Your Location:Home >Products >OLED intermediates >Carbazoles >1484-13-5
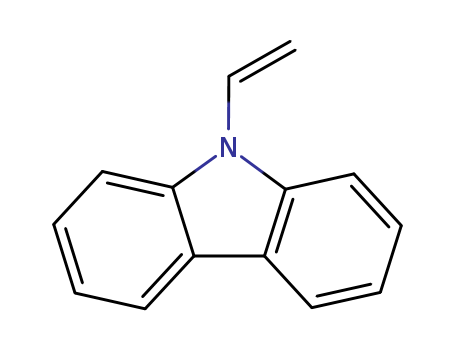

Product Details
Chemical Properties
slightly brown crystalline solid
Uses
Polymerizes to form heat-resistant and insulating resins somewhat similar to mica in dielectric properties.
Uses
9-Vinylcarbazole is used as a monomer in the production of poly(vinylcarbazole), a conductive polymer, in which conductivity is photon-dependent. It is also used in the photoreceptors of photocopiers.
Purification Methods
Crystallise N-vinylcarbazole repeatedly from MeOH in amber glassware. It sublimes in a vacuum. [Beilstein 20 II 282, 20 III/IV 3830, 20/8 V 19.]
InChI:InChI=1/C14H11N/c1-2-10-6-5-8-12-11-7-3-4-9-13(11)15-14(10)12/h2-9,15H,1H2
We report herein the substrate-controlled regio- and stereoselective hydroamination of carbazoles, aza-carbazoles, and γ-carbolines with functionalized aromatic as well as aliphatic alkynes in a KOH/DMSO system in good yields. The electronic effect of the substrates governs the stereochemistry of the product. Electron-donating alkynes provided (Z)-stereoselective products, and electron-withdrawing alkynes provided (E)-stereoselective products. This approach also provides an easy route for the synthesis of mono- and bis-hydroaminated product. The deuterium-labeling studies were also conducted to support the mechanistic pathway.
We developed a simple and efficient strategy to access N-vinyl secondary amines of various naturally occurring materials using readily available solid acetylene reagents (calcium carbide, KF, and KOH). Pyrrole, pyrazole, indoles, carbazoles, and diarylamines were successfully vinylated in good yields. Cross-linked and linear polymers were synthesized from N-vinyl carbazoles through free radical and cationic polymerization. Post-modification of olanzapine (an antipsychotic drug substance) was successfully performed.
Reaction of carbazole with dimethyl alkanedisulfonates in the presence of sodium hydride resulted in the formation of three main products: 2-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)alkylmethanesulfonates, 1,2-di-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)alkanes, and 9-alkenyl-9H-carbazoles.
The vinylation of various nucleophiles with acetylene at a maximum pressure of 1.5 bar is achieved by organocatalysis with easily accessible phosphines like tri-n-butylphosphine. A detailed mechanistic investigation by quantum-chemical and experimental methods supports a nucleophilic activation of acetylene by the phosphine catalyst. At 140 °C and typically 5 mol % catalyst loading, cyclic amides, oxazolidinones, ureas, unsaturated cyclic amines, and alcohols were successfully vinylated. Furthermore, the in situ generation of a vinyl phosphonium species can also be utilized in Wittig-type functionalization of aldehydes.
We present a base-mediated hydroamination protocol, using substoichiometric amounts of a hydrosilane and potassium tertbutoxide, that operates under mild conditions at 30 °C. Many aryl- and heteroatom-substituted olefins as well as arylamines are tolerated, affording the desired products with complete regioselectivity. Preliminary mechanistic investigations reveal a non-radical pathway for hydroamination. A sequential remote hydroamination strategy involving an initial Fe-catalysed olefin isomerisation followed by our base-mediated hydroamination was also developed to directly access-arylamines from terminal aliphatic alkenes.
Disclosed are a polymer, and a mixture or a formulation and an organic electronic device containing same, and applications thereof, and further a monomer of which the polymer is made; the polymer comprises on its side chain a repeating structure unit E, characterizing in that its S1(E)?T1(E))≤0.35 eV or even less, which may allow the said polymer having thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) property. Thus a TADF polymer suitable for printing processes is provided, thereby reducing OLED manufacturing costs.
The invention provides a novel method for synthesizing N-vinylcarbazole, and belongs to the field of organic synthesis. The method comprises the steps that under the KOH alkaline condition, carbazoleand methylbutynol react in an ethanol solvent to generate the N-vinylcarbazole, and the reaction temperature is 75-80 DEG C. The novel method has the advantages of mild condition, easy and convenientoperation, safety, low cost, high yield and the like.
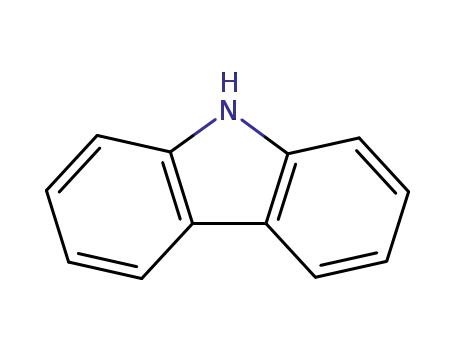
9H-carbazole
acetylene

