Your Location:Home >Products >OLED intermediates >Fluorenes >884336-44-1

Product Details
In this work, we report a novel spirobifluorene carbazole (SBFCbz) donor developed by fusion of carbazole with 9,9′-spirobi[fluorene] (SBF) unit. The newly synthesized SBFCbz donor combined with a diphenyl triazine acceptor to offer an 5'-(4,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-5′H-spiro[fluorene-9,11′-indeno[1,2-b]carbazole] (SBFTrz) host which played a role of an n-type host. An exciplex host of SBFTrz: 9-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)-9′-phenyl-9H,9′H-3,3′-bicarbazole (BPBPCz) was developed by combining it with a p-type BPBPCz host. The developed exciplex host showed triplet energy of 2.59 eV, making it a suitable host for the green and red phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes (PhOLEDs). The PhOLEDs fabricated using the exciplex host system offered excellent charge balance in the emitting layer, which resulted in above 20% external quantum efficiency (EQE) and resistance to the efficiency roll-off at high luminance. The green and red PhOLEDs developed showed the maximum EQE/EQE at 1000 cd/m2 of 22.0/21.7% and 26.2/23.2%, respectively. Besides, the SBFTrz: BPBPCz exciplex host-based green and red devices showed three- and five-fold enhancement, respectively, in the operational lifetime compared to their corresponding SBFTrz single host devices. Thus, the above results confirmed the suitability of the SBFTrz: BPBPCz exciplex as a host to develop PhOLEDs with high efficiency, improved stability at high luminance, and a long operational lifetime.
The invention provides a five-membered heterocyclic derivative and an organic electroluminescent device thereof, and relates to the technical field of organic photoelectric materials. The five-membered heterocyclic derivative is formed by combining a five-membered nitrogen-containing heterocycle and a rigid large group, and the specific structure enables the five-membered heterocyclic derivative to have good electron transport performance, high glass transition temperature and thermal stability, strengthens the rigidity and asymmetry of molecules, avoids intermolecular aggregation, and has non-crystalliability between molecules. The utility model has the advantages of uneasy aggregation and good film forming performance. The organic electroluminescent device manufactured by using the derivative has the characteristics of good photoelectric property, low driving voltage, high luminous efficiency, long service life and the like.
Frequency-upconverted fluorescence and stimulated emission induced by multiphoton absorption (MPA) have attracted much interest. As compared with low-order MPA processes, the construction of high-order MPA processes is highly desirable and rather attracti
The invention provides an organic compound and an electronic element and an electronic device thereof, and belongs to the technical field of organic electroluminescence. The organic compound has a structural formula shown 1, wherein the organic compound h
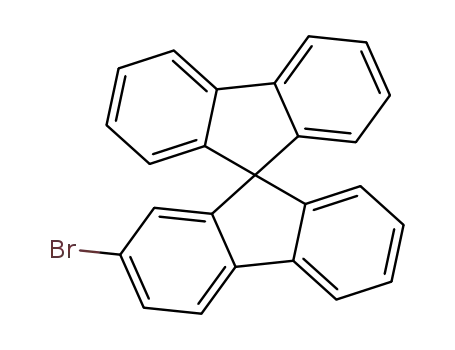
2-bromo-9,9'-spirobifluorene
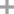
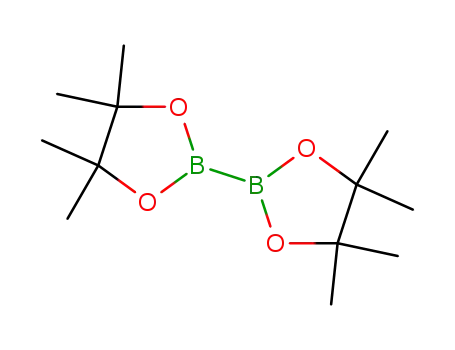
bis(pinacol)diborane

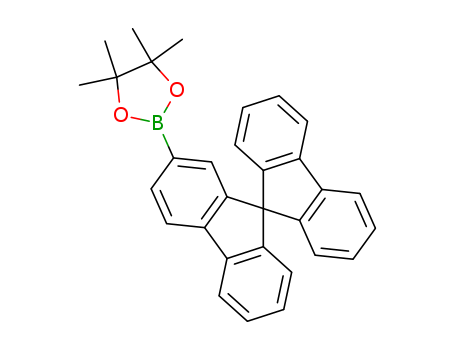
![2-(9,9′-spirobi[fluoren]-2-yl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane](/upload/2023/2/d5a2164c-cc26-4a07-9386-fed1b61d389f.png)
2-(9,9′-spirobi[fluoren]-2-yl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
(1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium(II) dichloride; potassium acetate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 90 ℃;
for 48h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
95% |
|
With
potassium acetate; palladium diacetate;
In
N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
at 80 ℃;
for 6h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
94% |
|
With
(1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium(II) dichloride; potassium acetate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 20 ℃;
for 8h;
Inert atmosphere;
Reflux;
|
90% |
|
With
(1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium(II) dichloride; potassium acetate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 85 ℃;
for 48h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
84% |
|
With
(1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium(II) dichloride; potassium acetate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
for 12h;
Reflux;
|
83% |
|
With
dichloro(1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphanyl)ferrocene)palladium(II)*CH2Cl2; potassium acetate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 85 ℃;
for 8h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
80% |
|
With
(1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium(II) dichloride; potassium acetate;
In
N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
for 24h;
|
74% |
|
With
potassium acetate; bis(dibenzylideneacetone)-palladium(0); tricyclohexylphosphine;
In
1,4-dioxane;
for 12h;
Reflux;
|
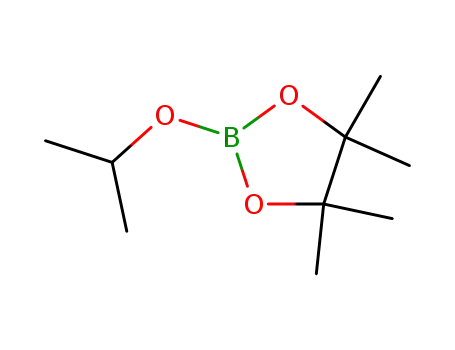
2-Isopropoxy-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane

