Your Location:Home >Products >OLED intermediates >Carbazoles >1150-62-5

Product Details
Chemical Properties
White solid
Uses
9-Phenylcarbazole has been used in the electrochemical synthesis of poly(9-phenylcarbazole) films via direct anodic oxidation in mixed electrolytes of boron trifluoride diethyl etherate and sulfuric acid.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Tetrahedron Letters, 29, p. 1115, 1988 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)86664-2
InChI:InChI=1/C18H13N/c1-2-8-14(9-3-1)19-17-12-6-4-10-15(17)16-11-5-7-13-18(16)19/h1-13H
We devised and synthesized a series of electron-rich compounds featuring diphenylamine, carbazole or dibenzo[c,g]carbazole connected via phenylacetylene linkers to an aromatic central unit. The key synthetic step was a high yielding cross coupling reaction between halogenated (bi)naphthalene and organometallic reagents prepared in situ from terminal alkynes (side-arms). By masking one of the iodo functions with a diethyltriazenyl group in the side-arm precursors, we efficiently circumvented the formation of doubly aminated by-products. Although one step longer, this approach led to higher yields of terminal alkynes than the direct coupling route. Spectroscopic and electrochemical measurements supported by computational evidence revealed that conjugation in the 1,4-disubstituted naphthalene backbone is superior to the 1,5 or 2,6 substituted cores. The diphenylamine derivative gets oxidized more readily when compared to its carbazole analogs. Expanding the core to binaphthalene did not alter electronic properties, but influenced the physical characteristics significantly.
(Figure Presented) Getting the green light: Highly efficient organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) have been synthesized from robust green-electrophosphorescent IrIII complexes based on carbazole derivatives (see picture, HT = hole transporting, EL = electroluminescence). The combination of short triplet lifetime, high emission efficiency, and improved charge-transporting properties allows these OLEDs to achieve peak efficiencies of 12% photons per electron and 38 cd A-1.
The palladium-catalyzed direct arylation of a series of 2-(diarylamino)phenyl triflates was examined. The triflates were first synthesized in moderate to good yields through the CuI-catalyzed aryl amination of aminophenol and aryl iodides, followed by triflation of the resulting triarylphenols. The thus-obtained 2-(diarylamino)phenyl triflates were subjected to direct C–H arylation under Pd catalysis to furnish the corresponding N-arylcarbazoles in excellent yields if Josiphos was used as the supporting ligand.
-
The photophysical properties and the organic synthesis using effective palladium-catalyzed Suzuki coupling reactions from a series of carbazole derivatives are described and the relationships of the donor and acceptor groups are also investigated. The purification of the materials and its applications along with the corresponding photo-physical characterizations were presented. With the advantages gained from 2DCOSY spectra, which provide more correlated information between immediate atoms than 1H-NMR spectra and a series of further investigations were undertaken including powder X-ray diffraction analysis, Infrared and Raman spectroscopy, constructing the composition conformation and chemical structure of the materials is more easily to achieve. Additionally, the optimized structure of the minimized energy geometries and spatial distributions of carbazole derivatives was calculated using density functional theory (DFT), new materials can be developed and designed selectively based on the method proposed in this work.
-
Multicolor mechanoluminescence (ML) was first realized by using the stable organic blue ML emitter N-phenylcarbazole as the host matrix. It is claimed that a good ML host should have a moderate melting point and be able to dissolve or disperse organic dyes but maintain high ML activity and crystallinity. This strategy is versatile and can avoid difficult molecular design and troublesome chemical synthesis.
A powerful method: A variety of sterically crowded, substituted carbazoles have been prepared from anilines and biphenyl compounds (see scheme). The method enabled the preparation of 2,2′-dicarbazolyl-1,1′-biaryl compounds, which show excimer (or exciplex) emissions with significant solvent dependency.
Nickel-catalyzed N-arylation reaction of N -trimethylsilyl-carbazole using aryl bromides is found to proceed in the presence of sodium acetate, giving N -aryl-carbazoles in high yields. Under these conditions, N -trimethylsilyl-carbazole could react with aryl bromides selectively even in the presence of other N -trimethylsilyl-amines or N -H-amines. This arylation reaction was applied to the polymerization to provide a polycarbazole.
