Your Location:Home >Products >Organic phosphines >CyclohexyI phosphines >251320-86-2

Product Details
Reaction
Ligand used for the Pd-catalyzed formation of a-arylketones. Ligand used for the Pd-catalyzed amination reaction. Ligand used for the Pd-catalyzed hydrazone arylation. Ligand used for the Pd-catalyzed synthesis of 5,5-disubstituted butenolides. Ligand used for the Pd-catlyzed direct arylation of polyfluorinated arenes at room temperature.
Chemical Properties
White crystals or crystalline powder
Uses
suzuki reaction
Uses
2-(Dicyclohexylphosphino)-2'-methylbiphenyl is a Ligand used for the Pd-catalyzed formation of a-arylketones
Uses
2-(Dicyclohexylphosphino)-2''-methyl-biphenyl (CAS# 251320-86-2) can be used as a catalyst precursor to produce higher alcohols from syngas. It can also be used as a delta-lactone derivatives.
A convenient, optimized and safe synthesis of N-arylhydrazines, useful as intermediates for active ingredients in agricultural and pharmaceutical applications, is reported. Starting from aryl halides (chlorides and bromides), a palladium-catalyzed carbon-nitrogen coupling reaction followed by an acidic treatment afforded the target molecules in good to excellent yields using low catalyst loadings. This technology has then been successfully applied on a large scale in a pilot plant. This contribution also describes the major improvements in ligand synthesis and the thermal data required to develop a process on a pilot scale.
A Pd catalyst system is described that allows very high chemoselective monoarylation on all three isomers of dichlorobenzene. Direct application of these commodity chemicals to high-value ligands, anilines, azides, and carbazoles was achieved through this process discovery.
Biphenyl-based phosphine ligands can be prepared on a significantly larger scale than previously possible as a result of the following discoveries and improvements to the original experimental procedure: the finding that CuCl catalyzes the coupling of hindered dialkylchlorophosphines with Grignard reagents; the development of conditions that permit ClPCy2 to be prepared and utilized in situ; the development of a more reliable large-scale preparation of 2-dimethylaminophenylmagnesium halide.
Functionalized dicyclohexyl- and di-tert-butylphosphinobiphenyl ligands are prepared by the reaction of arylmagnesium halides with benzyne, followed by the addition of a chlorodialkylphosphine. This one-pot procedure is considerably less expensive and time-consuming than the method used previously to prepare such ligands. The cost of introducing the dicyclohexylphosphine group can be decreased by preparing chlorodicyclohexylphosphine from PCl3 and cyclohexylmagnesium chloride, and using the reagent without further purification. The new method is significant, as a variety of ligands can be produced in useful amounts by a procedure that is simple, with starting materials that are relatively inexpensive, and, in most cases, without chromatographic purification.

2-bromo-2'-methylbiphenyl
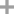
chlorodicyclohexylphosphane

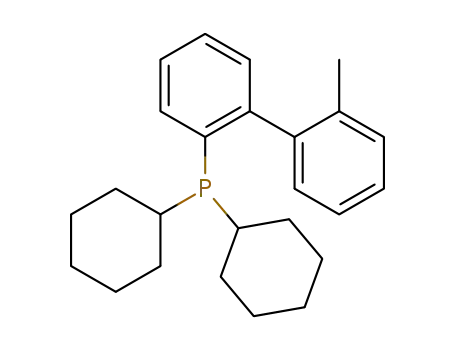
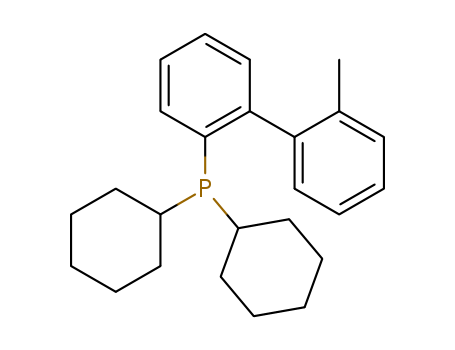
2-(dicyclohexylphosphino)-2'-methylbiphenyl
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
2-bromo-2'-methylbiphenyl;
With
n-butyllithium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at -78 ℃;
for 1.16667h;
chlorodicyclohexylphosphane;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
a) -78 deg C, 20 min, b) 0 deg C, 20 min, c) RT, 18 h;
|
65% |
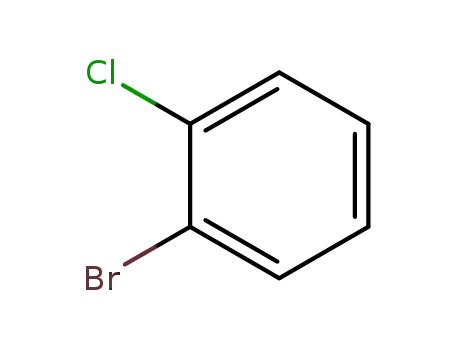
2-bromo-1-chlorobenzene

