Your Location:Home >Products >OLED intermediates >Fluorenes >25603-67-2
Product Details
Chemical Properties
White Powder
Uses
9-Phenyl-9-fluorenol (cas# 25603-67-2) is a compound useful in organic synthesis.
General Description
9-Phenyl-9-fluorenol is a fluorine derivative. It is formed as intermediate during the synthesis of 9-bromo-9-phenylfluorene. Competitive interactions in crystalline 9-phenyl-9-fluorenol has been reported. Spectral properties of 9-phenyl-9-fluorenol have been investigated. 9-Phenyl-9-fluorenol is reported as bichromphoric fluorine derivative and its absorption and emission characteristics have been investigated in non-polar and polar solvents at different temperatures.
InChI:InChI=1/C19H14O/c20-19(14-8-2-1-3-9-14)17-12-6-4-10-15(17)16-11-5-7-13-18(16)19/h1-13,20H
Triphenylmethanol was treated in subcritical and supercritical water. A radical species, triphenylmethyl radical, was directly generated from triphenylmethanol in subcritical and supercritical water without using any radical initiator. The radical formati
-
An Oxone-mediated oxidative ring-opening reaction of 4,5-disubstituted 9H-fluoren-9-ols by cleavage of a carbon-carbon bond is reported. 2-Hydroxy-2′-aroyl-1,1′-biaryls can be efficiently prepared by simply heating the mixture of fluoren-9-ols, Oxone, and 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoroisopropanol at 60 °C for 4 h. The persulfate-involved ring-expansion processes were proposed and supported by the DFT calculations.
Deep-blue-emissive host materials are crucial to achievement of high-performance full-color organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), simplifying the manufacturing process and reducing production costs. To develop efficient deep-blue-emissive host materials is still challenging. By incorporating 9,9-diphenylfluorene moiety into phenanthroimidazole via the insulating N1 position of imidazole, two fluorene-phenanthroimidazole hybrid near-ultraviolet-emitting materials FL-PI and FL-BPI were designed and synthesized. The photophysical property, thermal and amorphous ability, electrochemical property and electron structure could be effectively regulated by molecular design strategy. Both FL-PI and FL-BPI exhibited moderate near-ultraviolet emission (0.50/0.63), high triplet energy level (2.58/2.57eV), high thermostability (Td: 371/542 °C; Tg: 134/210 °C) and carrier-transporting nature. Non-doped near-ultraviolet OLEDs adopting FL-BPI emitter showed the maximum efficiencies of 5.4%, 3.8 cd A?1 and 2.8 lm W?1 with the CIE coordinates of (0.15, 0.05). In addition, FL-PI/FL-BPI-hosted green phosphorescent OLEDs demonstrated the maximum efficiencies of 16.3%, 28.8 cd A?1, 21.1 lm W?1 and 21.1%, 75.3 cd A?1, 27.8 lmW?1, respectively. Moreover, the external quantum efficiencies of FL-PI/FL-BPI-hosted green phosphorescent devices remained as high as 16.1% and 21.0% at 1000 cd m?2. This work demonstrates that the strategy for the development of near-ultraviolet high-emissive host materials is feasible.
The 9-phenyl-9-fluorenyl (PhF) group has been used as an Nα protecting group of amino acids and their derivatives mainly as a result of its ability to prevent racemization. However, installing this group using the standard protocol, which employs 9-bromo-9-phenylfluorene/K3PO4/Pb(NO3)2, often takes days and yields can be variable. Here, we demonstrate that the PhF group can be introduced into the amino group of Weinreb's amides and methyl esters of amino acids, as well as into alcohols and carboxylic acids, rapidly and in excellent yields, using 9-chloro-9-phenylfluorene (PhFCl)/N-methylmorpholine (NMM)/AgNO3. Nα-PhF-protected amino acids can be prepared from unprotected α-amino acids, rapidly and often in near quantitative yields, by treatment with N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide (BSA) and then PhFCl/NMM/AgNO3. Primary alcohols can be protected with the PhF group in the presence of secondary alcohols in moderate yield. Using PhFCl/AgNO3, a primary alcohol can be protected in good yield in the presence of a primary ammonium salt or a carboxylic acid. Primary sulfonamides and amides can be protected in moderate to good yields using phenylfluorenyl alcohol (PhFOH)/BF3·OEt2/K3PO4, while thiols can be protected in good to excellent yield using PhFOH/BF3·OEt2 even in the presence of a carboxylic acid or primary ammonium group.
