Your Location:Home >Products >Functional intermediates >2489-86-3

Product Details
Chemical Properties
Colorless liquid
InChI:InChI=1/C13H12/c1-2-6-11-8-5-9-12-7-3-4-10-13(11)12/h2-5,7-10H,1,6H2
New mono-, bis- and tetra-fluorophoric organosilicon naphthalene derivatives, that are able to form intramolecular excimers have been synthesized and characterized. The synthesized compounds show only monomeric fluorescence in dilute solutions of common organic solvents, but exhibit relatively strong excimer-like emission in DMSO-water and THF-water mixtures. In all cases, the intensity of excimer fluorescence increases with increasing water content and decreases with increasing temperature. Fully and partially overlapping excimer conformations have been modeled by DFT-based calculations. Properties of different intramolecular excimers in an ensemble of four naphthalene molecules linked to a cyclotetrasiloxane ring in an all-cis arrangement are considered.
-
Alkenes are used ubiquitously as starting materials and synthetic targets in all areas of chemistry. Controlling their geometry and position along a chain is vital to their reactivity and properties yet remains challenging. Alkene isomerization is an atom-economical process to synthesize targeted alkenes, and selectivity can be controlled using transition metal catalysts. The development of mild, selective isomerization reactivity has enabled efficient tandem catalytic systems for the remote functionalization of alkenes, a process in which a starting alkene is isomerized to a new position prior to the functionalization step. The key challenges in developing isomerization catalysts for remote functionalization applications are (i) a lack of modularity in the catalyst structure and (ii) the requirement of nonmodular and/or harsh additives during catalyst activation. We address both challenges with a modular (NHC)Ni(0)/silane catalytic system (NHC, N-heterocyclic carbene), demonstrating the use of triaryl silanes and readily accessible (NHC)Ni(0) complexes to form the proposed active (NHC)(silyl)Ni-H species in situ. We show that modification of the steric and electronic nature of the catalyst via modification of the ancillary ligand and silane partner, respectively, is easily achieved, creating a uniquely versatile catalytic system that is effective for the formation of internal alkenes with high yield and selectivity for the E-alkene. The use of silanes as mild activators enables isomerization of substrates with a variety of functional groups, including acid-labile groups. The broad substrate scope, enabled by catalyst design, makes this catalytic system a strong candidate for use in tandem catalytic applications. Preliminary mechanistic studies support a Ni-H insertion/elimination pathway.
Provided is a method for producing (alkyl)arene compounds represented by Formulae 3-1, 3-2, and 3-3 by the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction of alkyl halide compounds and arene compounds using organic phosphine compounds as a catalyst.
A copper-mediated oxidative isoperfluoropropylation of unactivated terminal alkenes with commercially available hexafluoropropylene (HFP) has been developed. With operational simplicity of the procedure and broad substrate applicability, this strategy pro
polyethylene

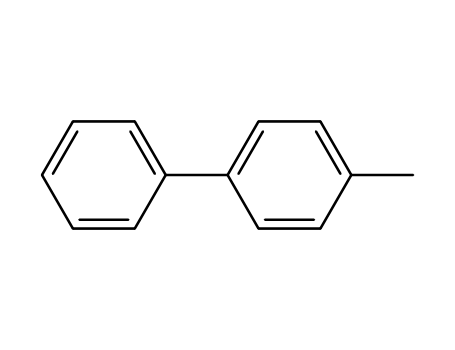
4-Methylbiphenyl
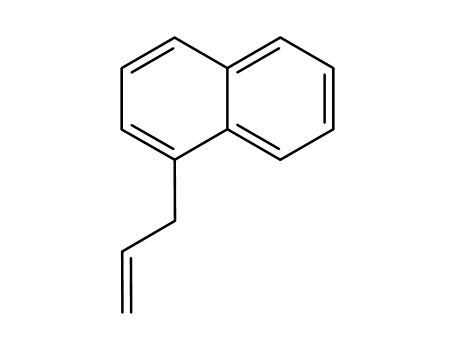
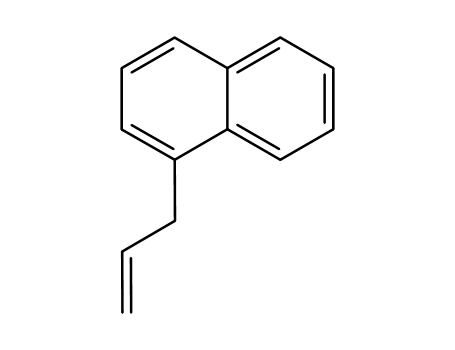
1-allylnaphthalene

