Your Location:Home >Products >OLED intermediates >Carbazoles >16807-13-9

Product Details
A wet- and dry-process feasible host material is crucial to realize, respectively, low cost roll-to-roll fabrication of large area and high performance organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) with precise deposition of organic layers. We demonstrate in this study high efficiency phosphorescent OLED devices by employing a newly synthesized carbazole based host material 1,6-bis[3-(2-methoxy-3-pyridinyl)carbazol-9-yl]hexane (compound 5). Moreover, two other carbazole hosts 1,6-bis[3-(6-methoxy-3-pyridinyl)carbazol-9-yl]hexane (compound 4) and 3,6-di(2-methoxy-3-pyridinyl)-9-ethylcarbazole (compound 6) are also synthesized for comparison. By doping a typical green emitter fac tris(2-phenylpyridine)iridium (Ir(ppy)3) in compound 5, for example, the resultant wet-processed device exhibits at 100 cd m-2 a current efficiency of 27 cd A-1 and a power efficiency of 16.1 lm W-1. The dry-processed device shows a current efficiency of 61 cd A-1 and a power efficiency of 62.8 lm W-1. The high efficiency may be attributed to the host possessing an effective host-to-guest energy transfer, effective carrier injection balance, and the device architecture enabling excitons to generate on both the host and the guest.
The synthesis of a series of carbazole-based monomers incorporating dibenzazepines at the 3 position is reported. Full characterization of their structures is presented. The monomers were subjected to cationic polymerization using BF3·O(C2H5)2 as an initiator. The synthesized low-molar-mass compounds and oligomers were examined by differential scanning calorimetry, UV spectrometry, electron photoemission and time of flight techniques. The electron photoemission spectra of the films of synthesized materials revealed the ionization potentials of 5.12-5.34 eV. Hole drift mobilities of low-molar-mass compounds molecularly dispersed in bisphenol Z polycarbonate range from 2.6 × 10-8 to 1.7 × 10-6 cm2/V s at high electric fields as it was established by xerographic time of flight technique.
A series of carbazole-thiophene dimers, P1-P9, were synthesized using Suzuki-Miyaura and Ullmann coupling reactions. In P1-P9, carbazole-thiophenes were linked at the N-9 position for different core groups via biphenyl, dimethylbiphenyl, and phenyl. Electronic properties were evaluated by UV-Vis, cyclic voltammogram, and theoretical calculations. Particularly, the effects of conjugation connectivity on photophysical and electrochemical properties, as well as the correlation between carbazole-thiophene and the core, were studied. Carbazole connecting with thiophenes at the 3,6-positions and the phenyl group as a core group leads to increased stabilization of HOMO and LUMO energy levels where the bandgap (Δ E) is significantly reduced.
Bis(pyridine)iodonium tetrafluoroborate (IPy2BF4) was successfully used as a diiodination reagent for carbazole and its derivatives to give 3,6-diiodocarbazoles in excellent yield. Subsequent rhodium-catalyzed disilylation of 3,6-diiodocarbazoles with triethoxysilane gave the corresponding 3,6-bis(triethoxysilyl)carbazoles, which are precursors for sol-gel polymerization, in good yield.
Carbazole (1) undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution with various iodinating reagents. Although, 3-iodocarbazole (1b) and 3,6-diiodocarbazole (1d) obtained by iodination of carbazole were isolated and characterized sometime ago, 1-iodocarbazole (1a
The synthesis of two A2B2 porphyrins, {5,15-bis-[4-(octyloxy)phenyl]-porphyrinato}zinc(ii) (4) and {5,15-bis-(carbazol-3-yl-ethynyl)-10,20-bis-[4-(octyloxy)phenyl]-porphinato}-zinc(ii) (9), is reported. Their photophysical properties were studied by steady-state absorption and emission. Substituting the carbazolylethynyl moieties at two of the meso positions results in a large bathochromic shift of all the absorption bands, a notable increase in the absorption coefficient of the Q(0,0) band, and higher fluorescence quantum yield compared to porphyrin 4, with two unsubstituted meso positions. Cyclic voltammetry and digital simulation show that electrogenerated radical ions of 9 are more stable than those of 4. The lack of substituents at the meso positions of 4 leads to dimerization reactions of the radical cation. Despite this, the annihilation reaction of 4 and 9 produces very similar electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) intensity. Spectroelectrochemical experiments demonstrate that the electroreduction of 9 leads to a strong absorption band that might quench the ECL.
