Your Location:Home >Products >Functional intermediates >7293-45-0
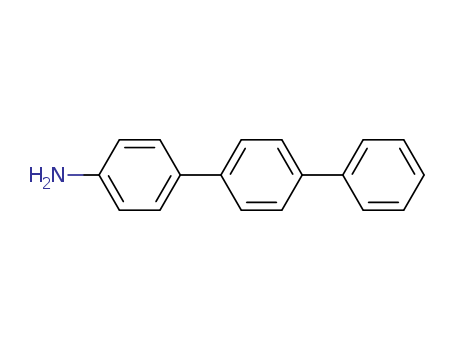

Product Details
Chemical Properties
light yellow powder
InChI:InChI=1/C18H15N/c19-18-12-10-17(11-13-18)16-8-6-15(7-9-16)14-4-2-1-3-5-14/h1-13H,19H2
An efficient method for palladium-catalyzed Suzuki cross-coupling reaction with simultaneous reduction of nitro- to amino-group has been developed. This method allows nitro-substituted aryl halides to readily react with arylboronic acids, to afford aryl substituted aniline in low to excellent yields. The reaction was catalyzed by Pd(OAc)2 (3 mol %) at 150 °C under atmospheric pressure in the presence of K2CO3 (3 equiv) in DMF/H2O (5/1).
A phenylnitrenium ion formed from N-phenylhydroxylamine in the presence of trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) containing polyphosphoric acid (PPA) interacts with the counterion -O2CCF3 and the unshared electron-pair of H2O, showing Hammett's ρ values -5.2 and -4.0 for N- and C-attacks on aromatics PhX (X = H, Me, Et, Ph and Cl), respectively. The ratio N-/C-attack for this nitrenium ion is lower than for the nitrenium ion interacting with only the counterion; the latter nitrenium ion is generated by the use of trifluoroacetic anhydride (TFAA) instead of PPA or by reaction of phenyl azide with aromatics in TFA. The ratio for the former nitrenium ion is affected by the aromatic substituent X:X = Me > X = Et > X = Ph > X = H > X = OMe at 20 and 50°C. The order for X = Cl is between those of X = H and X = Ph at 20°C, but highest at 50°C. The ratio is increased by higher reaction temperature and by decreased concentration of TFA. The results are demonstrated from the mechanistic viewpoint for the nitrenium ions.
Phenylnitrenium ions were generated from phenyl azides in the presence of trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) and/or trifluoromethanesulphonic acid (TFSA).Unsubstituted phenylnitrenium ions and those with an electron-withdrawing group such as NO2 or CN undergo aromatic N-substitution, whereas those with an electron-donating group such as Me, OMe, CH2Ph, or Ph undergo C-substitution, hydrogen abstraction, and tar formation.The special character of TFA and TFSA as compared with other acids is discussed.
Aromatic N-substitution by phenylnitrenium ions generated from phenyl azide in the presence of a catalytic amount of trifluoromethanesulphonic acid gave diarylamines (in especially good yield in the reaction with biphenyl or naphthalene), whereas naphthylnitrenium ions from 1-azidonaphthalene react with benzene to afford a C-substitution product, 1-amino-4-phenylnaphthalene.
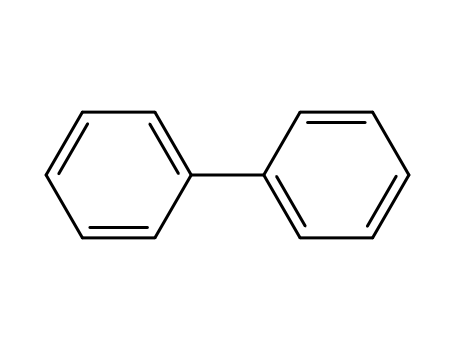
biphenyl
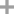
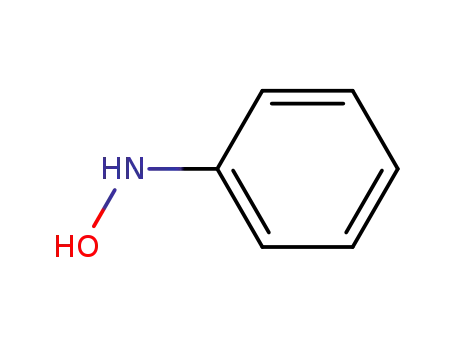
N-Phenylhydroxylamine

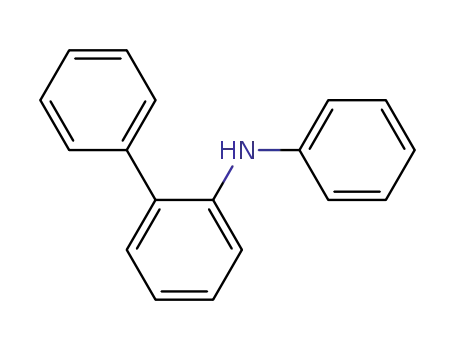
N-(2-biphenyl)aniline

![[1,1':4',1''-terphenyl]-2-amine](/upload/2023/2/4661c2fe-94bf-4d80-8c85-30604ba15e1f.png)
[1,1':4',1''-terphenyl]-2-amine

