Your Location:Home >Products >OLED intermediates >Carbazoles >502161-03-7
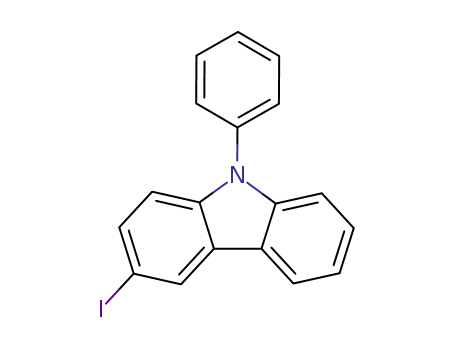

Product Details
Chemical Properties
White crystalline powder
InChI:InChI=1/C18H12IN/c19-13-10-11-18-16(12-13)15-8-4-5-9-17(15)20(18)14-6-2-1-3-7-14/h1-12H
Provided are an organic light-emitting device including a capping layer including an amine-based compound represented by a set or predetermined formula and a radical scavenger, and a light-emitting apparatus including the organic light-emitting device. The organic light-emitting device includes: a first electrode; a second electrode facing the first electrode; an organic layer between the first electrode and the second electrode and including an emission layer a capping layer on the second electrode, wherein the capping layer includes the amine-based compound.
In this study, ten fluorescent dyes were prepared based on three different kinds of central moiety, such as triphenylamine, diphenylsulfone or triphenyltriazine, which was coupled to either carbazole or naphthalimidinyl group via an acetylene linkage group. N-n-Butyl-carbazole, N-phenyl-carbazole or N-n-butyl-naphthalimide was coupled to the individual central moiety of triphenylamine, diphenyl sulfone, 2,4,6-triphenyl-1,3,5-trazine or diphenylamine using a Sonogashira coupling reaction in the final step. All dyes were confirmed their chemical structure by 1H NMR, GC-Mass and elemental analyses. The absorption properties and thermal stabilities of the fluorescent dyes were examined. Density Functional Theory (DFT) and Time-Dependent DFT calculations were carried out, in addition to geometry simulation, by using the Gaussian 09 program. In terms of fluorescence properties in this series, two dyes based on diphenyl sulfonyl and three dyes based on triphenylamine substituted by 1–3 of N-n-butyl-carbazole exhibited a blue emission, whereas three dyes based on triphenylamine substituted by 1–3 of N-n-butyl-naphthalimide were observed by a red emitter which can be attributable to both effects the bathochromic shifts in absorption maxima and larger Stokes shifts. In case of corresponding 2,4,6-triphenyl-1,3,5-trazine central moiety coupled to a carbazole ring, a green fluorescence was emitted. Results revealed that the fluorescence of the dyes is affected by the electron-donating strength of the acetylene linkages involved in the π-conjugation systems of the dyes.
A heterocyclic compound is represented by Formula 1 below. An organic light-emitting device includes a first electrode, a second electrode and an organic layer between the first electrode and the second electrode. The organic layer includes the heterocyclic compound. Organic light emitting devices including the heterocyclic compound of Formula 1 exhibit high efficiency, low voltages, high brightness, and long lifespans.
PURPOSE: An organic dye, photoelectric diode including the same and dye-sensitized solar battery are provided to have an absorbing band in long wavelength. CONSTITUTION: An organic dye is represented by chemical formula 1. A photoelectric diode includes porous oxide semiconductor membrane which includes the organic dye. A dye-sensitized solar cell comprises a first electrode, a second electrode which is formed on one side of the first electrode and includes a light absorptive layer, and electrolyte buried in a space between the first and second electrodes.
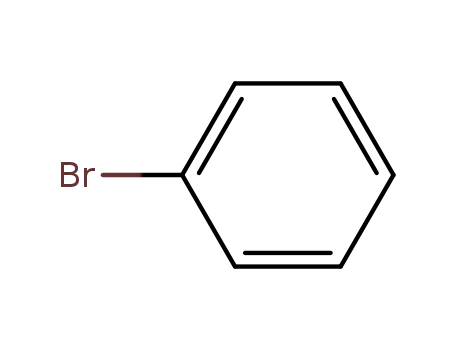
bromobenzene
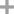
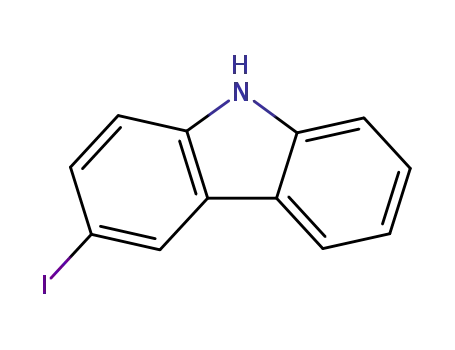
3-iodocarbazole