The synthesis and characterization of two hybrid N-methylated carbazole derivatives containing a thiazolyl or a thienyl ring is reported. The thiazolyl derivative has been also characterised by X-ray diffraction analysis. The study of its reactivity in front of [MCl2(dmso)2] (M = Pd or Pt) or Na2[PdCl4] in methanol has allowed us to isolate and characterize its complexes. However, for the thienyl analogue, the formation of any Pd(II) or Pt(II) complex was not detected, indicating that it is less prone to bind to the M(II) ions than its thiazolyl analogue. Density Functional Theory (DFT) and Time-Dependent Density Functional Theory (TD-DFT) calculations have also been carried out in order to rationalize the influence of the nature of the thiazolyl or thienyl group on the electronic delocalization. Molecular mechanics calculations show that the free rotation of the thiazolyl in relation to the carbazole requires a greater energy income than for its thienyl analogue. Studies of the cytotoxic activity of the new compounds on colon (HCT116) and breast (MDA-MB231 and MCF7) cancer cell lines show that the thiazolyl carbazole ligand and its Pt(II) complex are the most active agents of the series and in the MCF7 line their potency is higher than that of cisplatin. In the non-tumoral human skin fibroblast BJ cell line, all the compounds were less toxic than cisplatin. Their potential ability to modify the electrophoretic mobility of pBluescript SK+ plasmid DNA and to act as inhibitors of Topoisomerases I and IIα or cathepsin B has also been investigated.
Three new bipolar star-shaped derivatives of 2,4,6-triphenyl-1,3,5-triazine containing carbazolyl groups were designed, synthesized and characterized. All the materials possess high thermal stability and high glass transition temperatures ranging 97-226 °C. Photophysical study of the dilute solutions and neat films of the synthesized compounds was performed. Lippert-Mataga plots revealed linear dependence of Stokes shifts on the orientation polarizability for all the compounds. The dilute solutions of the triazine derivatives exhibited high photoluminescence quantum yields reaching 0.85, while for the neat films photoluminescence efficiency of 0.20-0.33 was observed. Ionization potentials of the solid layers of carbazole-triazine adducts estimated by photoelectron spectroscopy were found to be in the range of 5.49-5.97 eV. Hole drift mobility of the materials well exceeded the magnitude of 10-3 cm2 V-1 s-1 at an electric field of 6.4 · 105 V/cm. The selected compounds were tested as light emitting materials in organic light emitting diodes based on host-guest systems.
An efficient regioselective iodination of the Fischer-Borsche ring has been achieved using molecular iodine, in a one-pot synthesis. The acid-, metal-, and oxidant-free conditions of the present method are highly convenient and practical. Furthermore, the one-pot direct iodination process is extended to the concise synthesis of glycozoline, 3-formyl-6-methoxy-carbazole, and 6-methoxy-carbazole-3-methylcarboxylate natural alkaloids. This method has been proven to be tolerant to a broad range of functional groups, with good to excellent yields.
New carbazole-based monomers with two reactive functional groups such as epoxypropyl, oxetanyl and vinyloxethyl were synthesized and their cationic photopolymerization was performed. The monomer containing epoxypropyl groups exhibited the highest conversion in photopolymerization (78%). The monomers and polymers exhibited ability of glass formation with the glass transition temperatures up to 98?°C for low-molecular-weight compounds and those observed for polymers ranging from 89 to 150?°C. The synthesized derivatives absorb electromagnetic irradiation in the range of 200–390?nm with the band gaps of 3.14–3.16?eV. The compounds exhibit blue photoluminescence with the intensity maxima at 400?nm. The compounds were found to have high triplet energies of ca. 2.78?eV. The electron photoemission spectra of the layers of the synthesized compounds revealed ionization potentials of 5.20–5.37?eV. The time-of-flight hole drift mobilities of the layers of the compounds exceed 10??5?cm2/V?×?s at high electric fields.
