Your Location:Home >Products >OLED intermediates >Thiophenes >1795-01-3
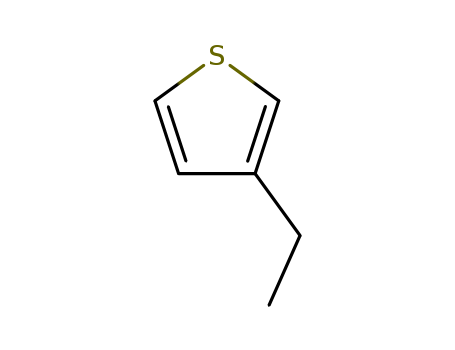

Product Details
Chemical Properties
Colorless to light yellow liquid
Uses
3-Ethylthiophene is used in preparation of 2-amino-N-(amino-oxo-aryl-λ6-sulfanylidene)acetamide compounds and their therapeutic use.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Synthetic Communications, 16, p. 689, 1986 DOI: 10.1080/00397918608057741
InChI:InChI=1/C6H8S/c1-2-6-3-4-7-5-6/h3-5H,2H2,1H3
A series of organometallic complexes [Cl(dppe)2Ru?C≡C-(3-R?C4H2S)-C≡C?Ru(dppe)2Cl] (3-R-C4H2S=3-substituted thienyl moiety; R=?H, ?C2H5, ?C3H7, ?C4H9, ?C6H13, ?OMe, ?CN in 5 a–5 g respectively) have been synthesized by systematic variation of 3-substituents at the thienylethynyl bridging unit. The diruthenum(II) wire-like complexes (5 a–5 g) have been achieved by the reaction of thienylethynyl bridging units, HC≡C-(3-R-C4H2S)-C≡CH (4 a–4 g) with cis-[Ru(dppe)2Cl2]. The wire-like diruthenium(II) complexes undergo two consecutive electrochemical oxidation processes in the potential range of 0.0 - 0.8 V. Interestingly, the wave separation between the two redox waves is greatly influenced by the substituents at the 3-position of the thienylethynyl. Thus, the substitution on 3-position of the thienylethynyl bridging unit plays a pivotal role for tuning the electronic properties. To understand the electronic behavior, density functional theory (DFT) calculations of the selected diruthenium wire-like complexes (5 a–5 e) with different alkyl appendages are performed. The theoretical data demonstrate that incorporation of alkyl groups to the thienylethynyl entity leaves unsymmetrical spin densities, thus affecting the electronic properties. The voltammetric features of the other two Ru(II) alkynyl complexes 5 f and 5 g (with ?OMe and ?CN group respectively) show an apparent dependence on the electronic properties. The electronic properties in the redox conjugate, (5 a+) with Kc of 3.9×106 are further examined by UV-Vis-NIR and FTIR studies, showing optical responses in NIR region along with changes in “?Ru?C≡C?“ vibrational stretching frequency. The origin of the observed electronic transition has been assigned based on time-dependent DFT (TDDFT) calculations.
In terms of the in-depth development of organic dyes, targeted and selective energy control is becoming a more and more important objective. Herein, four indoline sensitizers based on D-π-A-π-A construction were designed and synthesized with exactly the same donor and acceptor segments. Their molecular planarity was regulated by introducing various side chains into donor bridges. Interestingly, along with an improvement of planarity at a donor bridge, the HOMO levels of the dyes lift gradually, and more importantly, their LUMO levels remain at around the same value. Besides, better molecular planarity is obviously preferred to obtain higher charge injection efficiency but, an overly planar molecule may cause an overly high HOMO level, leading to poor dye regeneration efficiency. Furthermore, an appropriate side chain also restrains charge recombination to some extent, while an overly large side chain gives more chance for I3- to recombine with charge in the conduction band. Accordingly, our results demonstrated that regulation of planarity at a donor bridge not only provides targeted and selective control of the HOMO of the dye, but also enable fine adjustment with multiple interfacial charge transfer processes. Molecular planarity deserves to play an important role in the design of organic dyes, providing a significant strategy for the further development of organic sensitizers.
The transformations of alkylthiophenes in the presence of amorphous aluminosilicate and decationated zeolite HNaY were studied. Substituted thiophenes with R = 2- and 3-Me, 2-Et, and 2-iso-Pr undergo dealkylation to thiophene with close rates, migration of the alkyl group from the 9α- to the β-position of the thiophene ring (or in the opposite direction with an elevated rate), and decomposition with H2S elimination. The dealkylation rate of 2-substituted thiophenes with a branched-chain radical (R = iso-Pr, terf-Bu) is much higher and the elimination rate with this radical is lower than those for normal-chain radicals; the isomerization step is virtually absent. Di-, tri-, and tetrasubstituted thiophenes with R = Et and iso-Pr undergo stepwise dealkylation, which is facilitated by an increase in the degree of substitution on the thiophene ring. Thiophene and its lower homologues can be obtained by the transformation of a mixture of high-molecular thiophenes. Copyright
Congeners of the potent dopamine (DA) re-uptake inhibitor l-[1-(2- benzo[b]thiophenyl)cyclohexyl]piperidine (BTCP) are unexpectedly able to bind in the rat cerebellum, although this structure is devoid of dopaminergic nerve endings. In line with previous studies the hypothesis that they bind to low affinity PCP sites labelled with [3H]TCP in the rat cerebellum, even though they do not bind to the high affinity PCP sites in the forebrain, was considered. Analogues of l-[1-(2-thiophenyl)cyclohexyl]piperidine (TCP) and BTCP with a modified aromatic moiety and with O or S atoms substituted in the cyclohexyl ring were prepared and tested in competition experiments both in rat forebrain and cerebellum membranes labelled with [3H]TCP, and in rat striatum membranes labelled with [3H]BTCP. Results indicated that BTCP and congeners could bind to low affinity PCP sites labelled with [3H]TCP in the rat cerebellum with a decrease of the selectivity for the DA transporter. On the contrary, some TCP analogues displayed a very high selectivity for these low affinity sites: they might be important pharmacological tools to elucidate the nature and function at yet unknown of these sites. (C) 2000 Editions scientifiques et medicales Elsevier SAS.
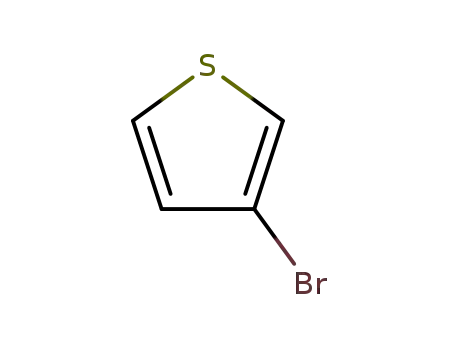
3-Bromothiophene
ethyl bromide