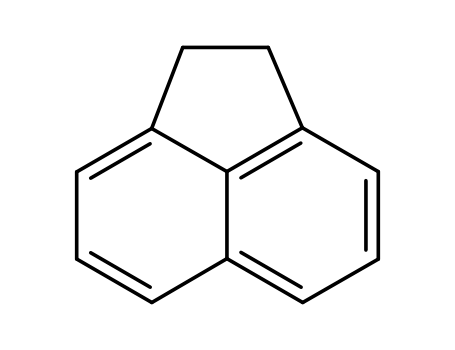
acenaphthene

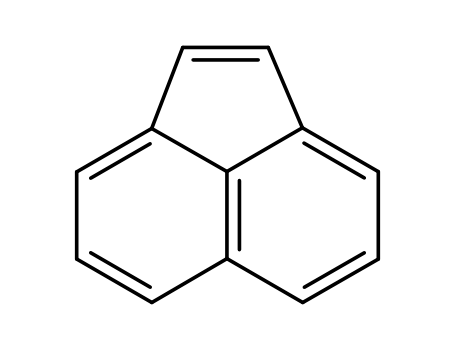
acenaphthylene
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
air;
at 600 - 900 ℃;
Further byproducts given;
Formation of xenobiotics;
|
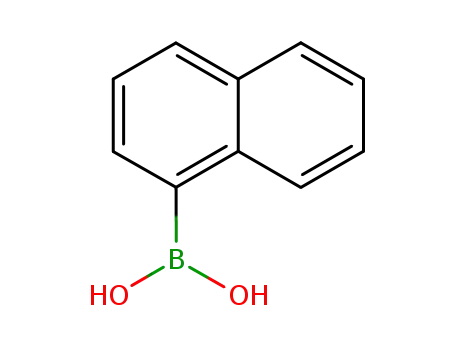
1-Naphthylboronic acid