Various diarylamino-substituted 1,3,5-triazine derivatives have been synthesized by Cu catalyzed Ullmann-type arylamino-aryl coupling reaction. Full characterization of the compounds structures by mass spectrometry, IR and electronic absorption, as well as 1H NMR spectroscopy is presented. Some of the compounds represent amorphous materials with glass transition temperatures exceeding 84C and with thermal decomposition starting at temperatures330C. The electron photoemission spectra of the materials were recorded and the ionisation potentials of ca. 5.3-5.8eV were established. Time-of-flight hole drift mobility of some diarylamino-substituted triazines molecularly dispersed in bisphenol Z polycarbonate approached 10-5cm2/Vs at high electric field.
Gene therapies, including genome editing, RNAi, anti-sense technology and chemical DNA editing are becoming major methods for the treatment of genetic disorders. Techniques like CRISPR-Cas9, zinc finger nuclease (ZFN) and transcription activator-like effector-based nuclease (TALEN) are a few such enzymatic techniques. Most enzymatic genome editing techniques have their disadvantages. Thus, non-enzymatic and non-invasive technologies for nucleic acid editing has been reported in this study which might possess some advantages over the older methods of DNA manipulation. 3-cyanovinyl carbazole (CNVK) based nucleic acid editing takes advantage of photo-cross-linking between a target pyrimidine and the CNVK to afford deamination of cytosine and convert it to uracil. This method previously required the use of high temperatures but, in this study, it has been optimized to take place at physiological conditions. Different counter bases (inosine, guanine and cytosine) complementary to the target cytosine were used, along with derivatives ofCNVK (NH2VK andOHVK) to afford the deamination at physiological conditions.
Chiral bisboronic acid chemosensors based on ethynylated carbazole were prepared. The chiral chemosensors show red-shifted emission than the chemosensors with unsubstituted carbazole fluorophore. a-PET effect was found for the chemosensors, which is different from our previous observation of the d-PET effect for boronic acid chemosensors based on carbazole. Enantioselective recognition of tartaric acids was implicated with these chemosensors. Consecutive fluorescence emission enhancement/diminishment were observed with increasing the concentration of the tartaric acids, which is tentatively assigned to the transition of the binding stoichiometry from 1:1 binding to 1:2 binding. In particularly interesting is the improved fluorescence response at acidic pH for recognition of tartaric acids, which is rarely observed for a-PET chemosensors. We propose that the sensing is due to hybrid mechanism of a-PET/d-PET and conformational restriction upon binding. Our results will be useful for design of chiral boronic acid chemosensors with improved fluorescence response at acidic pH, which are rarely reported.
In reaction of iodine monochloride with CF3COOAg, CH 3COONa or (CH3COO)2Pb in acetonitrile and acetic acid the chloride is bonded by metal cations, and electrophilic iodine is generated able to easily iodinate a
Solution-processable molecular hole transporting materials (HTMs) are extremely crucial in order to realize low cost, high throughput, and roll-to-roll fabrication of large area organic light emitting diodes for display and lighting applications. In this report, a series of naphthalene and phenyl substituted carbazole core based HTMs, 3-(1-naphthyl)-9-(2-phenylvinyl)carbazole (NPVCz), 3,6-di-(1-naphthyl)-9-phenylvinylcarbazole (DNPVCz), and 3,6-diphenyl-9-(2-phenylvinyl)carbazole (DPPVCz) are successfully synthesized and characterized. The synthesized HTMs possess excellent solubility in common organic solvents. By using a fluorescent tris(8-hydroxyquinolinato)aluminium emitter, we demonstrate an enhancement of 135%, from 1.7 to 4.5 cd A-1, in the current efficiency of an organic light emitting diode (OLED) by replacing the conventional HTM, N,N′-di(1-naphthyl)-N,N′-diphenyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4,4′-diamine (NPB), with the NPVCz counterpart. Moreover, the current efficiency of a conventional tris[2-phenylpyridinato-C2,N]iridium(iii) based phosphorescent green OLED device increases from 46.4 to 66.2 cd A-1 by substituting the NPB with NPVCz. These findings suggest that this type of solution-processable molecular HTM will be a promising contender for high efficiency OLED devices.
