Your Location:Home >Products >Organic phosphines >Phenyl phosphines >13885-09-1
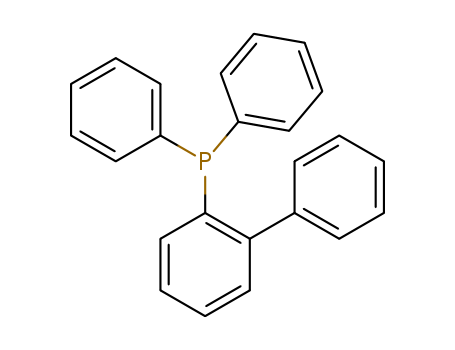
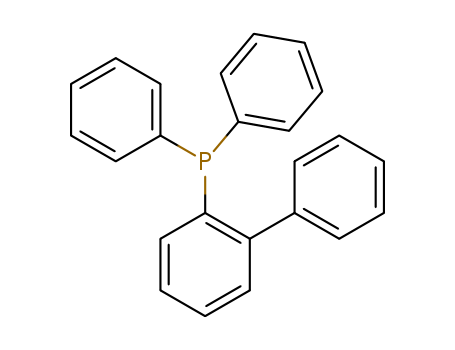
Product Details
Uses
suzuki reaction
Uses
2-(Diphenylphosphino)biphenyl is used as an organic chemical synthesis intermediate.
InChI:InChI=1/C24H19P/c1-4-12-20(13-5-1)23-18-10-11-19-24(23)25(21-14-6-2-7-15-21)22-16-8-3-9-17-22/h1-19H
The Pd(II)-catalyzed Ph2(O)P-directed C-H olefination to synthesize alkene-phosphine compounds is reported. In contrast to previous examples of various directing groups that guide selective C-H activation, the Ph2(O)P group not only acts as the directing group but also serves to construct the alkene-phosphine ligands. The monoprotected amino acid (MPAA) ligand Ac-Leu-OH is found to promote this reaction in a significant manner.
An effective synthesis of chiral atropoisomeric biaryl phosphine-olefin compounds via palladium-catalyzed enantioselective C-H olefination has been developed for the first time. The reactions are operationally simple, tolerate wide functional groups, and have a good ee value. Notably, P(O)R2 not only acts as the directing group to direct C-H activation in order to make a useful ligand but also serves to facilitate composition of the product in a useful manner in this transformation.
Spectacular progress has recently been achieved in transition metal-catalyzed C?H borylation of phosphines as well as directed electrophilic C?H borylation. As shown here, P-directed electrophilic borylation provides a new, straightforward, and efficient access to phosphine–boranes. It operates under metal-free conditions and leverages simple, readily available substrates. It is applicable to a broad range of backbones (naphthyl, biphenyl, N-phenylpyrrole, binaphthyl, benzyl, naphthylmethyl) and gives facile access to various substitution patterns at boron (by varying the boron electrophile or post-derivatizing the borane moiety). NMR monitoring supports the involvement of P-stabilized borenium cations as key intermediates. DFT calculations reveal the existence and stabilizing effect of π-arene/boron interactions in the (biphenyl)(i-Pr)2P→BBr2+ species.
Palladium-catalyzed C-P bond formation reaction of ArBr/ArOTf using acylphosphines as differential phosphination reagents is reported. The acylphosphines show practicable reactivity with ArBr and ArOTf as the phosphination reagents, though they are inert to the air and moisture. The reaction affords trivalent phosphines directly in good yields with a broad substrate scope and functional group tolerance. This reaction discloses the acylphosphines' capability as new phosphorus sources for the direct synthesis of trivalent phosphines.
An efficient homogeneous palladium-catalyzed selective deoxygenation of 2,2′-biphenols by reduction of aryl triflates with HCO 2H as the hydrogen source is reported. This protocol complements the current method based on heterogeneous Pd/C-catalyzed hydrogenation with hydrogen gas. This process provided the reduction products in good to excellent yields, which could be readily converted to various synthetically useful molecules, especially ligands for catalytic synthesis.
To provide europium complexes having high photostability. A europium complex expressed with the following formula (A): {wherein, RA and RB are independently a cyclic alkyl group with 3 to 10 carbons, respectively, and RC is a cyclic alkyl group with 3 to 10 carbons or a phenyl group expressed with the following formula (B): (wherein, XA, XB, AC, XD and XE independently represent a hydrogen atom; a fluorine atom; an alkyl group with 1 to 3 carbon(s); an alkyloxy group with 1 to 3 carbon(s); an aryloxy group with 6 to 10 carbons; a fluoroalkyl group with 1 to 3 carbon(s); a fluoroalkyloxy group with 1 to 3 carbon(s); or a phenyl group that may be substituted with a fluorine atom, an alkyl group with 1 to 3 carbon(s), an alkyloxy group with 1 to 3 carbon(s), a fluoroalkyl group with 1 to 3 carbon(s), a fluoroalkyloxy group with 1 to 3 carbon(s), a fluorophenyl group, a hydroxyl group or a cyano group, respectively); RA is a cyclic alkyl group with 3 to 10 carbons; RB and RC are a phenyl group expressed with the formula (B), provided, however, that a case where RA a cyclohexyl group, and, RB and RC are a phenyl group is excluded; or RA, RB and RC independently represent an ortho-substituted phenyl group expressed with the following formula (Ba): (wherein, XE represents a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group with 1 to 3 carbon(s), an alkyloxy group with 1 to 3 carbon(s), a fluoroalkyl group with 1 to 3 carbon(s), a fluoroalkyloxy group with 1 to 3 carbon(s), a naphthyl group that may be substituted with a fluorine atom, a pyridyl group that may be substituted with a fluorine atom, or a phenyl group that is expressed with a formula (C): [wherein, ZA, ZC and ZE independently represent a hydrogen atom, a fluorine atom, an alkyl group with 1 to 3 carbon(s), an alkyloxy group with 1 to 3 carbon(s), a fluoroalkyl group with 1 to 3 carbon(s), a fluoroalkyloxy group with 1 to 3 carbon(s), a phenyl group that may be substituted with a fluorine atom, a hydroxyl group or a cyano group; ZB and ZD independently represent a hydrogen atom or a fluorine atom, respectively], provided, however, that a case where RA, RB and RC are all a phenyl group is excluded), respectively; RD represents a hydrogen atom, a deuterium atom or a fluorine atom; WA and WB independently represent an alkyl group with 1 to 6 carbon(s), a fluoroalkyl group with 1 to 6 carbon(s), a phenyl group, a 2-thienyl group or a 3-thienyl group; and ‘n’ represents an integer of 1 to 3}.
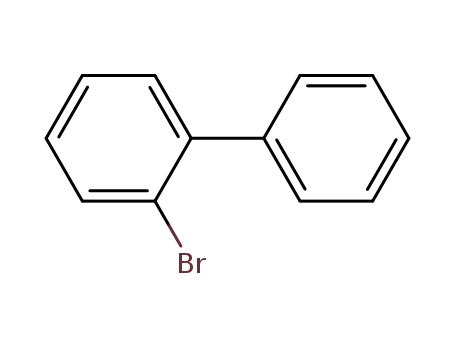
2-Bromobiphenyl
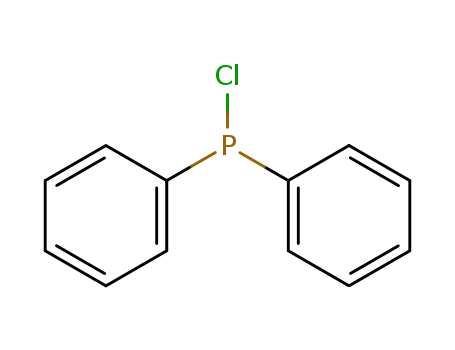
chloro-diphenylphosphine