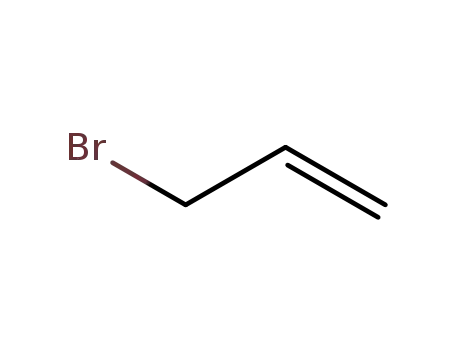
allyl bromide


1-allylnaphthalene
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
tris-(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0); potassium carbonate;
In
toluene;
at 110 ℃;
for 12h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
99% |
|
With
2C2H3O2(1-)*Pd(2+)*3Na(1+)*C18H12O9PS3(3-); potassium tert-butylate; glycerol;
at 100 ℃;
for 2h;
Schlenk technique;
Inert atmosphere;
|
92% |
|
With
tris-(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0); potassium carbonate;
In
toluene;
at 110 ℃;
for 15h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
85% |
|
With
2C2H3O2(1-)*Pd(2+)*3Na(1+)*C18H12O9PS3(3-); triethylamine; glycerol;
at 100 ℃;
for 2h;
Schlenk technique;
Inert atmosphere;
|
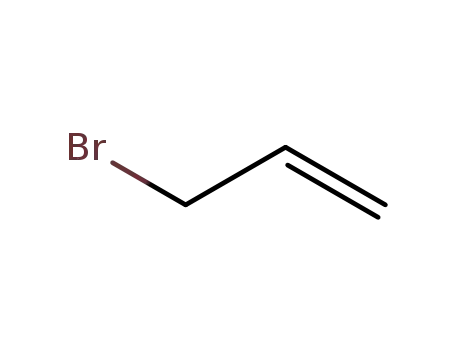
allyl bromide
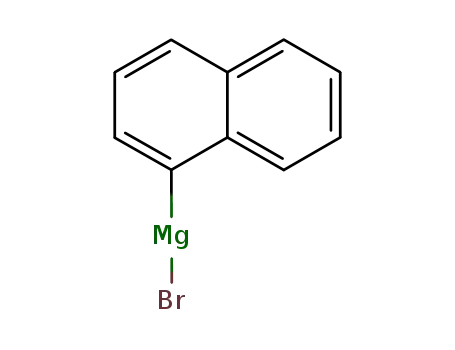
1-naphthylmagnesiumbromide
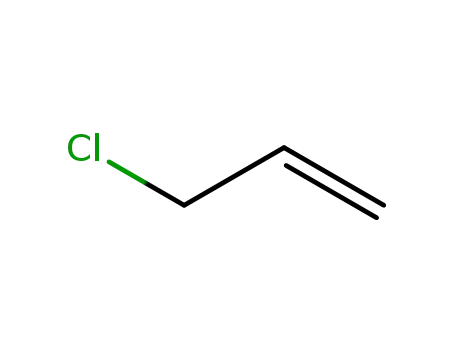
3-chloroprop-1-ene

1-Bromonaphthalene
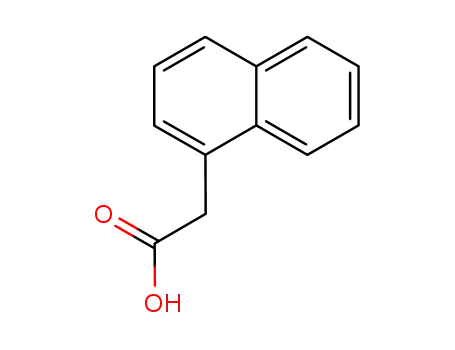
naphth-1-yl acetic acid
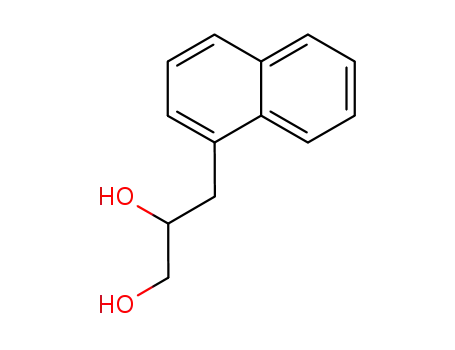
3-[1]naphthyl-propane-1,2-diol
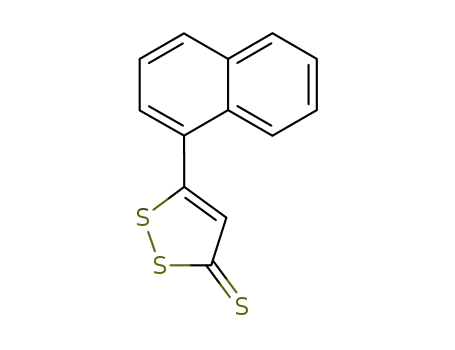
5-(1-naphtyl)-3H-1,2-dithiol-3-thione
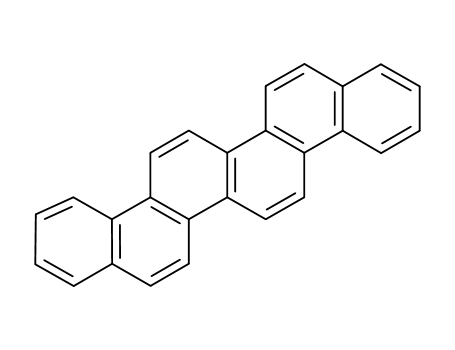
benzo[c]picene
CAS:14126-37-5
CAS:400607-16-1
CAS:1700-02-3
Molecular Formula:C<sub>9</sub>H<sub>5</sub>C<sub>l2</sub>N<sub>3</sub>
Molecular Weight:226.06