Your Location:Home >Products >Functional intermediates >728039-63-2

Product Details
We synthesized four hyper-conjugated aromatic hole transporting materials with different molecular geometry and energy levels by attaching arylamino moiety attached to the carbazole core. A brominated carbazole moiety reacted with an arylamino moiety using a Buchwald-Hartwig reaction. The characteristics of these hole transporting materials were investigated using TGA, DSC, UV–Vis and luminescence spectroscopy. The energy levels of all materials used in this study were estimated from cyclic voltammograms and absorption spectra. The hole transporting properties of the synthesized molecules were measured using single-carrier devices. All four hole transporting materials showed similar hole mobility. The effectiveness of hole transporting materials was compared by fabricating green-emitting organic light emitting diode (OLED) devices. It turned out that the device performances were critically dependent on the relative energy levels of the hole transporting layer and emission layer. However, the molecular geometry greatly influenced the device lifetime, determining thermally induced crystallization by the heat produced during device operation.
The invention discloses an aromatic amine compound containing a carbazole group and an organic light emitting diode thereof, and relates to the technical field of organic photoelectric materials. Thearomatic amine compound structurally contains the specific carbazole group, on one hand, the carbazole group has a high triplet state energy level and a high hole mobility, on the other hand, the carbazole group has a relatively high redox potential value and has good stability under the condition of air or illumination, in addition, four hydrogen bonds of a phenyl group on a N site of the substituted carbazole group are replaced by four deuterium bonds, deuterium is non-toxic and non-radioactive and is 6-9 times more stable than a carbon-hydrogen bond, and therefore the compound with more stable property is obtained; in addition, by means of the carbazole and ortho-position connected biphenyl, conjugating of the structure is extended, and the hole transmission is facilitated; and the obtained aromatic amine compound is used as a hole-transport material or an optical extraction layer material in the organic light emitting diode and has the advantages of being high in efficiency, high in brightness and long in service life.
Belonging to the technical field of photoelectric material applied science and technology, the invention in particular relates to a triarylamine derivative, a preparation method and application thereof. The triarylamine derivative provided by the invention adopts triarylamine and fluorenocarbazole as the basic structural unit, and after modification, an asymmetric structure can be obtained so as to compose compounds rich in holes and with high glass transition temperature. When the compounds are used as a hole transport material, compared with the commonly used hole transport material like N,N'-diphenyl-N, N'-bis(3-methylphenyl)-1, 1'-biphenyl-4, 4'-diamine (TPD) in the prior art, the hole transport ability is significantly improved, in OLEDs, the series of compounds have significantly improved starting voltage and glass transition temperature compared with the traditional hole transport materials, and are ideal hole transport materials. In addition, when the series of compounds are used as a light-emitting layer, the efficiency of OLEDs is greatly improved, and the series of compounds are ideal light-emitting layer materials.
The present invention relates to a compound for an organic electronic element, an organic electronic element using the same, and an electronic device thereof and, more specifically, to a novel compound comprising O atom heterocycles capable of improving luminous efficiency, stability, and service life of an element, an organic electronic element using the same, and an electronic device thereof.
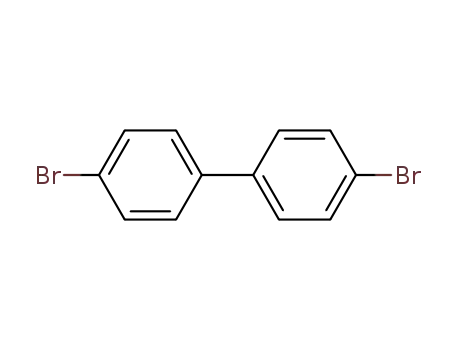
4-(4-bromophenyl)bromobenzene
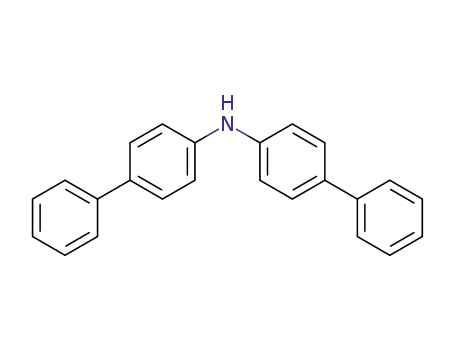
bis(biphenyl-4-yl)amine