![[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yldiphenylphosphane](/upload/2023/2/27c09de3-93d2-4211-85d0-a3e31193cb62.png)
[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yldiphenylphosphane
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
2-Bromobiphenyl;
With
n-butyllithium;
In
diethyl ether; hexane;
at -15 ℃;
Inert atmosphere;
chloro-diphenylphosphine;
In
diethyl ether; hexane;
at 20 ℃;
for 3h;
Cooling;
Inert atmosphere;
|
79% |
|
2-Bromobiphenyl;
With
magnesium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
Inert atmosphere;
Reflux;
chloro-diphenylphosphine;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
Inert atmosphere;
|
67% |
|
2-Bromobiphenyl;
With
n-butyllithium;
In
diethyl ether; hexane;
at 0 ℃;
for 2h;
chloro-diphenylphosphine;
In
diethyl ether; hexane;
at 20 ℃;
for 1h;
|
|
|
2-Bromobiphenyl;
With
n-butyllithium;
In
diethyl ether; hexane;
at 0 ℃;
for 2h;
Inert atmosphere;
chloro-diphenylphosphine;
In
diethyl ether; hexane;
at 20 ℃;
for 1h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
|
|
2-Bromobiphenyl;
With
n-butyllithium;
In
diethyl ether; hexane;
at 0 ℃;
for 2h;
chloro-diphenylphosphine;
In
diethyl ether;
at 20 ℃;
for 1h;
|