Two methods for the determination of pKa values of weak acids are described, a direct titration with dimsyl potassium in the presence of an indicator and a back-titration in which an analyte/indicator mixture is deprotonated and then titrated with ammonium chloride. Both methods have been validated by measuring pKa values of compounds, for which values had been determined previously. The back-titration method was applied to measure pKa values of two 1,3-dithiane-derived bissulfoxides and a monosulfone.
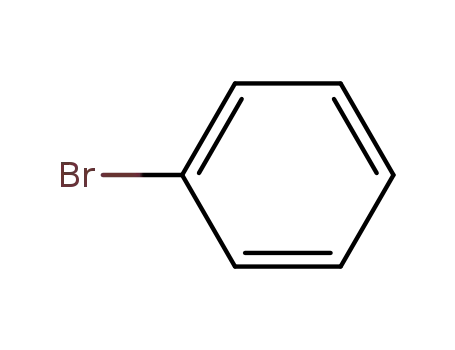
bromobenzene
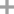
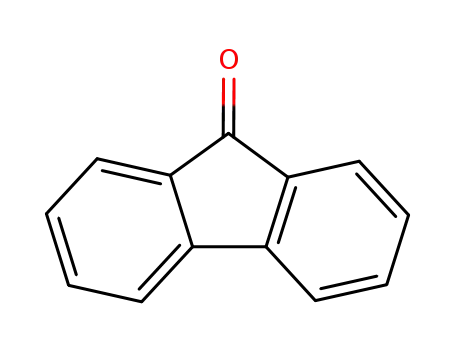
9-fluorenone

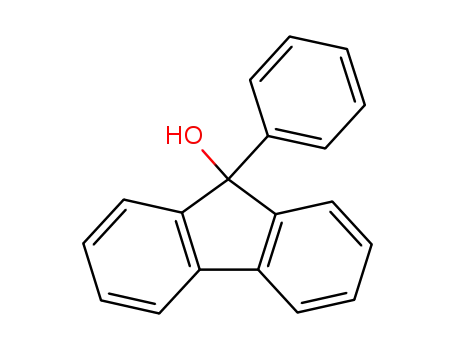
9-phenyl-fluoren-9-ol
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
bismuth(III) chloride; silver(I) bromide; magnesium; copper(ll) bromide;
In
tetrahydrofuran; toluene;
at 96 ℃;
for 12h;
|
99% |
|
bromobenzene;
With
magnesium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 0 - 20 ℃;
for 2h;
Inert atmosphere;
9-fluorenone;
With
cerium(III) chloride bis(lithium chloride);
In
tetrahydrofuran;
for 0.25h;
|
95% |
|
bromobenzene;
With
magnesium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 55 - 60 ℃;
for 2.5h;
Inert atmosphere;
9-fluorenone;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 55 - 60 ℃;
for 2.5h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
88% |
|
bromobenzene;
With
magnesium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 60 ℃;
for 2h;
Inert atmosphere;
9-fluorenone;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 85 ℃;
for 6h;
|
80% |
|
bromobenzene;
With
iodine; magnesium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
for 2h;
Reflux;
9-fluorenone;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
for 12h;
|
80% |
|
bromobenzene;
With
