Your Location:Home >Products >OLED intermediates >Carbazoles >6299-16-7


Product Details
InChI:InChI=1/C24H17N/c1-2-8-18(9-3-1)19-14-16-20(17-15-19)25-23-12-6-4-10-21(23)22-11-5-7-13-24(22)25/h1-17H
The present invention relates to: a compound for an organic optoelectronic device, which is represented by chemical formula 1; a composition for an organic optoelectronic device; and an organic optoelectronic device and a display device to which the compound and composition are applied. The details of the chemical formula 1 are as defined in the specification. One embodiment provides the compound for the organic optoelectronic device, which can realize the organic optoelectronic device having high efficiency and long lifetime.
A subset of coordination cages have garnered considerable recent attention for their potential permanent porosity in the solid state. Herein, we report a series of functionalized carbazole-based cages of the structure type M12(R-cdc)12 (M = Cr, Cu, Mo) where the functional groups include a range of aromatic substituents. Single-crystal X-ray structure determinations reveal a variety of intercage interactions in these materials, largely governed by pi-pi stacking. Density functional theory for a subset of these cages was used to confirm that the nature of the increased stability of aryl-functionalized cages is a result of inter-cage ligand interactions. This journal is
Disclosed in the present application is an organic mixture. The organic mixture comprises two organic compounds H1 and H2. The organic compound H1 has electron transmission performance, and the organic compound H1 satisfies: Δ((LUMO+1)?LUMO)≥0.1 eV, and min((LUMO(H1)?HOMO(H2), LUMO(H2)?HOMO(H1))≤min(ET(H1), ET(H2)). The organic compound H1 and the organic compound H2 are easy to form exciplexes and have balanced electron transmission properties, the organic compound Hi has high stability of electron transmission, and accordingly the efficiency and the service life of related electronic components can be effectively improved, and a feasible solution for improving overall performance of the electronic components is provided.
A Rh(III)-catalyzed C-H activation of boronic acid with aryl azide to obtain unsymmetric carbazoles, 1H-indoles, or indolines has been developed. The reaction constructs dual distinct C-N bonds via sp2/sp3 C-H activation and rhodium nitrene insertion. Synthetically, this approach represents an access to widely used carbazole derivatives. The practical application to CBP and unsymmetric TCTA derivatives has also been performed. Mechanistic experiments and DFT calculations demonstrate that a five-membered rhodacycle species is the key intermediate.
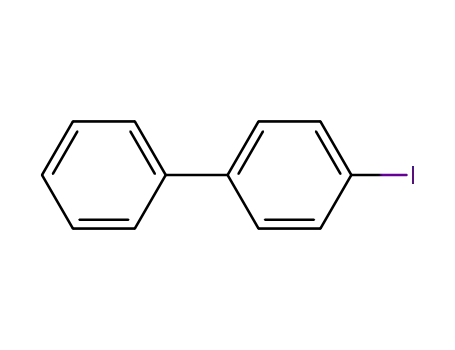
4-iodo-biphenyl
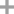
9H-carbazole

![9-([1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl)-9H-carbazole](/upload/2023/2/6dda6e17-6177-4050-8469-d2ae1685f7a6.png)
9-([1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl)-9H-carbazole
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
copper(l) iodide; 1,10-Phenanthroline; caesium carbonate;
In
N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
at 153 ℃;
Inert atmosphere;
|
88.75% |
|
With
tris-(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0); tri-tert-butyl phosphine; sodium t-butanolate;
In
toluene;
for 18h;
Reflux;
Inert atmosphere;
|
86% |
|
With
bis(tetrapropylammonium) tetraiododicuprate(I); trans-1,2-cyclohexanediamine methanesulfonic acid; caesium carbonate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 130 ℃;
for 24h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
85% |
|
With
copper(l) iodide; potassium carbonate; N,N`-dimethylethylenediamine;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 110 ℃;
for 72h;
|
85% |
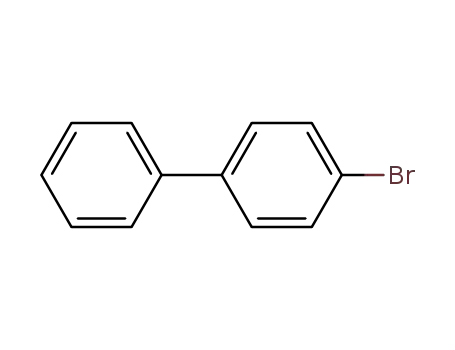
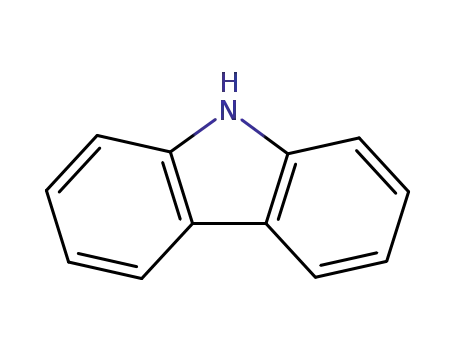
4-bromo-1,1'-biphenyl