2-iodobiphenyl

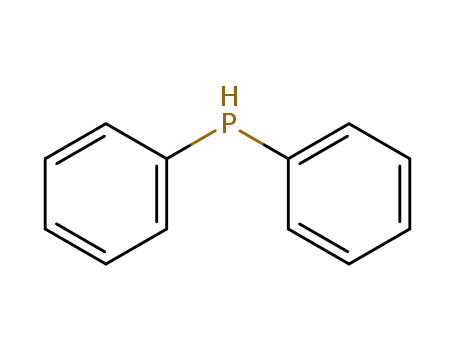
diphenylphosphane

![[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yldiphenylphosphane](/upload/2023/2/27c09de3-93d2-4211-85d0-a3e31193cb62.png)
[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yldiphenylphosphane
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
diphenylphosphane;
With
copper(l) iodide; N,N`-dimethylethylenediamine;
In
toluene;
2-iodobiphenyl;
With
caesium carbonate;
In
toluene;
at 110 ℃;
for 20h;
|
81% |
|
diphenylphosphane;
With
copper(l) iodide; N,N`-dimethylethylenediamine;
In
toluene;
for 0.166667h;
Inert atmosphere;
2-iodobiphenyl;
With
caesium carbonate;
In
toluene;
at 110 ℃;
for 24h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
73% |
|
With
caesium carbonate;
In
toluene;
at 115 ℃;
for 24h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
64% |
|
With
potassium acetate;
In
N,N-dimethyl acetamide;
at 130 ℃;
for 3h;
Schlenk technique;
Inert atmosphere;
|
61% |
[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yldimethylphosphine oxide
(2-bromophenyl)diphenylphosphane
phenylboronic acid

2-iodobiphenyl
(acetylacetonato)carbonylrhodium(I)(2-phenylphenyl)diphenylphosphane
[(2-(diphenylphosphanyl)-3-phenylphenyl-(C(1),P))tris(trimethylphopshane)cobalt(I)]
trans-dichlorobis[diphenyl(o-phenylphenyl)phosphane]palladium(II)
trans-di-μ-chlorodichlorobis[diphenyl(o-phenylphenyl)phosphane]dipalladium(II)
CAS:1402393-56-9
Molecular Formula:C23H31BrO2
Molecular Weight:419.4
CAS:855-38-9
CAS:2071-20-7