n-butyllithium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at -78 - 20 ℃;
for 3.5h;
Inert atmosphere;
9-fluorenone;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 20 ℃;
for 16h;
|
77% |
|
bromobenzene;
With
iodine; magnesium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 40 - 80 ℃;
for 4h;
Inert atmosphere;
9-fluorenone;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
for 15h;
Inert atmosphere;
Reflux;
|
74.7% |
|
bromobenzene;
With
iodine; magnesium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 40 - 80 ℃;
for 4h;
Inert atmosphere;
9-fluorenone;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
for 15h;
Inert atmosphere;
Reflux;
|
74.7% |
|
With
magnesium;
Yield given. Multistep reaction;
1) Et2O, 2)Et2O, 2a) reflux, 2 h, 2b) r. t., 2 h;
|
|
|
With
n-butyllithium;
Multistep reaction;
1.) ether, hexane, 0 deg C, 30 min, 2.) 20 deg C, 2 h;
|
|
|
bromobenzene;
With
n-butyllithium;
In
diethyl ether; hexane;
at 0 ℃;
for 0.833333h;
Inert atmosphere;
9-fluorenone;
In
tetrahydrofuran; diethyl ether; hexane;
at 0 - 24 ℃;
for 2.42h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
|
|
bromobenzene;
With
iodine; magnesium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 65 ℃;
for 2h;
9-fluorenone;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 65 ℃;
|
|
|
bromobenzene;
With
iodine; magnesium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 20 ℃;
Inert atmosphere;
9-fluorenone;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 50 ℃;
Inert atmosphere;
|
|
|
bromobenzene;
With
iodine; magnesium;
In
tetrahydrofuran; water;
at 0 - 45 ℃;
for 2h;
Inert atmosphere;
9-fluorenone;
With
iodine; magnesium;
In
tetrahydrofuran; water;
at 80 ℃;
for 24h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
|
|
bromobenzene;
With
iodine; magnesium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
for 2h;
Reflux;