Two oligoethers containing electroactive pendent pyridinyl-carbazole moieties have been synthesized by the multi-step synthetic route. Full characterization of their structures is presented. The oligomers represent derivatives of very high thermal stability with initial thermal degradation temperatures exceeding 400 °C. Glass transition temperatures of the amorphous materials were also very high and reached values of 124 °C and 145 °C, respectively. Bipolar chemical structure having oligomer, i.e. poly{3-(2-methoxy-3-pyridinyl)-9-(3-methyloxetan-3-yl)methyl-carbazole} was tested as host material for green phosphorescent organic light emitting diode using tris(2-phenylpyridine)iridium(III) as a triplet emitter. A green device containing 10 wt% of the green guest demonstrated among all the devices the best performance with current efficiency of 8.8 cd/A and power efficiency of 5.1 lm/W at 100 cd/m2. At higher brightness, such as 1000 cd/m2, used for illumination applications, this PhOLED showed enhanced efficiency of 11.7 cd/A (5.4 lm/W) with brightness exceeding 4000 cd/m2.
The thermal, optical, electrochemical and charge transport properties of a series of nine straightforward carbazole-based compounds have been analysed and interpreted according to their molecular structure by means of the X-ray analysis of single crystals. A non-doped OLED device with low turn-on voltage and maximum luminance up to 1.4 × 104 cd m?2 was achieved. DFT calculations have been performed to explain the high efficiency of radiative exciton production.
Two low-cost 9-(2,2-diphenylvinyl)carbazole-based derivatives with aryl substitutions were synthesized by simple procedure and then investigated. The respective glass transition temperatures of the materials were estimated to be higher than 90 °C, which can provide morphologically-stable amorphous films for applications in organic light emitting diodes. The compounds possess adequate ionization potentials and suitable triplet energies, which make them suitable hole transporting materials for use in red phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes. The respective peak efficiencies of the red devices with the p-type dopants were recorded at 8.7% (5.6 cd/A and 3.9 lm/W) and at 8.7% (5.4 cd/A and 3.8 lm/W), correspondingly, demonstrating high potential of the material for applications in light emitting diodes. The characteristics indicated that the devices with the aryl substituted 9-(2,2-diphenylvinyl)carbazoles exhibit better performance than those of widely used hole transporting 1,1-bis[(di-4-tolylamino)phenyl]cyclohexane (TAPC) -based device.
Dynamic combinatorial chemistry (DCC) has emerged as a promising strategy for template-driven selection of high-affinity ligands for biological targets from equilibrating combinatorial libraries. However, only a few examples using disulfide-exchange-based DCC are reported for nucleic acid targets. Herein, we have demonstrated that gold-coated magnetic nanoparticle-conjugated DNA targets can be used as templates for dynamic selection of ligands from an imine-based combinatorial library. The implementation of DCC using DNA nanotemplates enables efficient identification of the lead compounds, from the dynamic combinatorial library via magnetic decantation. It further allows quick separation of DNA nanotemplates for reuse in DCC reactions. The identified lead compound exhibits significant quadruplex versus duplex DNA selectivity and suppresses promoter activity of c-MYC gene that contains G-quadruplex DNA forming sequence in the upstream promoter region. Further cellular experiments indicated that the lead compound is able to permeate into cell nuclei and trigger a DNA damage response in cancer cells.
A series of star-shaped carbazole derivatives were prepared via Suzuki-Miyaura and Stille coupling procedures. Received monomers were characterized by UV-Vis spectroscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy and cyclic voltammetry in order to estimate their basic spectral, electrochemical and electronic properties important for wide scale of applications in organic electronics and photovoltaics. Experimental results were supported by DFT calculations. Synthesised compounds were also used as monomers in the electrodeposition of conjugated polymers. Spectroelectrochemical EPR and UV-Vis-NIR measurements were carried out in order to study the influence of structure on charge carrier formation.
