Your Location:Home >Products >Functional intermediates >5455-13-0

Product Details
Various embodiments of the present disclosure are directed to compounds having Formula (I), Formula (IA), Formula (IB), Formula (IC), Formula (ID), Formula (IE), and/or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. The compounds can be suitable for inhibiting lipoxygenases, and/or treating associated diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease. In some embodiments, the compounds may be administered to a patient as part of a pharmaceutical formulation.
Various embodiments of the present disclosure are directed to compounds having Formula I, Formula II, Formula IIA, Formula III, Formula IIIA, Formula IIIB, and/or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. The compounds can be suitable for inhibiting lipoxygenases and/or treating associated diseases. In some embodiments, subject compounds are used to prepare a composition that is effective in treating neurodegenerative diseases.
The invention discloses a synthesis method of aryl halides (including aryl bromide shown as a formula (2) and aryl iodide shown as a formula (3)). All the systems are carried out in an air atmosphere,visible light is utilized to excite a substrate or a photosensitizer to catalyze the reaction; and in a reaction solvent, when aromatic hydrocarbon shown in the formula (1) and sodium bromide serve as raw materials, aryl bromide shown in the formula (2) is obtained through a reaction under the auxiliary action of an additive (protonic acid); or when aromatic hydrocarbon shown in the formula (1) and sodium iodide are used as raw materials, under the auxiliary action of an additive (protonic acid), aryl iodide shown in the formula (3) is obtained through reaction. The synthesis method has the advantages of cheap and accessible raw materials, simple reaction operation and mild reaction conditions. The method is compatible with the arylamine which is liable to be oxidized. The invention provides a new method for the synthesis of aryl halides, realizes the amplification of basic chemicals aryl halides including aryl bromide shown in the formula (2) and aryl iodide shown in the formula (3),and has wide application prospect and practical value.
Organic halides are critical building blocks that participate in various cross-coupling reactions. Furthermore, they widely exist as natural products and artificial molecules in drugs with important physiological activities. Although halogenation has been well studied, to the best of our knowledge, studies focussing on sensitive systems (e.g.aryl amines) have not been reported. Herein, we describe a compatible oxidative halogenation of (hetero)arenes with air as the oxidant and halide ions as halide sources under ambient conditions (visible light, air, aqueous system, room temperature, and normal pressure). Moreover, this protocol is practically feasible for gram-scale synthesis, showing potential for industrial application.
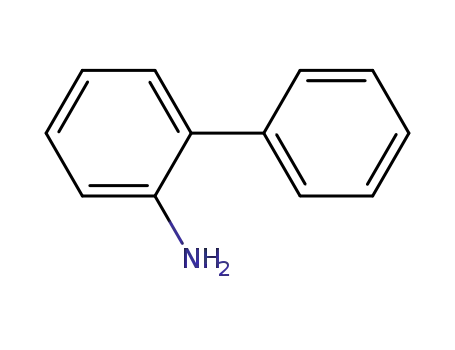
2-phenylaniline

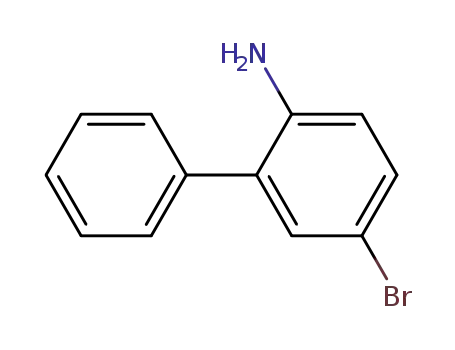
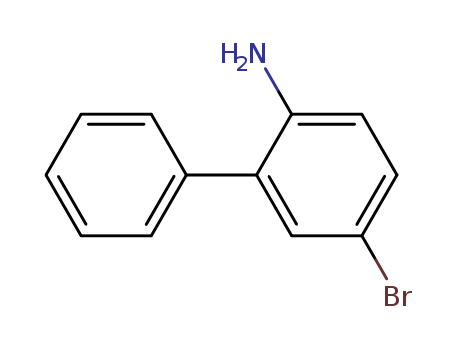
2-amino-5-bromobiphenyl
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
N-Bromosuccinimide;
In
N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
at 0 ℃;
for 2h;
|
90% |
|
With
N-Bromosuccinimide;
In
N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
at 0 ℃;
for 1h;
|
71% |
|
With
N-Bromosuccinimide;
In
N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
for 2h;
Cooling with ice;
|
71% |
|
With
4-(2-phenylethynyl)benzonitrile; water; sodium bisulfate hydrate; sodium bromide;
In
acetonitrile;
for 48h;
Irradiation;
|
70% |
|
With
sodium hydrogensulfate monohydrate; 4-(2-phenylethynyl)benzonitrile; water; sodium bromide;
In
acetonitrile;
at 20 ℃;
for 72h;
Schlenk technique;
Irradiation;
Green chemistry;
|
70% |
|
With
dihydrogen peroxide; ammonium bromide; acetic acid;
at 20 ℃;
Schlenk technique;
|
67% |
|
2-phenylaniline;
With
ammonium bromide; acetic acid;
for 2h;
With
dihydrogen peroxide;
|
65% |
|
With
N-Bromosuccinimide;
In
N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
at 0 ℃;
|
57.6% |
|
With
tetrachloromethane; bromine;
|
|
|
Multi-step reaction with 3 steps
1: 0 °C
2: glacial acetic acid; bromine
3: alcoholic hydrobromic acid / Hydrolysis
With
hydrogen bromide; bromine; acetic acid;
|
|
|
Multi-step reaction with 3 steps
1: 0 °C
2: glacial acetic acid; bromine
3: alcoholic hydrobromic acid / Hydrolysis
With
hydrogen bromide; bromine; acetic acid;
|
|
|
Multi-step reaction with 3 steps
1: pyridine / 0 °C
2: glacial acetic acid; bromine
3: alcoholic hydrobromic acid / Hydrolysis
With
pyridine; hydrogen bromide; bromine; acetic acid;
|
|
|
Multi-step reaction with 2 steps
1: aqueous NaN3 / Diazotization
2: acetic acid; HBr
With
sodium azide; hydrogen bromide; acetic acid;
|
|
|
Multi-step reaction with 3 steps
1: acetic acid / 2 h / Cooling with ice
2: hydrogen bromide; acetic acid / tetrachloromethane / 20 °C / Cooling with ice
3: hydrogenchloride; water / ethanol / Reflux; Cooling with ice
With
hydrogenchloride; water; hydrogen bromide; acetic acid;
In
tetrachloromethane; ethanol;
|
![N-(5-bromo-[1,1'-biphenyl]-2-yl)acetamide](/upload/2023/2/ef08e445-152c-4d35-83cd-86f0ac8fa4df.png)
N-(5-bromo-[1,1'-biphenyl]-2-yl)acetamide


