Your Location:Home >Products >Organic phosphines >CyclohexyI phosphines >247940-06-3
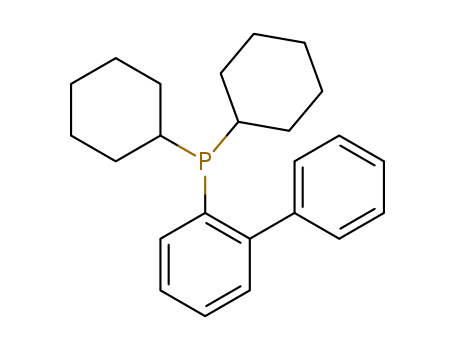
Product Details
Reaction
Ligand used in the palladium-catalyzed synthesis of aromatic amines from aryl chlorides, bromides and triflates. Ligand employed in Suzuki coupling reactions involving aryl chlorides, bromides and triflates. Useful ligand for the Pd-catalyzed oxidation of alcohols in the presence of chlorobenzenes. Useful ligand for the Pd-catalyzed amination with ammonia equivalents. Ligand for the gold(I)-catalyzed intramolecular [4+2] cycloadditions involving 1,3-enynes and arylalkynes with alkenes. Ligand used in the palladium-catalyzed borylation of aryl bromdies. Ligand used in the palladium-catalyzed siliylation of aryl chlorides.
Chemical Properties
white to light yellow crystal powde
Uses
Ligand employed in an extremely general method for the Pd-catalyzed synthesis of aromaticamines using aryl chlorides, bromides and triflates.
Uses
suzuki reaction
Uses
2-(Dicyclohexylphosphino)biphenyl is used as a catalyst for Suzuki coupling reactions.
General Description
CyJohnPhos [(2-Biphenyl)dicyclohexylphosphine] is an air-stable, bulky and electron-rich monodentate biarylphosphine ligand developed by the Buchwald group to enhance the reactivity of palladium catalysis during cross-coupling reactions.
InChI:InChI=1/C24H31P/c1-4-12-20(13-5-1)23-18-10-11-19-24(23)25(21-14-6-2-7-15-21)22-16-8-3-9-17-22/h1,4-5,10-13,18-19,21-22H,2-3,6-9,14-17H2
The metal-free reduction of a range of phosphine(V) oxides employing oxalyl chloride as an activating agent and hexachlorodisilane as reducing reagent has been achieved under mild reaction conditions. The method was successfully applied to the reduction of industrial waste byproduct triphenylphosphine(V) oxide, closing the phosphorus cycle to cleanly regenerate triphenylphosphine(III). Mechanistic studies and quantum chemical calculations support the attack of the dissociated chloride anion of intermediated phosphonium salt at the silicon of the disilane as the rate-limiting step for deprotection. The exquisite purity of the resultant phosphine(III) ligands after the simple removal of volatiles under reduced pressure circumvents laborious purification prior to metalation and has permitted the facile formation of important transition metal catalysts.
Palladium-catalyzed C-P bond formation reaction of ArBr/ArOTf using acylphosphines as differential phosphination reagents is reported. The acylphosphines show practicable reactivity with ArBr and ArOTf as the phosphination reagents, though they are inert to the air and moisture. The reaction affords trivalent phosphines directly in good yields with a broad substrate scope and functional group tolerance. This reaction discloses the acylphosphines' capability as new phosphorus sources for the direct synthesis of trivalent phosphines.
Transition-metal-mediated metalation of an aromatic C?H bond that is adjacent to a tertiary phosphine group in arylphosphines via a four-membered chelate ring was first discovered in 1968. Herein, we overcome a long-standing problem with the ortho-C?H activation of arylphosphines in a catalytic fashion. In particular, we developed a rhodium-catalyzed ortho-selective C?H borylation of various commercially available arylphosphines with B2pin2 through PIII-chelation-assisted C?H activation. This discovery is suggestive of a generic platform that could enable the late-stage modification of readily accessible arylphosphines.
Aryl(dicyclohexyl)phosphines were prepared by a catalytic C-P bond-forming cross-coupling reaction of haloarenes with dicyclohexylphosphine under heterogeneous conditions in water containing an immobilized palladium complex coordinated to an amphiphilic polystyrene-poly(ethylene glycol) resin supported di(tert -butyl)phosphine ligand.
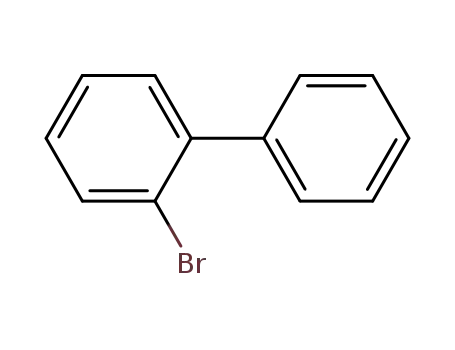
2-Bromobiphenyl
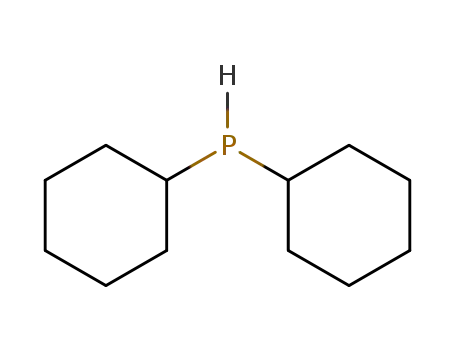
dicyclohexylphosphane