-
We report the synthesis, gelation abilities and aggregation-induced, blue-shifted emission (AIBSE) properties of two minimalistic diketopiperazine-based gelators. Despite containing a highly insoluble luminophore that makes up more than half of their respective molecular masses, efficient hydrogelation by multiple stimuli for one and efficient organogelation for the other compound are reported. Insights into the aggregation and gelation properties were gained through examination of the photophysical and material properties of selected gels, which are representative of the different modes of gelation. The synthesis of the gelators is highly modular and based on readily available amino acid building blocks, allowing the efficient and rapid diversification of these core structures and fine-tuning of gel properties.
Synthesis of the novel thiophenyl carbazole phosphoramidite DNA building block 5 was accomplished in four steps using a Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reaction from the core carbazole and it was seamlessly accommodated into a 9-mer DNA-based oligonucleotide by incorporation at the flanking 5′-end in combination with a central insertion of an LNA-T nucleotide. The carbazole-containing oligonucleotide was combined in different duplex hybrids, which were characterized by thermal denaturation, circular dichroism and fluorescence studies. The carbazole monomer modulates the duplex stability in various ways. Thus, monomer Z increased the thermal stability of the 9-mer towards the complementary 9-mer/15-mer DNA duplex by 4.2 °C. Furthermore, indications of its intercalation into the duplex were obtained by modeling studies and robust decreases in fluorescence emission intensities upon duplex formation. In contrast, no clear intercalating tendency was corroborated for monomer Z within the DNA/RNA hybrid duplex as indicated by moderate quenching of the fluorescence and similar duplex thermal stabilities relative to the corresponding control duplex. The recognition efficiencies of the carbazole modified oligonucleotide toward single nucleotide mismatches were studied with two 15-mer model targets (DNA and RNA). For both systems, mismatches positioned at the juxtaposition of the carbazole monomer showed pronounced deceases in thermal denaturation temperature. Steady-state fluorescence emission studies of all mismatched duplexes with incorporation of Z monomer typically displayed efficient fluorescence quenching.
In this study, ten fluorescent dyes were prepared based on three different kinds of central moiety, such as triphenylamine, diphenylsulfone or triphenyltriazine, which was coupled to either carbazole or naphthalimidinyl group via an acetylene linkage group. N-n-Butyl-carbazole, N-phenyl-carbazole or N-n-butyl-naphthalimide was coupled to the individual central moiety of triphenylamine, diphenyl sulfone, 2,4,6-triphenyl-1,3,5-trazine or diphenylamine using a Sonogashira coupling reaction in the final step. All dyes were confirmed their chemical structure by 1H NMR, GC-Mass and elemental analyses. The absorption properties and thermal stabilities of the fluorescent dyes were examined. Density Functional Theory (DFT) and Time-Dependent DFT calculations were carried out, in addition to geometry simulation, by using the Gaussian 09 program. In terms of fluorescence properties in this series, two dyes based on diphenyl sulfonyl and three dyes based on triphenylamine substituted by 1–3 of N-n-butyl-carbazole exhibited a blue emission, whereas three dyes based on triphenylamine substituted by 1–3 of N-n-butyl-naphthalimide were observed by a red emitter which can be attributable to both effects the bathochromic shifts in absorption maxima and larger Stokes shifts. In case of corresponding 2,4,6-triphenyl-1,3,5-trazine central moiety coupled to a carbazole ring, a green fluorescence was emitted. Results revealed that the fluorescence of the dyes is affected by the electron-donating strength of the acetylene linkages involved in the π-conjugation systems of the dyes.
Orthogonal phenoxazine-styryl BODIPY compact electron donor/acceptor dyads were prepared as heavy atom-free triplet photosensitizers (PSs) with strong red light absorption (?=1.33×105 M?1 cm?1 at 630 nm), whereas the previously reported triplet photosensitizers based on the spin-orbit charge transfer intersystem crossing (SOCT-ISC) mechanism show absorption in a shorter wavelength range (T=333 μs) was observed for the new dyads. In comparison, the triplet state lifetime of the same chromophore accessed with the conventional heavy atom effect (HAE) is much shorter (τT=1.8 μs). Long triplet state lifetime is beneficial to enhance electron or energy transfer, the primary photophysical processes in the application of triplet PSs. Our approach is based on SOCT-ISC, without invoking of the HAE, which may shorten the triplet state lifetime. We used bisstyrylBodipy both as the electron acceptor and the visible light-harvesting chromophore, which shows red-light absorption. Femtosecond transient absorption spectra indicated the charge separation (109 ps) and SOCT-ISC (charge recombination, CR; 2.3 ns) for BDP-1. ISC efficiency of BDP-1 was determined as ΦT=25 % (in toluene). The dyad BDP-3 was used as triplet PS for triplet-triplet annihilation upconversion (upconversion quantum yield ΦUC=1.5 %; anti-Stokes shift is 5900 cm?1).