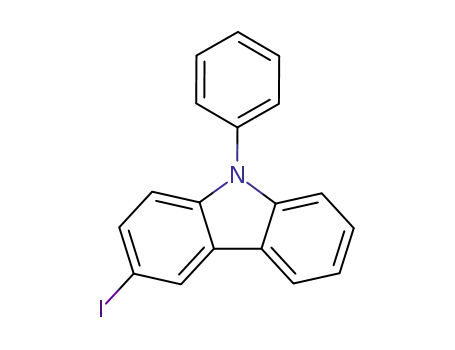
3-iodo-9-phenyl-9H-carbazole
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
3-iodocarbazole;
With
sodium hydride;
In
N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
at 80 ℃;
for 1h;
bromobenzene;
In
N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
|
65.1% |
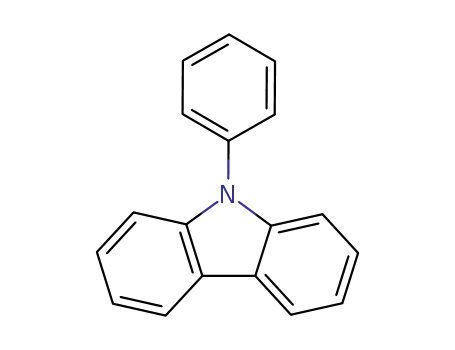
N-phenylcarbazole


3-iodo-9-phenyl-9H-carbazole
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
iodine; acetic acid; periodic acid;
In
water;
at 80 ℃;
for 2h;
|
87% |
|
With
iodine; acetic acid; periodic acid;
In
water;
at 80 ℃;
for 2h;
|
87% |
|
With
iodine; acetic acid; periodic acid;
at 80 ℃;
for 2h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
87% |
|
With
iodine; acetic acid; periodic acid;
at 80 ℃;
for 2h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
87% |
|
With
iodine; acetic acid; periodic acid;
at 80 ℃;
for 2h;
|
85% |
|
With
potassium iodate; sulfuric acid; potassium iodide;
In
ethanol;
at 75 ℃;
for 2h;
|
81% |
|
With
iodine; acetic acid; periodic acid;
at 80 ℃;
for 4h;
|
78% |
|
With
sulfuric acid; iodine;
In
methanol; water;
for 20h;
|
77% |
|
With
sulfuric acid; iodine;
In
methanol; water;
at 5 ℃;
for 20h;
Cooling;
|
77% |
|
With
N-iodo-succinimide;
In
acetic acid;
at 20 ℃;
Product distribution / selectivity;
|
67% |
|
With
N-iodo-succinimide;
In
acetic acid;
at 20 ℃;
Product distribution / selectivity;
|
67% |
|
With
potassium iodate; potassium iodide;
In
acetic acid;
at 120 ℃;
for 1h;
Product distribution / selectivity;
Heating / reflux;
|
50% |
|
With
N-iodo-succinimide;
In
acetic acid;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; sulfuric acid; potassium iodide;
In
ethanol;
at 75 ℃;
for 2h;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; potassium iodide;
In
acetic acid;
at 80 ℃;
for 2h;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; sulfuric acid; potassium iodide;
In
ethanol;
at 75 ℃;
for 2h;
Product distribution / selectivity;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; sulfuric acid; potassium iodide;
In
ethanol;
at 75 ℃;
for 2h;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; sulfuric acid; potassium iodide;
In
ethanol;
at 75 ℃;
for 2h;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; sulfuric acid;
In
ethanol; water;
at 75 ℃;
for 2h;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; sulfuric acid; potassium iodide;
In
ethanol;
at 75 ℃;
for 2h;
|
|
|
With
potassium iodate; sulfuric acid; potassium iodide;
In
ethanol;
at 75 ℃;
for 2h;
|
21.8 g |
|
With
potassium iodate; sulfuric acid; potassium iodide;
In
ethanol;
at 75 ℃;
for 2h;
|
21.8 g |