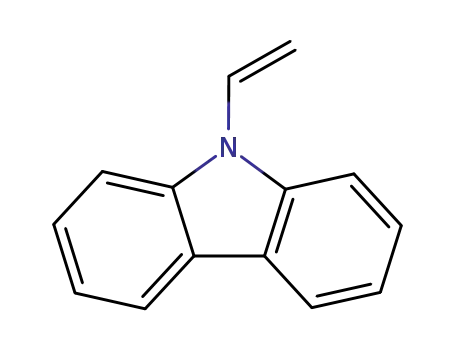
9-vinyl-9H-carbazole
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
tributylphosphine;
In
N,N-dimethyl acetamide;
at 140 ℃;
for 16h;
under 1.5 Torr;
Glovebox;
Sealed tube;
Autoclave;
|
95% |
|
In
5,5-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene;
at 140 ℃;
for 9h;
Reagent/catalyst;
Temperature;
|
90% |
|
With
sodium hydroxide; cyclohexane; zinc(II) oxide;
at 145 ℃;
|
|
|
With
1-methyl-pyrrolidin-2-one; potassium hydroxide;
at 150 ℃;
|
|
|
With
soda lime;
at 320 ℃;
|
|
|
With
potassium hydroxide; cyclohexane; zinc(II) oxide; zinc;
at 180 ℃;
|
|
|
With
potassium hydroxide; decalin;
at 170 ℃;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; cyclohexane; zinc(II) oxide;
at 145 ℃;
|
|
|
With
soda lime;
at 270 ℃;
under 20 Torr;
|
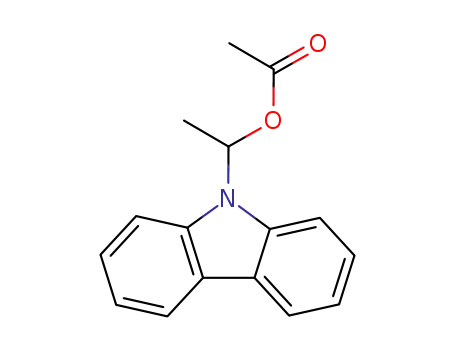
9-(1-acetoxyethyl)carbazole


9-vinyl-9H-carbazole
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
1-methyl-pyrrolidin-2-one;
at 120 - 140 ℃;
for 2.5h;
Temperature;
Reagent/catalyst;
|
81% |
|
With
diisopropylamine;
In
chlorobenzene;
at 120 - 140 ℃;
for 4h;
Reagent/catalyst;
Solvent;
Temperature;
|
80% |
|
With
sodium carbonate;
at 140 ℃;
for 5h;
under 760.051 Torr;
Reagent/catalyst;
Pressure;
Pyrolysis;
|
76% |
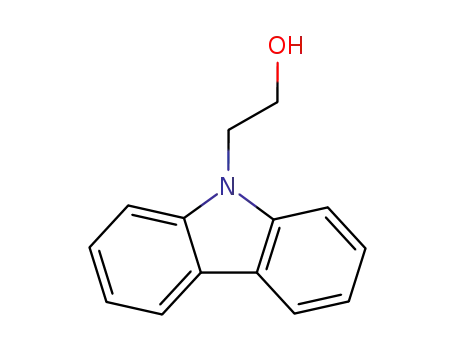
2-carbazol-9-yl-ethanol
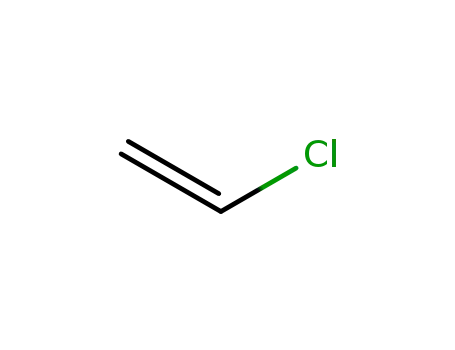
chloroethylene
potassium carbazole

9H-carbazole
9-(2-p-tolylmercapto-ethyl)-carbazole
N-ethylcarbazole
4-benzoyl-6-carbazol-9-yl-2-phenyl-5,6-dihydro-4H-[1,3,4]oxadiazine
9-(3,4,4-tricyano-1,3-butadienyl)carbazole
CAS:479094-62-7
CAS:16807-13-9