 3-substituted alkyl thiophenecarbaldehydes, specifically 3-butyl-2-thiophenecarbaldehyde and 3-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-2-thiophenecarbaldehyde, exhibited strong citrus and citral-like notes. Several alkyl thiophenecarbaldehydes were tested in high acid stability trials (4 °C vs 38 °C) and outperformed citral both in terms of maintaining freshness over time and minimizing off-notes. Additional measurements were completed to calculate the odor thresholds for a select group of thiophenecarbaldehydes, which were found to be between 4.7-215.0 ng/L in air.
A practical and convenient Co-catalyzed alkylation method for the facile introduction of various alkyl chains into organic electronically significant heteroaryl compounds, including thiophenes, furans, selenophenes, and pyrroles, is reported. Under well-optimized reaction conditions, a wide range of alkylated heteroaryl compounds have beeen efficiently prepared in moderate to good isolated yields. Notably, 2- or 3-alkylthiophenes, which play a decisive role in polymer chemistry and organic materials, have been synthesized step-economically for the first time by this reductive-coupling methodology using inexpensive cobalt salts as catalysts. This straightforward synthetic procedure avoids the preparation of moisture-unstable organometallic reagents (RMgX or RZnX) required in conventional alkylation protocols. Various alkyl chains have been introduced into organic, electronically important heteroaryl compounds step-economically through Co-catalyzed reductive alkylation reactions. The resulting alkylheteroarenes are indispensable building blocks for polymer chemistry and π-functional organic materials.
This paper reports the synthesis and the linear and non-linear absorption properties of a series of new tetrazine-based D-π-A-π-D and D-π-A type dyes. In these derivatives, a central tetrazine core was connected with one or two terminal triphenylamine moi
Conjugated systems built by connecting one electron-donor triphenylamine to an electron-withdrawing tetrazine have been prepared using various linkers. We describe here the synthesis, the electrochemical properties and some photophysical properties of the
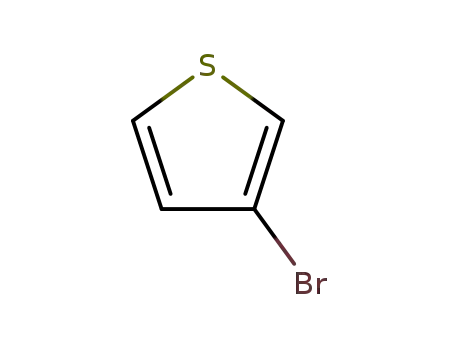
3-Bromothiophene

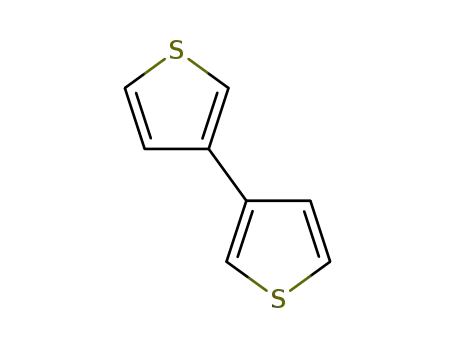
3,3'-bithiophene
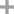

3-decylthiophene
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
1-bromo dodecane;
With
magnesium;
1,3-bis[(diphenylphosphino)propane]dichloronickel(II);
In
2-methyltetrahydrofuran;
at 20 ℃;
for 2.5h;
3-Bromothiophene;
In
2-methyltetrahydrofuran;
at 20 ℃;
Product distribution / selectivity;
|
30.0 - 94.6 %Chromat. 0.9 - 2.3 %Chromat. |