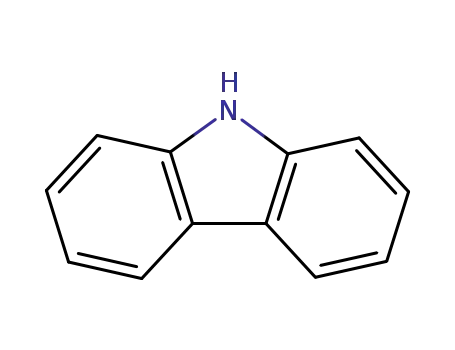
9H-carbazole

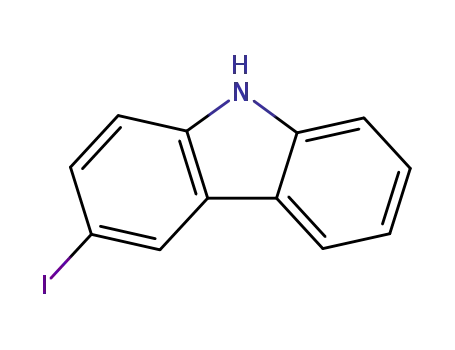
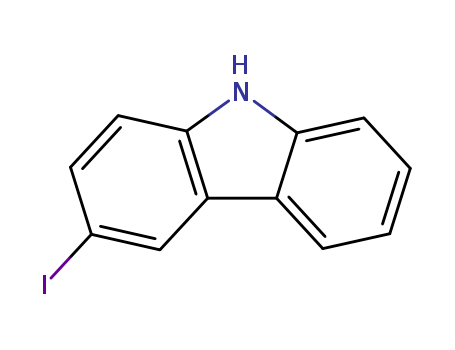
3-iodocarbazole
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
N-iodo-succinimide;
In
acetic acid;
at 20 ℃;
|
97% |
|
9H-carbazole;
With
N-iodo-succinimide; acetic acid;
at 20 ℃;
for 12h;
With
sodium hydrogencarbonate;
In
water; ethyl acetate;
|
97% |
|
With
iodine;
In
dimethyl sulfoxide;
at 110 ℃;
for 6h;
Temperature;
Concentration;
regioselective reaction;
|
95% |
|
With
N-iodo-succinimide;
In
acetic acid;
at 20 ℃;
for 1h;
|
86% |
|
With
diphenyliodonium tetrafluoroborate; copper(II) sulfate;
In
acetonitrile;
at 65 ℃;
for 0.166667h;
Inert atmosphere;
Schlenk technique;
|
79% |
|
With
[bis(pyridine)iodine]+ tetrafluoroborate; copper(II) sulfate;
In
acetonitrile;
at 65 ℃;
for 0.166667h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
79% |
|
With
potassium iodate; potassium carbonate; acetic acid; potassium iodide;
at 80 ℃;
for 5h;
|
72% |
|
9H-carbazole;
With
acetic acid; potassium iodide;
at 110 ℃;
With
potassium iodate;
at 100 ℃;
for 0.166667h;
|
72.7% |
|
With
iodine; silver nitrate; acetic acid;
at 20 ℃;
|
70% |
|
9H-carbazole;
With
potassium iodide;
In
acetic acid;
at 100 ℃;
for 1h;
With
potassium iodate;
In
acetic acid;
at 100 ℃;
for 2h;
|
70% |
|
With
iron(III) chloride; sodium iodide;
In
acetonitrile;
for 8h;
|
68% |
|
9H-carbazole;
With
acetic acid; potassium iodide;
at 85 ℃;
Reflux;
With
potassium iodate;
at 85 ℃;
for 0.166667h;
|
62% |
|
With
sodium periodate; sulfuric acid; iodine;
In
ethanol;
at 60 ℃;
for 2h;
|
49% |
|
With
sodium periodate; sulfuric acid; iodine;
In
isopropyl alcohol;
at 65 ℃;
for 6h;
|
48% |
|
With
potassium iodate; potassium iodide;
In
acetic acid;
at 45 ℃;
|
47% |
|
9H-carbazole;
With
ammonium iodide;
In
methanol;
for 0.0333333h;
In
methanol;
at 75 ℃;
|
47% |
|
With
potassium iodate; potassium iodide;