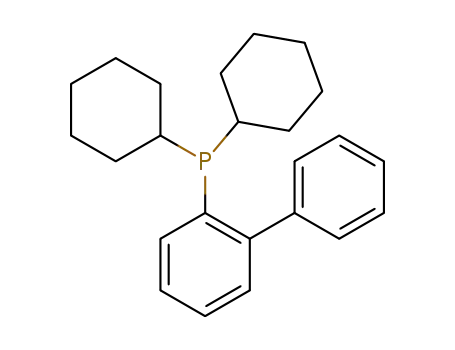
CyJohnPhos
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
bis(η3-allyl-μ-chloropalladium(II)); potassium hydroxide;
In
water;
at 100 ℃;
Inert atmosphere;
|
81% |
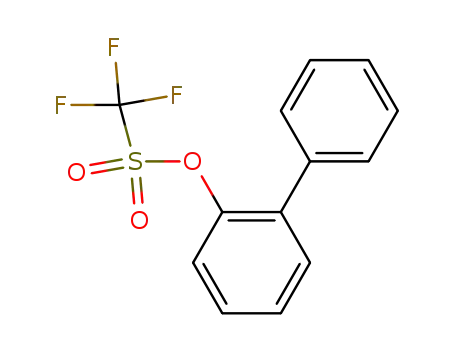
biphenyl-2-yl trifluoromethanesulfonate


dicyclohexylphosphane

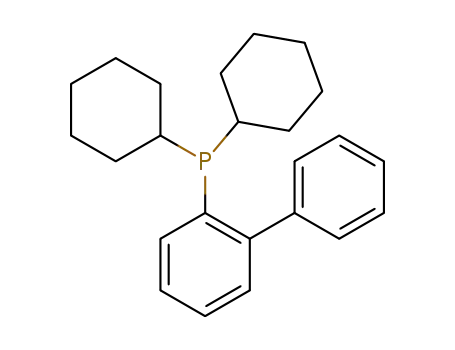
CyJohnPhos
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene;
1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane nickel(II) chloride;
In
N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
at 100 ℃;
for 18.67h;
Product distribution / selectivity;
|
77% |
|
With
1,4-diaza-bicyclo[2.2.2]octane;
1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane nickel(II) chloride;
In
N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
at 100 ℃;
for 18.67h;
Product distribution / selectivity;
|
8 %Chromat. |
|
With
1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene;
nickel dichloride;
In
water; N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
at 100 ℃;
for 18.67h;
Product distribution / selectivity;
|
90 %Chromat. |
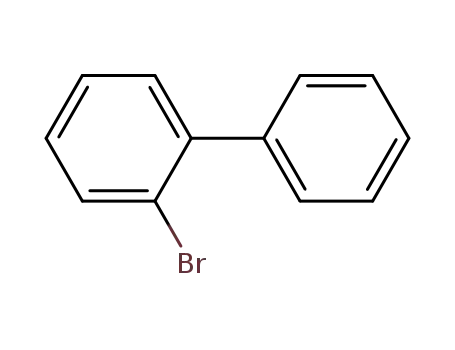
2-Bromobiphenyl
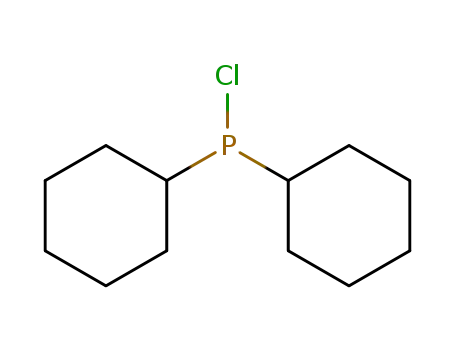
chlorodicyclohexylphosphane