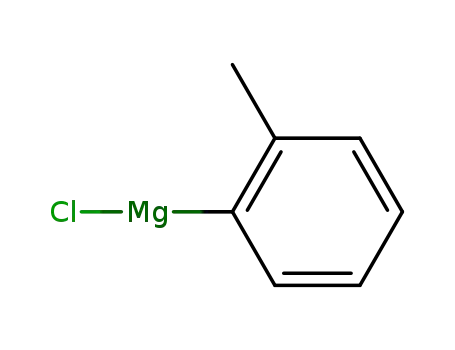
o-tolyl magnesium chloride


chlorodicyclohexylphosphane


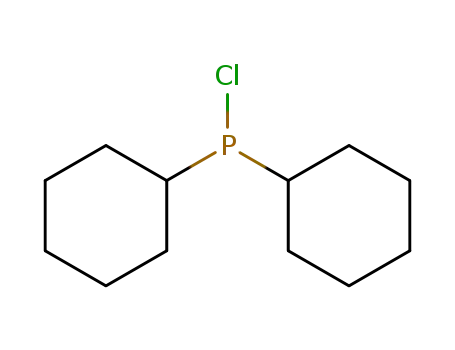
2-(dicyclohexylphosphino)-2'-methylbiphenyl
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
o-tolyl magnesium chloride;
With
magnesium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
for 0.25h;
Heating;
2-bromo-1-chlorobenzene;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
for 2h;
Heating;
chlorodicyclohexylphosphane;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 20 ℃;
for 14h;
Further stages.;
|
51% |

2-bromo-2'-methylbiphenyl

chlorodicyclohexylphosphane

2-bromo-1-chlorobenzene
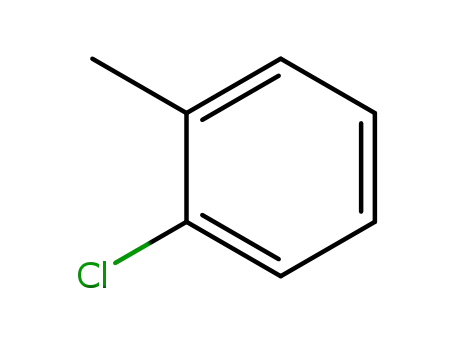
2-methylchlorobenzene
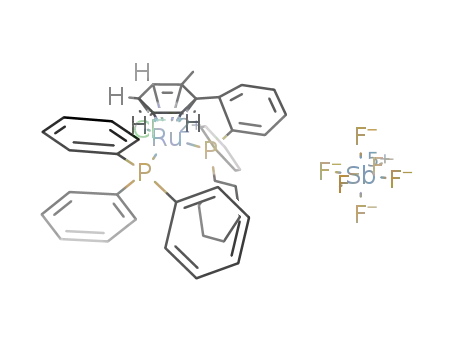
[Ru(η6:η1-2-(dicyclohexylphosphino)-2'-methylbiphenyl-P)(PPh3)Cl]SbF6
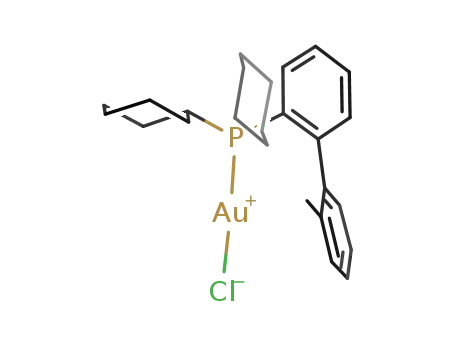
dicyclohexyl(2'-methylbiphenyl-2-yl)phosphinegold(I) chloride
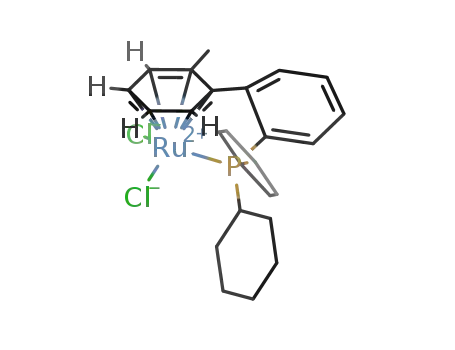
[Ru(η6:η1-2-(dicyclohexylphosphino)-2-methylbiphenyl-P)Cl2]
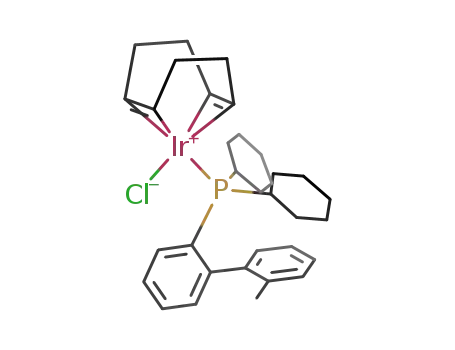
[IrCl(COD)(2-dicyclohexylphosphino-2'-methylbiphenyl)]
CAS:6224-63-1
CAS:247940-06-3
CAS:657408-07-6
Molecular Formula:C26H35O2P
Molecular Weight:410.5