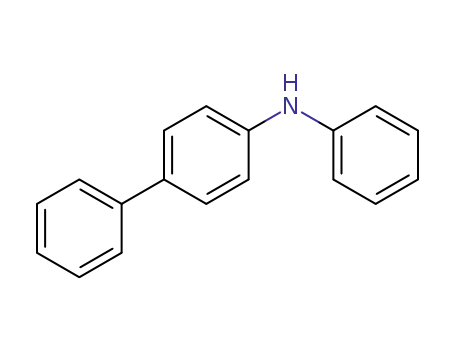
4-phenyldiphenylamine


4-aminoterphenyl
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
PPA; trifluoroacetic acid;
In
dichloromethane;
at 20 ℃;
for 3h;
Further byproducts. Title compound not separated from byproducts.;
|
1.2 % Chromat. 17 % Chromat. 30 % Chromat. 7.7 % Chromat. |

biphenyl

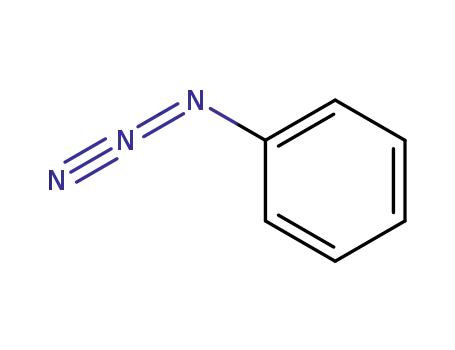
Phenyl azide


N-(2-biphenyl)aniline


4-phenyldiphenylamine


4-aminoterphenyl
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
trifluoroacetic acid;
Ambient temperature;
|
68% 3% 24% |
|
With
dichloromethane; trifluorormethanesulfonic acid;
Ambient temperature;
|
68% 3% 24% |
|
With
dichloromethane; trifluoroacetic acid;
Ambient temperature;
|
18% 43% 6% |
|
In
benzene;
Ambient temperature;
reactivity relative to benzene in the presence of trifluoromethanesulfonic acid and trifluoroacetic acid;
|

biphenyl

Phenyl azide
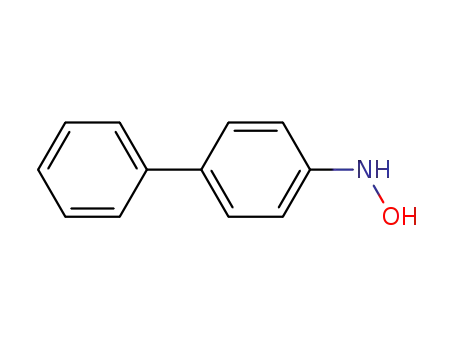
4-hydroxylaminobiphenyl
benzene
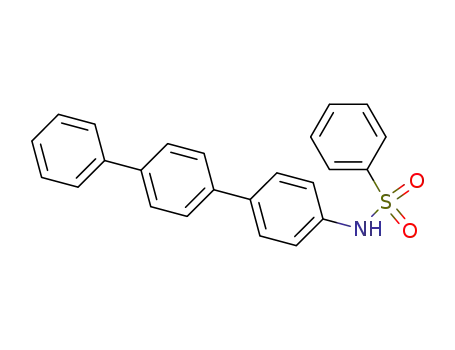
N-p-terphenyl-4-yl-benzenesulfonamide
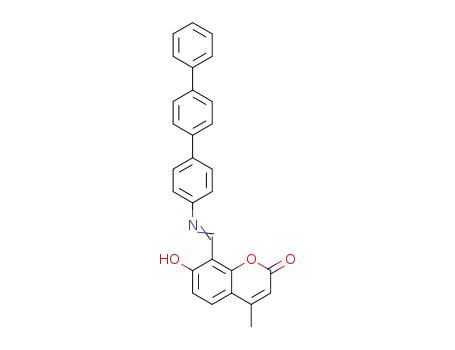
7-hydroxy-4-methyl-8-([1,1';4',1'']terphenyl-4-ylimino)methyl-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one
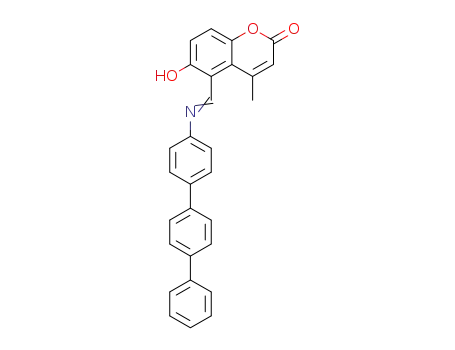
6-hydroxy-4-methyl-5-([1,1';4',1'']terphenyl-4-ylimino)methyl-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one

N-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)-[1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl]-4-amine
CAS:400607-04-7
Molecular Formula:C24H15Br
Molecular Weight:383.3
CAS:76186-72-6
CAS:65344-26-5