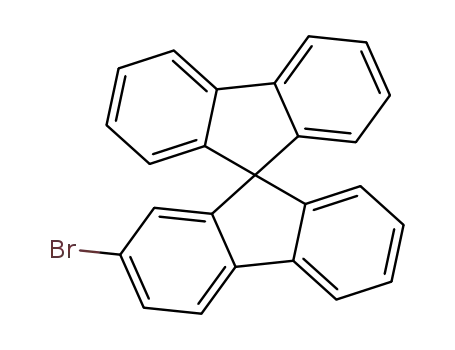
2-bromo-9,9'-spirobifluorene

![2-(9,9′-spirobi[fluoren]-2-yl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane](/upload/2023/2/d5a2164c-cc26-4a07-9386-fed1b61d389f.png)
2-(9,9′-spirobi[fluoren]-2-yl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
2-bromo-9,9'-spirobifluorene;
With
n-butyllithium;
In
tetrahydrofuran; hexane;
at -78 ℃;
for 2h;
2-Isopropoxy-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane;
In
tetrahydrofuran; hexane;
at -78 - 20 ℃;
|
65% |
|
2-bromo-9,9'-spirobifluorene;
With
n-butyllithium;
In
tetrahydrofuran; hexane;
at -78 - -70 ℃;
for 1.5h;
Inert atmosphere;
2-Isopropoxy-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane;
In
tetrahydrofuran; hexane;
at -70 - 20 ℃;
Inert atmosphere;
|
65% |
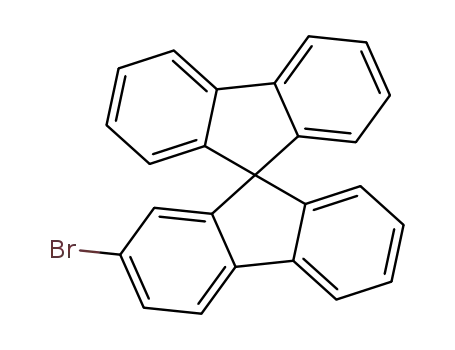
2-bromo-9,9'-spirobifluorene

bis(pinacol)diborane
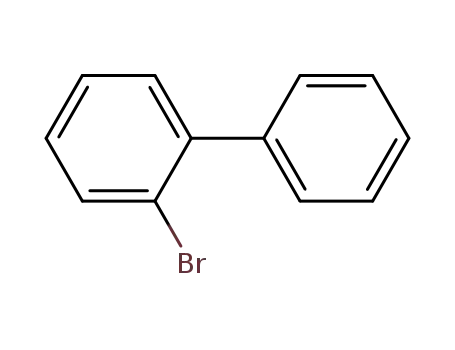
2-Bromobiphenyl
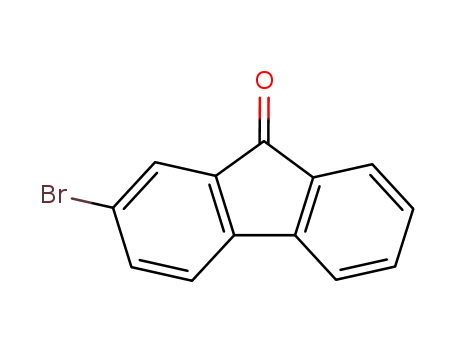
2-bromofluoren-9-one

4-(9,9'-spirobifluorene-2-yl)phenyltriphenylsilane
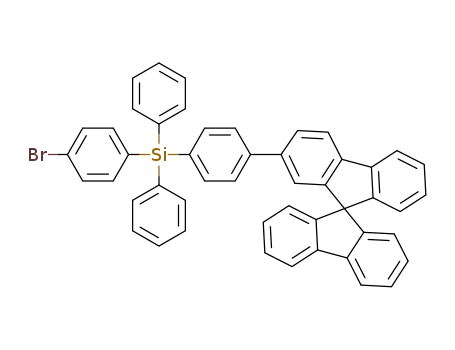
C49H33BrSi

C61H41NSi
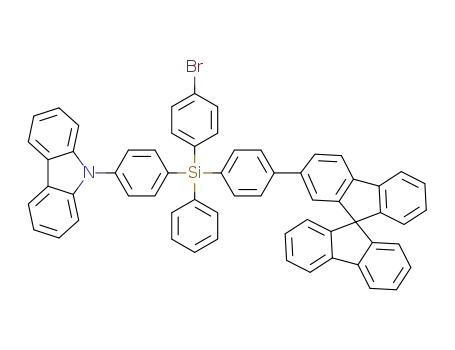
C61H40BrNSi
CAS:10537-08-3
CAS:240417-00-9
CAS:25603-67-2
CAS:159-62-6