Your Location:Home >Products >OLED intermediates >Thiophenes >3140-93-0
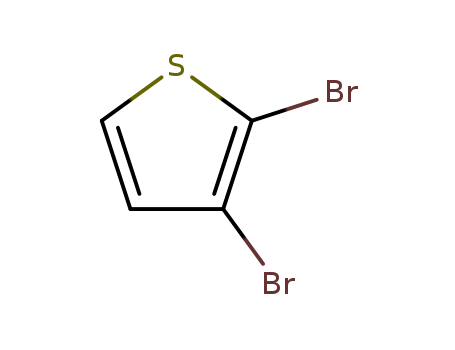

Product Details
Chemical Properties
clear yellowish to brownish liquid
Uses
2,3-Dibromothiophene (cas# 3140-93-0) is a compound useful in organic synthesis.
InChI:InChI=1/C4H2Br2S/c5-3-1-2-7-4(3)6/h1-2H
Two new conjugated D-A polymers P3 (PBTT-d-BTT) and P4 (PBTT-d-TPD) based on same benzo[1,2-b:3,4-b′:6,5-b″] trithiophene (BTT) donor and different acceptors monomers 5,8-dibromo-2-dodecanoylbenzo[1,2-b:3,4-b′:6,5-b″] trithiophene (d-BTT), and 1,3-dibromo-5-(2-ethylhexyl)thieno[3,4]pyrrol-4,6-dione (d-TPD) respectively, were synthesized by Stille cross-coupling reaction and characterized by gel permeation chromatography (GPC), 1H NMR, UV-Vis absorption, thermal analysis and electrochemical cyclic voltammetry (CV) tests. Photovoltaic properties of the polymers were studied by using the polymers as donor and PC71BM as acceptor with a weight ratio of polymer:PC71BM 1:1, 1:2 and 1:2.5. The optimized photovoltaic device was fabricated with an active layer of a blend P3:PC71BM and P4:PC71BM with a blend ratio of 1:2 showed PCE 3.16% and 2.42%, respectively under illumination of AM 1.5 at 100 mW/cm2 with solar simulator. The PCE of the device based on P3:PC71BM processed with DIO/o-DCB has been further improved up to 4.64% with Jsc of 10.52 mA/cm2 and FF of 0.58 attributed to the increase in crystalline nature of active layer and more balanced charge transport in the device, induced by DIO additive.
Two new conjugated D-A copolymers P1 (PBTT-TQ) and P2 (PBTT-TPz) based on the same benzo[1,2-b:3,4-b′:6,5-b′′] trithiophene (BTT) donor and different acceptor monomers 4,9-bis(5-bromithiophen-2-yl)-6,7-bis(2-ethylhexyl)[1,2,5] thiadiazolo[3,4-g] quinoxaline (TQ) and 5,7-bis(5-bromothiophen-2-yl)-2,3-bis(5-octylthiophen-2-yl) thieno[3,4-b] pyrazine (TPy), respectively, were synthesized by Stille cross-coupling reaction and characterized by gel permeation chromatography (GPC), 1H NMR, UV-Vis absorption, thermal analysis and electrochemical cyclic voltammetry (CV) tests. The optical bandgaps of P1 and P2 measured from the onset of optical absorption of these copolymers in thin films were 1.14 eV and 1.38 eV, respectively. Photovoltaic properties of the bulk heterojunction (BHJ) devices were studied using P1 and P2 as the donor and PC61BM or PC71BM as the acceptor with weight ratios of polymer:PC61BM of 1:1, 1:2 and 1:3. The optimized photovoltaic devices fabricated with active blend layers of P1:PC71BM (1:2) and P2:PC71BM (1:2) cast from o-diclorobenzene (o-DCB) showed PCEs of 2.05% and 3.14%, respectively, whereas P2:PC61BM and P2:PC71BM yielded PCEs of 1.44% and 2.11%, respectively. The PCEs of BHJ solar cells based on P1:PC71BM and P2:PC71BM processed from 1-chloronapthanene (CN)/o-DCB solvent were further improved up to 5.28% and 2.6%, respectively. This journal is
Catalyst systems that include a chain transfer agent and a metal-ligand complex according to formula (I).
The application of sterically hindered palladium catalysts to the regioselective hydrodebromination of 2,3,5-tribromothiophene has been studied in detail, including the effects of catalyst choice, solvent, reaction time, and temperature, as well as the method of NaBH4 addition and the role of chelating additives to effect NaBH4 solubility. Ultimately it was determined that the background reaction between NaBH4 and bromothiophenes is too facile to allow both total conversion and high selectivity. Optimized conditions finally allowed a selectivity of ca. 16:1 with overall conversion of 100%. However, complications of overdebromination under these conditions still limit the yield of the desired 2,3-dibromothiophene to 65%.
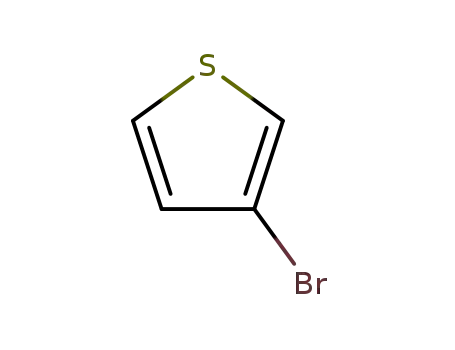
3-Bromothiophene