3-Bromothiophene

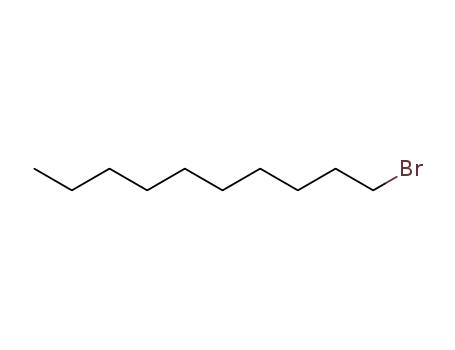
1-bromo dodecane


3,3'-bithiophene


3-(1-methylpentyl)thiophene


3-decylthiophene
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
3-Bromothiophene; 1-bromo dodecane;
With
magnesium;
1,3-bis[(diphenylphosphino)propane]dichloronickel(II);
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 20 ℃;
for 48h;
3-Bromothiophene;
In
2-methyltetrahydrofuran;
at 20 ℃;
Product distribution / selectivity;
|
1.7 - 64.5 %Chromat. 0.5 - 9.8 %Chromat. 3.34 %Chromat. |
|
3-Bromothiophene; 1-bromo dodecane;
With
magnesium;
1,3-bis[(diphenylphosphino)propane]dichloronickel(II);
In
tetrahydrofuran; tert-butyl methyl ether;
at 20 ℃;
for 15h;
3-Bromothiophene;
In
2-methyltetrahydrofuran;
at 20 ℃;
Product distribution / selectivity;
|
86.7 %Chromat. 5.6 %Chromat. 1.59 %Chromat. |

3-Bromothiophene
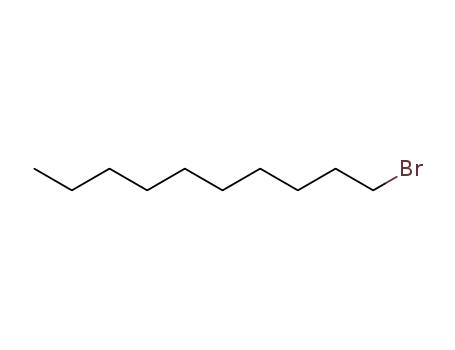
1-bromo dodecane
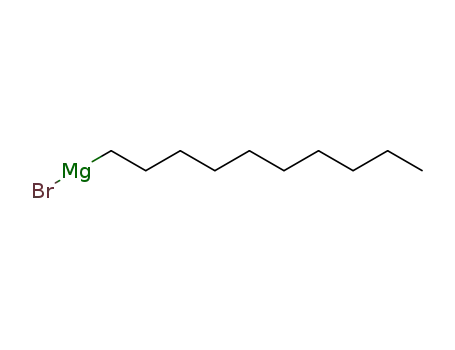
n-decyl magnesium bromide

Iododecane
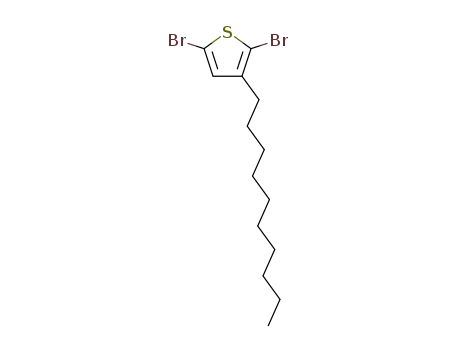
2,5-dibromo-3-decylthiophene

2-bromo-3-decylthiophene
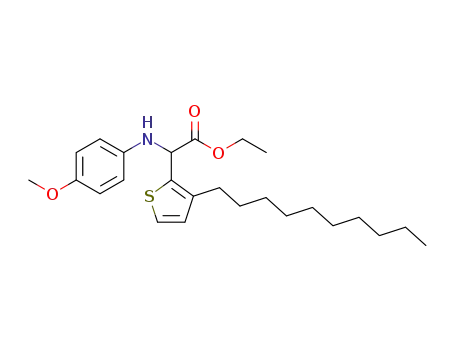
ethyl (4-methoxyphenylamino)(3-decylthiophen-2-yl)acetate

5,5'''-dibromo-3,3'''-didecyl-2,2':5',2'':5'',2'''-quaterthiophene
CAS:56131-46-5
Molecular Formula:C6H5BrClN
Molecular Weight:206.47
Purity:99%
CAS:19438-60-9
Molecular Formula:C9H12O3
Molecular Weight:168.19
CAS:144012-09-9
CAS:139100-06-4