2-amino-5-bromobiphenyl
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
hydrogen bromide;
Hydrolysis;
|
|
|
With
hydrogenchloride;
|
|
|
With
hydrogenchloride; water;
In
ethanol;
Reflux;
Cooling with ice;
|
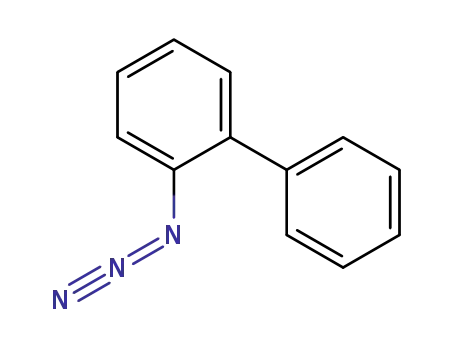
2-azidobiphenyl
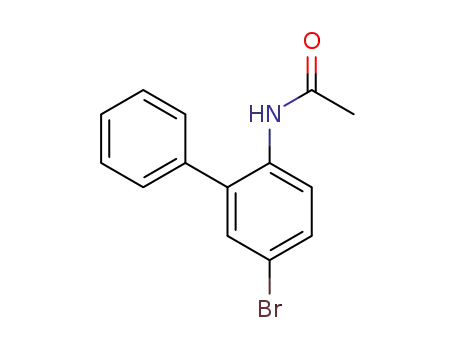
N-(5-bromo-[1,1'-biphenyl]-2-yl)acetamide

2-phenylaniline
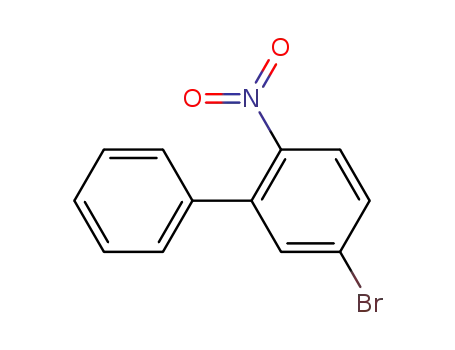
5-bromo-2-nitro-biphenyl
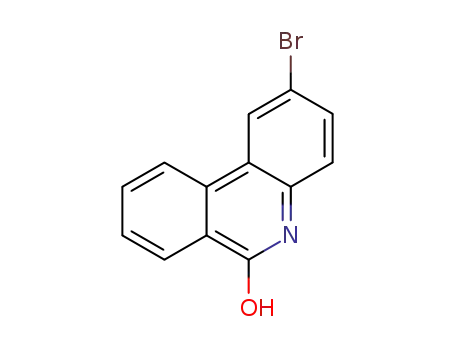
2-bromo-phenanthridin-6-ol
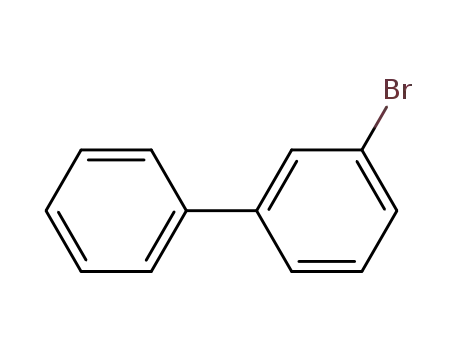
3-bromobiphenyl
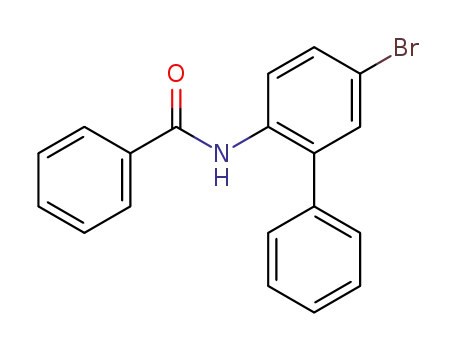
2-benzamido-5-bromobiphenyl
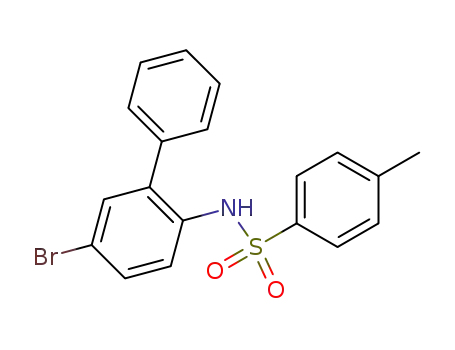
N-(5-bromo-biphenyl-2-yl)-toluene-4-sulfonamide
CAS:1038-95-5
CAS:54446-36-5
CAS:1762-84-1