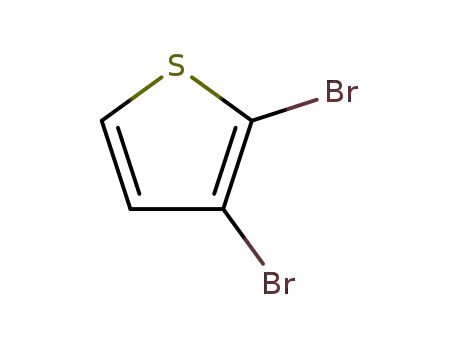
2,3-dibromothiophen
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
N-Bromosuccinimide;
perchloric acid;
In
tetrachloromethane;
for 24h;
Ambient temperature;
|
99% |
|
With
bromine;
In
acetic acid;
|
89% |
|
3-Bromothiophene;
With
N-Bromosuccinimide; perchloric acid;
In
hexane; water;
at 20 ℃;
for 24h;
With
potassium carbonate;
In
hexane; water;
|
89% |
|
With
N-Bromosuccinimide; perchloric acid;
In
hexane; water;
at 20 ℃;
for 24h;
|
89% |
|
With
N-Bromosuccinimide; perchloric acid;
In
hexane; water;
at 20 ℃;
for 24h;
|
89% |
|
With
bromine;
In
acetic acid;
|
83% |
|
With
bromine;
In
acetic acid;
at 18 ℃;
Thermodynamic data;
other temperatures: 26, 34, 42 deg C; Ea = 12.1 kcal/mol;
|
|
|
With
bromine; lithium bromide;
In
water; acetic acid;
at 26 ℃;
Kinetics;
Thermodynamic data;
Mechanism;
Ea, ΔS(excit.), ΔG(excit.); further temperatures: 18, 34, 42 deg C;
|
|
|
With
bromine; benzene;
|
|
|
With
bromine; sodium acetate;
In
dichloromethane;
at 0 ℃;
|
|
|
With
N-Bromosuccinimide; acetic acid;
In
chloroform;
at 20 ℃;
|
|
|
With
ammonium bromide; acetic acid;
In
water;
for 20h;
regioselective reaction;
Green chemistry;
|
86 %Chromat. |
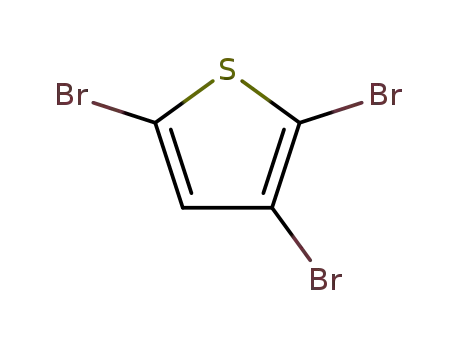
2,3,5-tribromothiophene