In
acetic acid;
for 0.166667h;
Reflux;
|
45% |
|
With
potassium iodate; acetic acid; potassium iodide;
for 0.166667h;
Reflux;
|
45% |
|
With
potassium iodate; acetic acid; potassium iodide;
Heating;
|
44.3% |
|
With
N-iodo-succinimide; acetic acid;
at 20 ℃;
for 5h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
44% |
|
With
N-iodo-succinimide; acetic acid;
at 20 ℃;
for 5h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
44% |
|
With
N-iodo-succinimide; acetic acid;
at 20 ℃;
for 5h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
44% |
|
With
N-iodo-succinimide; acetic acid;
at 20 ℃;
for 5h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
44% |
|
With
N-iodo-succinimide; acetic acid;
at 20 ℃;
for 5h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
44% |
|
With
N-iodo-succinimide; acetic acid;
at 20 ℃;
for 5h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
44% |
|
With
potassium iodate; acetic acid; potassium iodide;
at 100 ℃;
for 2h;
|
40% |
|
With
potassium iodate; acetic acid; potassium iodide;
at 85 ℃;
for 0.166667h;
|
39% |
|
With
periodic acid dihydrate; sulfuric acid; iodine;
In
ethanol;
at 20 ℃;
for 4h;
|
18.8% |
|
With
potassium iodate; acetic acid; potassium iodide;
at 80 ℃;
for 1h;
|
15% |
|
With
potassium iodate; potassium iodide;
|
|
|
With
sulfuric acid; iodine; periodic acid;
acetic acid;
In
water;
at 70 ℃;
for 1h;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; potassium iodide;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; potassium iodide;
In
acetic acid;
|
|
|
With
sulfuric acid; iodine; periodic acid;
In
water; acetic acid;
at 70 ℃;
for 1h;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; potassium iodide;
In
acetic acid;
at 50 ℃;
for 2h;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; acetic acid; potassium iodide;
|
|
|
With
Iodine monochloride;
In
acetonitrile;
at 0 - 20 ℃;