biphenyl-2-yl trifluoromethanesulfonate

dicyclohexylphosphane
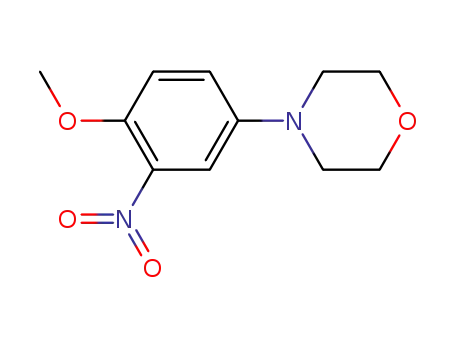
4-(4-methoxy-3-nitrophenyl)morpholine
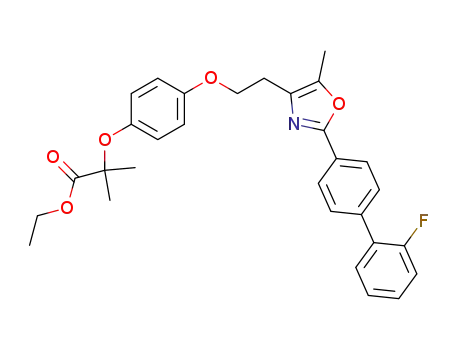
2-(4-{2-[2-(2'-fluoro-biphenyl-4-yl)-5-methyloxazol-4-yl]-ethoxy}-phenoxy)-2-methylpropionic acid ethyl ester
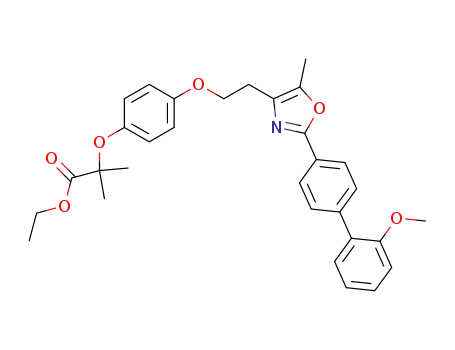
2-(4-{2-[2-(2'-methoxy-biphenyl-4-yl)-5-methyloxazol-4-yl]-ethoxy}-phenoxy)-2-methylpropionic acid ethyl ester
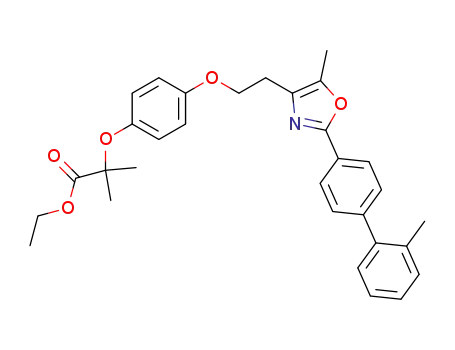
2-methyl-2-(4-{2-[5-methyl-2-(2'-methyl-biphenyl-4-yl)-oxazol-4-yl]-ethoxy}-phenoxy)propionic acid ethyl ester
CAS:400607-04-7
Molecular Formula:C24H15Br
Molecular Weight:383.3
CAS:6224-63-1
CAS:58656-04-5
Molecular Formula:C18H34BF4P
Molecular Weight:368.2
CAS:251320-86-2