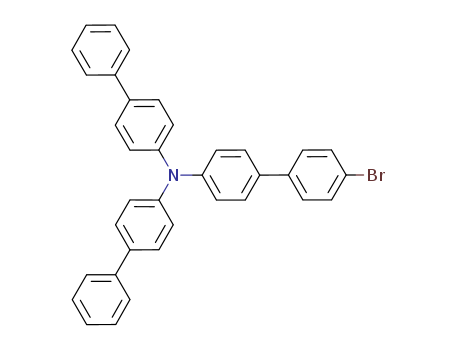
![N,N-di([1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4′-bromo-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-amine](/upload/2023/2/80976770-f3be-4dbe-b77d-f8679d057f7b.png)
N,N-di([1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4′-bromo-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-amine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
palladium diacetate; triphenylphosphine; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
Inert atmosphere;
Reflux;
|
78% |
|
With
tri-tert-butyl phosphine; palladium diacetate; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
for 2h;
Reflux;
|
75% |
|
With
(1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium(II) dichloride; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
at 80 ℃;
for 25h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
74% |
|
With
tris-(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0); tri-tert-butyl phosphine; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
at 60 ℃;
for 12h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
68% |
|
With
tris-(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0); tri-tert-butyl phosphine; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
at 60 ℃;
for 12h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
68% |
|
With
tris-(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0); tri-tert-butyl phosphine; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
at 60 ℃;
for 12h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
68% |
|
With
tris-(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0); tri-tert-butyl phosphine; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
at 60 ℃;
for 12h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
68% |
|
With
tris-(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0); triphenylphosphine; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
at 60 ℃;
for 12h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
68% |
|
With
tri-tert-butyl phosphine; bis(dibenzylideneacetone)-palladium(0); sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
at 120 ℃;
for 18h;
|
53% |
|
With
sodium t-butanolate;
bis-triphenylphosphine-palladium(II) chloride;
In
xylene;
at 130 ℃;
for 24h;
|
|
|
bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(II)-chloride;
In
5,5-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene; water; argon;
|
|
|
With
sodium t-butanolate;
bis-triphenylphosphine-palladium(II) chloride;
In
xylene;
at 130 ℃;
for 24h;
|
|
|
With
bis-triphenylphosphine-palladium(II) chloride; sodium t-butanolate;
In
xylene;
at 130 ℃;
for 24h;
|
|
|
With
sodium t-butanolate;
bis-triphenylphosphine-palladium(II) chloride;
In
xylene;
at 130 ℃;
for 24h;
|
|
|
With
sodium t-butanolate;
bis-triphenylphosphine-palladium(II) chloride;
In
xylene;
at 130 ℃;
for 24h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
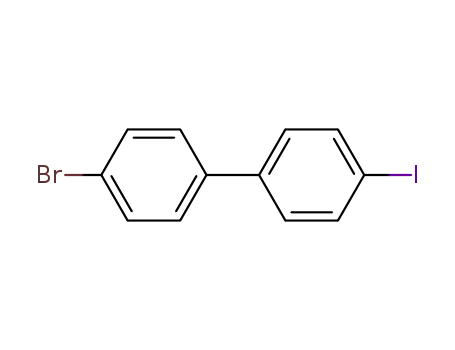
4-bromo-4'-iodobiphenyl


bis(biphenyl-4-yl)amine

![N,N-di([1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4′-bromo-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-amine](/upload/2023/2/80976770-f3be-4dbe-b77d-f8679d057f7b.png)
N,N-di([1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4′-bromo-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-amine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
tri-tert-butyl phosphine; palladium diacetate; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
for 2h;
Reflux;
|
90% |
|
With
palladium diacetate; triphenylphosphine; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
at 80 ℃;
for 8h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
83% |
|
With
copper(l) iodide; 1,10-Phenanthroline; potassium tert-butylate;
In
toluene;
at 100 ℃;
for 48h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
82% |
|
With
tri-tert-butyl phosphine; palladium diacetate; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
at 115 ℃;
for 24h;
Inert atmosphere;
Sonication;
|
76% |
|
With
tris-(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0); tri-tert-butyl phosphine; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
for 8h;
Inert atmosphere;
Reflux;
|
72% |
|
With
tris-(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0); tri-tert-butyl phosphine; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
for 8h;
Reflux;
|
72% |
|
With
palladium diacetate; 4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene; sodium t-butanolate;
In
5,5-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene;
at 120 ℃;
for 2h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
68% |
|
With
bis-triphenylphosphine-palladium(II) chloride; sodium t-butanolate;
In
5,5-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene;
at 130 ℃;
for 24h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
61% |
|
With
bis-triphenylphosphine-palladium(II) chloride; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
at 130 ℃;
for 24h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
61% |
|
With
tris-(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0); tri-tert-butyl phosphine; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
at 60 ℃;
|
58% |
|
With
tris-(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0); tri-tert-butyl phosphine; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
at 60 ℃;
|
58% |
|
With
tris-(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0); tri-tert-butyl phosphine; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
at 60 ℃;
|
58% |
|
With
tri-tert-butyl phosphine; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
at 60 ℃;
|
58% |
|
With
tris-(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0); tri-tert-butyl phosphine; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
at 90 ℃;
for 3h;
|
55% |
|
With
palladium diacetate; 4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
at 100 ℃;
for 24h;
|
3.35 g |
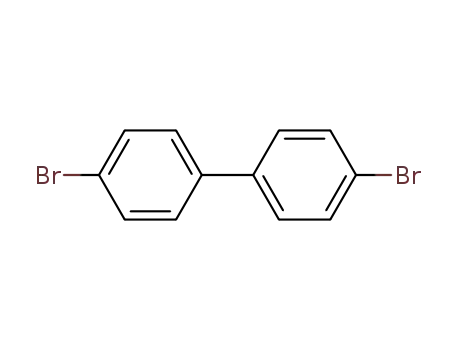
4-(4-bromophenyl)bromobenzene

bis(biphenyl-4-yl)amine

N,N-di-(4-biphenyl)benzylamine

palladium

C64H46N2S

C55H39N3S

C54H36N2

C60H40N2
CAS:26590-20-5
Molecular Formula:C<sub>9</sub>H<sub>10</sub>O<sub>3</sub>