for 4h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; acetic acid; potassium iodide;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; potassium iodide;
|
|
|
With
Iodine monochloride;
at 0 - 20 ℃;
for 4h;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; potassium iodide;
|
|
|
With
Iodine monochloride;
In
acetonitrile;
at 0 - 20 ℃;
for 4h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; acetic acid; potassium iodide;
Reflux;
|
|
|
With
periodic acid dihydrate; sulfuric acid; iodine;
In
ethanol; water;
for 4h;
|
5.1 g |
|
With
potassium iodate; potassium iodide;
In
acetic acid;
for 0.333333h;
Reflux;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; potassium iodide;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; acetic acid; potassium iodide;
at 120 ℃;
for 0.166667h;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; potassium iodide;
at 130 ℃;
|
|
|
With
sodium periodate; sulfuric acid; iodine;
In
ethanol;
|
|
|
With
sodium periodate; sulfuric acid; iodine;
In
ethanol;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; acetic acid; potassium iodide;
Reflux;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; acetic acid; potassium iodide;
at 110 ℃;
for 2h;
|
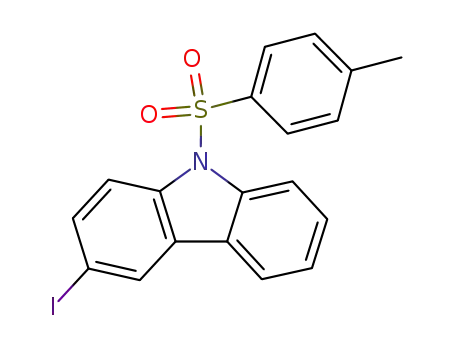
3-iodo-9-(p-tolylsulfonyl)carbazole


3-iodocarbazole
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
sodium hydride;
In
N,N-dimethyl acetamide;
at 60 ℃;
for 3.5h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
85% |

9H-carbazole
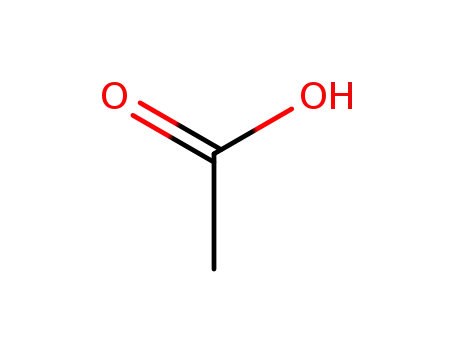
acetic acid
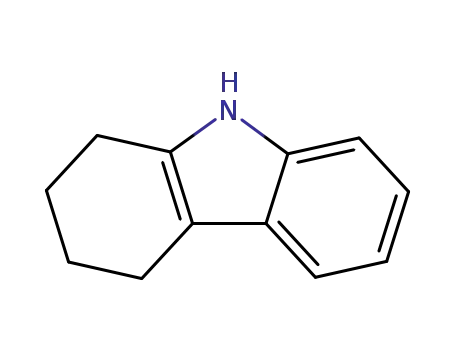
1,2,3,4-tetrahydrocarbazole
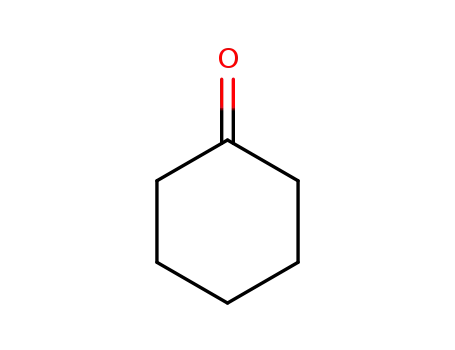
cyclohexanone

3-iodo-9-(p-tolylsulfonyl)carbazole
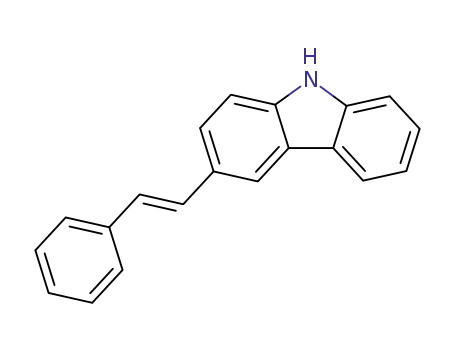
(E)-3-(2-phenylethenyl)carbazole
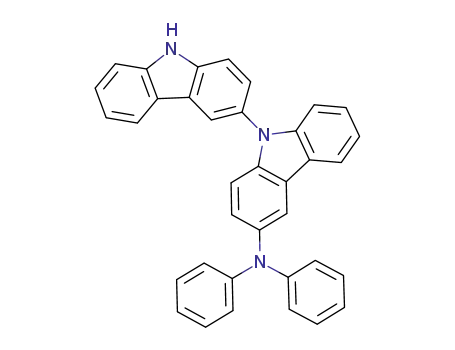
C36H25N3
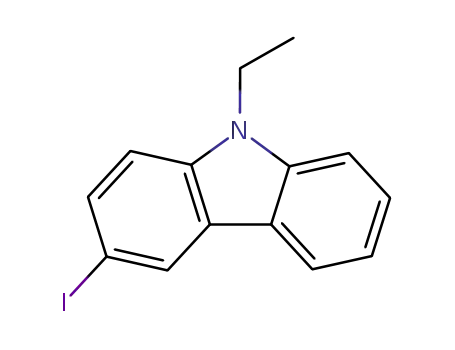
3-iodo-9-ethylcarbazole
CAS:152670-41-2
CAS:1081-34-1
CAS:1484-13-5