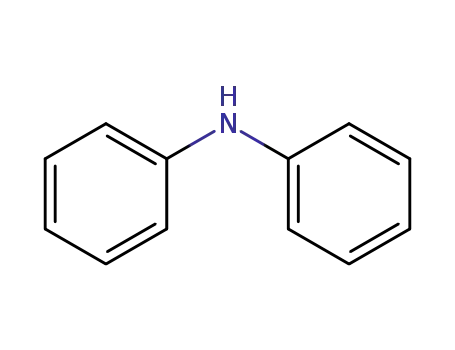
diphenylamine

![9-([1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl)-9H-carbazole](/upload/2023/2/6dda6e17-6177-4050-8469-d2ae1685f7a6.png)
9-([1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl)-9H-carbazole
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
sodium t-butanolate;
1,1'-bis-(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene; palladium diacetate;
In
xylene;
at 120 ℃;
for 7.5h;
|
87% |
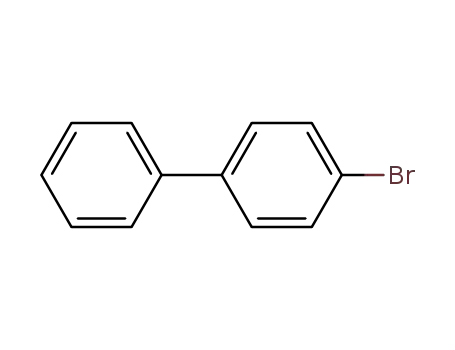
4-bromo-1,1'-biphenyl

9H-carbazole

diphenylamine
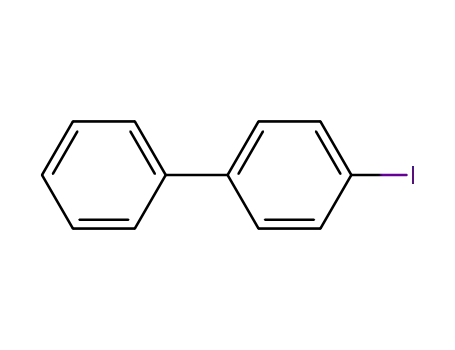
4-iodo-biphenyl
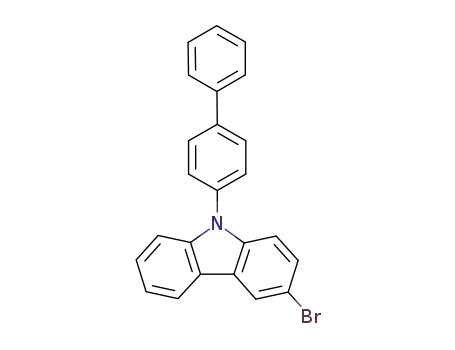
9-[1,1′-biphenyl-4-yl]-3-bromo-9H-carbazole
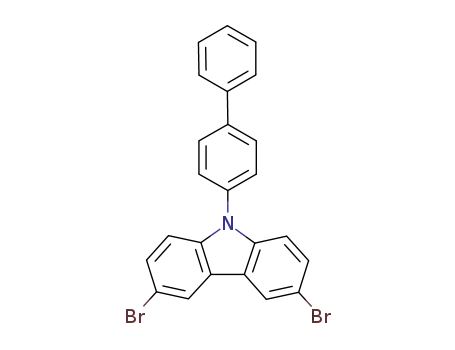
9-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-3,6-dibromo-9H-carbazole
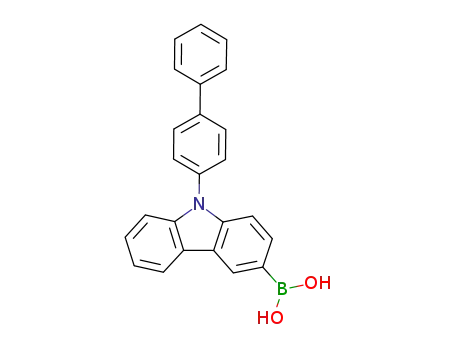
9‐{[1,1'‐biphenyl]‐4‐yl}carbazol‐3‐ylboronic acid

C53H35N3
CAS:126747-14-6
CAS:85-43-8
Molecular Formula:C<sub>8</sub>H<sub>8</sub>O<sub>3</sub>
Molecular Weight:152.15
CAS:864377-33-3
Molecular Formula:C18H14BNO2
Molecular Weight:287.1