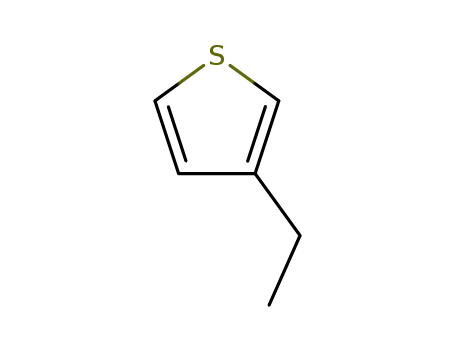
3-ethylthiophene
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
1,3-bis[(diphenylphosphino)propane]dichloronickel(II); magnesium;
1.) Et2O, 2.) heating, 15 h;
|
67% |
|
With
1,3-bis[(diphenylphosphino)propane]dichloronickel(II); magnesium;
Yield given. Multistep reaction;
1.) ether, 2.) ether, reflux, 15 h;
|
|
|
With
1,3-bis[(diphenylphosphino)propane]dichloronickel(II); magnesium;
Yield given. Multistep reaction;
1.) diethyl ether, room temperature, 1 h, 2.) diethyl ether, -78 deg C -> room temperature;
|
|
|
With
1,3-bis[(diphenylphosphino)propane]dichloronickel(II); magnesium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
for 24h;
Reflux;
|
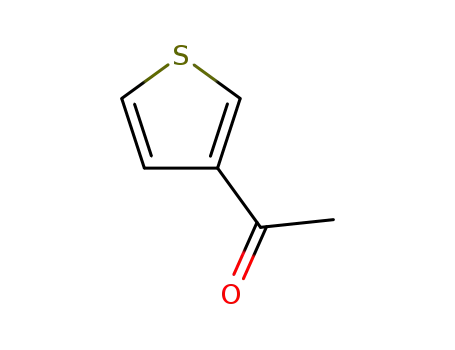
1-(thiophen-3-yl)-ethanone