9-fluorenone;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 20 ℃;
for 1.5h;
|
|
|
bromobenzene;
With
iodine; magnesium;
In
diethyl ether;
for 1.33333h;
Reflux;
9-fluorenone;
In
tetrahydrofuran; diethyl ether;
at 0 - 20 ℃;
|

9-fluorenone

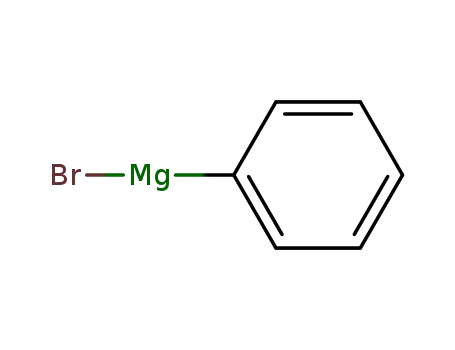
phenylmagnesium bromide


9-phenyl-fluoren-9-ol
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 0 - 20 ℃;
|
92% |
|
|
86% |
|
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at -15 - 25 ℃;
for 2h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
86% |
|
9-fluorenone; phenylmagnesium bromide;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 0 - 20 ℃;
for 16h;
Inert atmosphere;
With
ammonium chloride;
In
tetrahydrofuran; water;
|
76% |
|
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 0 - 20 ℃;
for 24h;
|
70% |
|
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 0 - 20 ℃;
for 24h;
|
70% |
|
9-fluorenone; phenylmagnesium bromide;
With
sodium hydride;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 25 ℃;
for 8h;
With
hydrogenchloride;
In
tetrahydrofuran; water;
|
|
|
9-fluorenone; phenylmagnesium bromide;
In
tetrahydrofuran; diethyl ether;
at 0 - 20 ℃;
With
water; sodium hydroxide;
In
tetrahydrofuran; diethyl ether;
at 0 ℃;
|

9-fluorenone
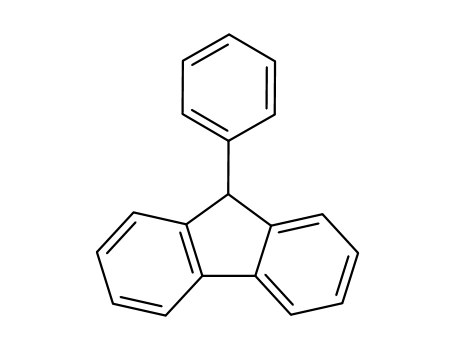
9-Phenylfluorene
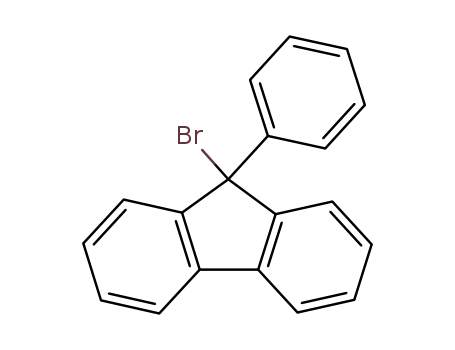
9-bromo-9-phenyl-9H-fluorene
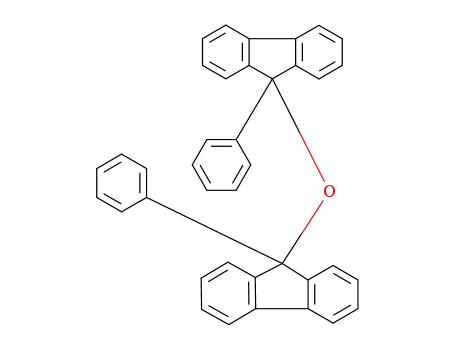
9,9'-oxybis(9-phenyl-9H-fluorene)
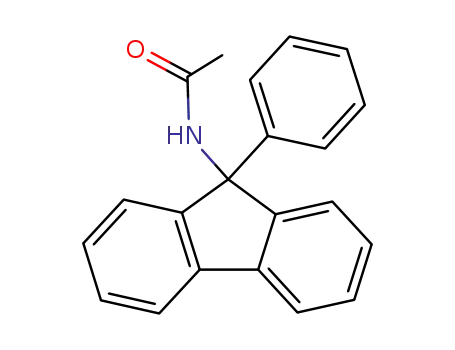
N-(9-phenyl-9-fluorenyl)acetamide
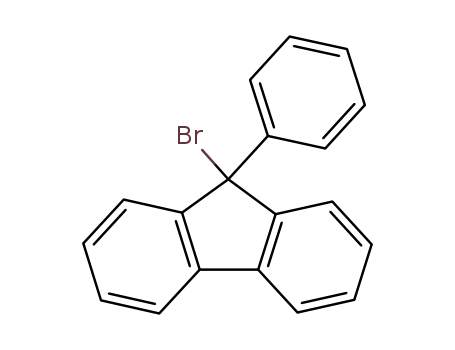
9-bromo-9-phenyl-9H-fluorene
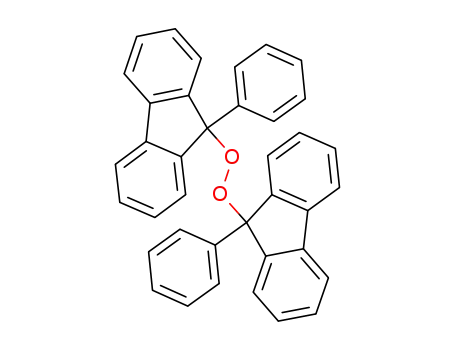
bis(9-phenyl-9-fluorenyl) peroxide
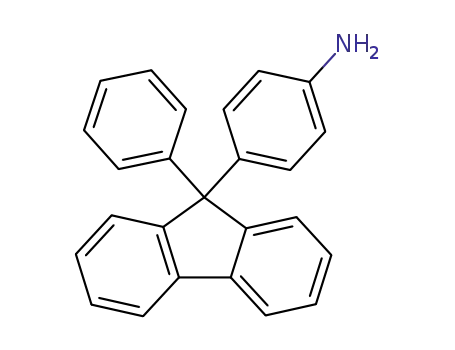
4-(9-phenyl-9H-fluoren-9-yl)aniline
CAS:128055-74-3
Molecular Formula:C25H12Br4
Molecular Weight:632
CAS:1693-86-3
CAS:884336-44-1