N-phenylcarbazole
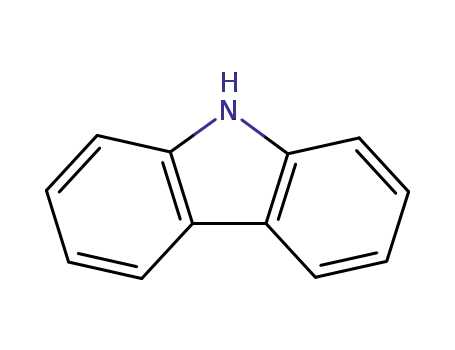
9H-carbazole
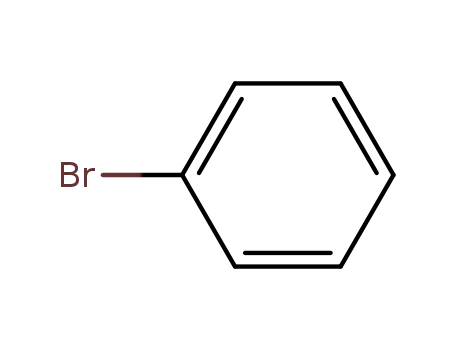
bromobenzene

3-iodocarbazole
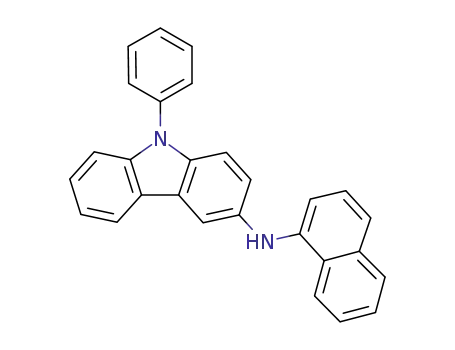
N-(naphthalen-2yl)-9-phenyl-9H-carbazol-3-amine
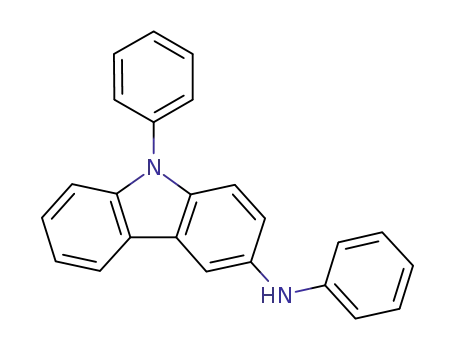
(N-phenyl)-N-(9-phenyl-9H-carbazole-3-yl)amine
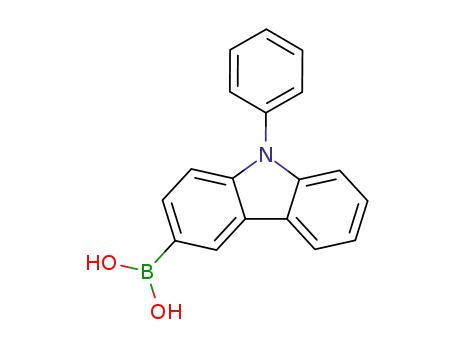
N-phenyl-9H-carbazol-3-boronic acid
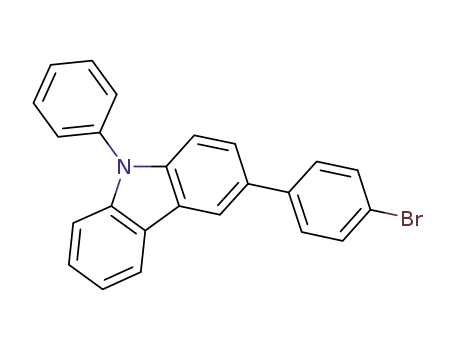
3-(4-bromophenyl)-9-phenyl-9H-carbazole
CAS:5518-52-5
CAS:25134-21-8
CAS:57103-20-5
CAS:1028647-93-9
Molecular Formula:C24H16BrN
Molecular Weight:398.3