3-ethylthiophene
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
potassium hydroxide; hydrazine hydrate;
In
ethylene glycol;
at 160 - 180 ℃;
for 1h;
|
86% |
|
With
potassium hydroxide; hydrazine hydrate;
In
ethylene glycol;
for 1h;
Heating;
|

3-Bromothiophene

ethyl bromide

1-(thiophen-3-yl)-ethanone
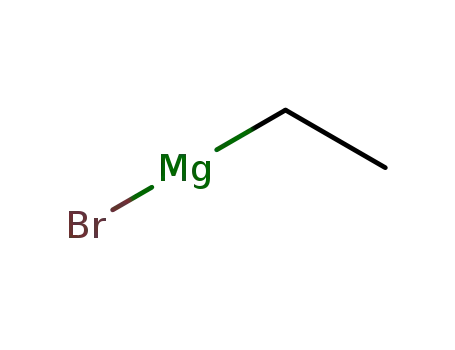
ethylmagnesium bromide
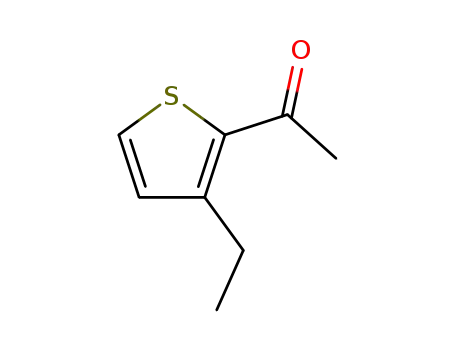
2-acetyl-3-ethylthiophene
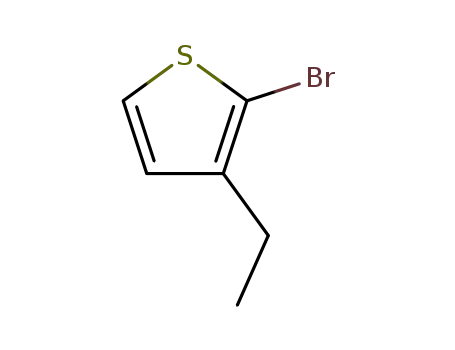
2-bromo-3-ethylthiophene
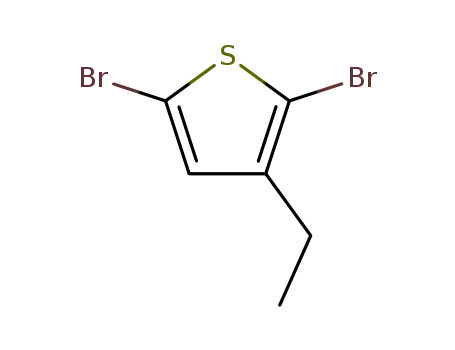
2,5-dibromo-3-ethylthiophene
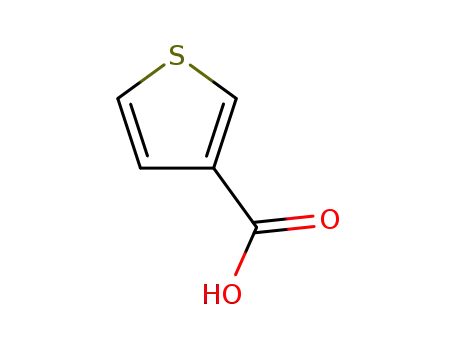
3-Thiophene carboxylic acid
CAS:145965-14-6
CAS:51792-34-8
CAS:4805-22-5