2,3-dibromothiophen
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
sodium tetrahydroborate; tetrakis(triphenylphosphine) palladium(0);
In
acetonitrile;
for 24h;
Heating;
|
83% |

3-Bromothiophene

2,3,5-tribromothiophene
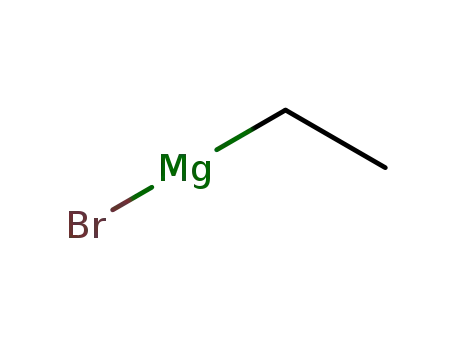
ethylmagnesium bromide
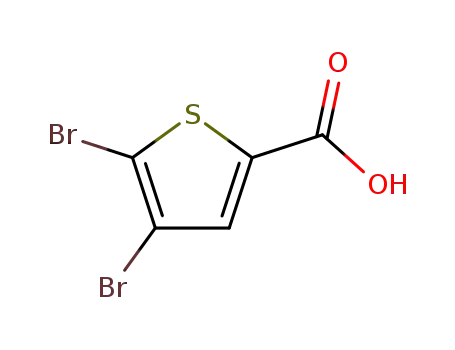
4,5-Dibromo-thiophene-2-carboxylic acid
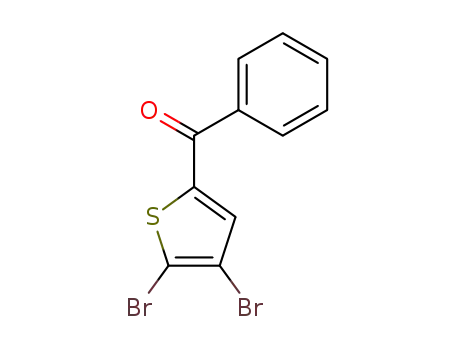
4,5-dibromo-2-benzoylthiophene
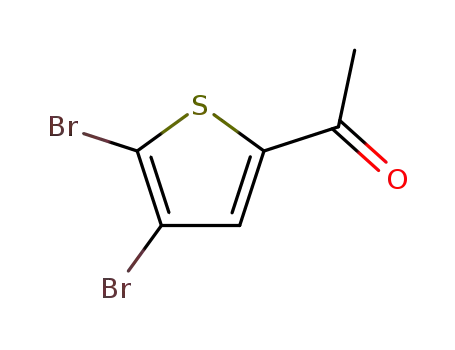
1-(4,5-dibromothiophen-2-yl)ethanone

3-Bromothiophene
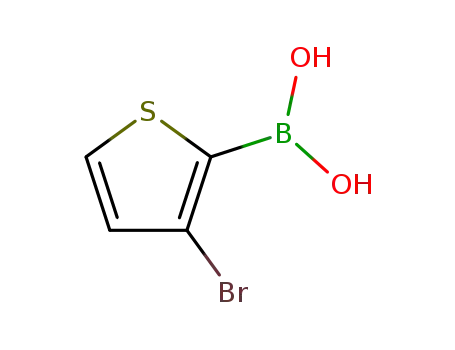
(3-bromothiophen-2-yl)boronic acid
CAS:571-57-3
CAS:90-41-5
CAS:3141-24-0
CAS:52431-30-8