Carbon encapsulated copper oxide nanoparticles (CuONPs@C) fabricated using copper metal organic frameworks (Cu-MOFs) used as reusable nanocatalysts in Ullmann C[sbnd]N coupling reactions for synthesizing optoelectronic triphenylamine (TPA) and carbazole (CBZ) derivatives. The formation of CuONPs in carbon matrix was confirmed by powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM). The catalytic activity of CuONPs@C was performed with diphenylamine/carbazole with substituted aryl halides in presence of mild K2CO3 base that produced triarylamines with 63–83% yields. Carbazole triarylamines exhibited strong solid state fluorescence (Φf = 14.54–36.32%) with λmax between 370 and 420 nm.
Ternary donor (D)-acceptor (A)-acceptor (A) molecules are commonly considered as low triplet (T1) energy systems for specific applications. In this work, exception to this behavior was observed in a triangle-shaped D-A-A molecule PCImbPO with unusually high triplet energy of 3.0 eV. Profiting from the enhanced D-A electronic coupling, electron injecting and transporting ability of PCImbPO was dramatically improved with negligible influences on its highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) characteristics. Its particular T1 configuration adjustment further gives rise to the separated frontier MO and T1 locations, beneficial to suppress quenching effects. By utilizing PCImbPO as host in blue phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes (PHOLEDs) and thermally activated delayed fluorescence devices, impressively high external quantum efficiency of 22% and 12% were achieved, respectively. This work established a new understanding of high-energy-gap complicated D-A systems.
An efficient strategy for carbazole synthesis from arylureas and cyclohexanones under transition metal-free conditions has been developed. The combined use of potassium iodide and iodine could significantly improve the reaction efficiency to provide 2,6-disubstituted 9-arylcarbazoles in moderate to good yields. In this kind of transformation, the whole carbazole moiety (except the nitrogen atom) comes from two equivalents of cyclohexanones. (Figure presented.).
The dimerization reaction processes of the 9-phenylcarbazole cation radical (PCZ>=+) in acetonitrile (AN) were observed using an electron-transfer stopped-flow method. Although the lifetime of PCZ >=+ in AN is less than a few hundred milliseconds, the dynamic transformation of the absorption spectra of PCZ>=+ was successfully observed in AN for the first time with the proposed method. By observing the changes in the absorption spectra in the visible region, the decrease in PCZ>=+ and the concurrent increase in the dimer cation radical were observed with isosbestic points. In addition, in the presence of neutral PCZ, the acceleration of the dimerization of PCZ >=+ was clearly confirmed. Consequently, in the presence of PCZ, the rate law was determined to be -d[PCZ>=+]/dt = 3Kk′[PCZ>=+]2 [PCZ], where 3Kk′ is 1.4 × 109 M-2 s-1. This means that the reaction mechanism involves a two-step interaction with the catalytic effect of neutral PCZ. Although the difference in the reactivity had already been known between PCZ>=+ and the triphenylamine cation radical, the reaction mechanism has been clarified to be different in both cases.
-
A Rh(III)-catalyzed C-H activation of boronic acid with aryl azide to obtain unsymmetric carbazoles, 1H-indoles, or indolines has been developed. The reaction constructs dual distinct C-N bonds via sp2/sp3 C-H activation and rhodium nitrene insertion. Synthetically, this approach represents an access to widely used carbazole derivatives. The practical application to CBP and unsymmetric TCTA derivatives has also been performed. Mechanistic experiments and DFT calculations demonstrate that a five-membered rhodacycle species is the key intermediate.
A simple and cost-effective protocol for the C–N cross coupling of indole derivatives with aryl iodides using CuI/phenanthroline catalytic system in aqueous and DME/H2O solvent mixture is described. The reactions were performed in the absence of phase-transfer catalyst, and afforded N-arylated products in moderate to excellent yields under mild reaction conditions. A systematic tuning of reaction conditions using DME as a co-solvent enables to improve product yields of N-arylation reactions. The broad substrate scope, easy performance, and low loading of catalyst as well as ligand render this approach appropriate for large scale processes. The mechanism of “on water” Cu-catalyzed N-arylation reaction is investigated using kinetic and computational studies, which reveal interesting mechanistic aspects of the reaction. A series of kinetic experiments showed significant rate enhancement for “on water” Cu-catalyzed N-arylation over the reaction performed in the organic solvent (DME). Computational studies corroborated “on water” rate acceleration by delineating the role of water in the reaction. The water induces rate acceleration by stabilizing the transition state of oxidative addition through hydrogen bonding interactions, presumably at the oil-water interface, and thus helps to reduce the free energy of activation of oxidative addition of iodobenzene to the Cu complex, which is identified as the rate-limiting step of reaction.
We report here the synthesis of a novel polymeric electrochromic material containing carbazole (Cbz)-donor and 1,8-napthalimide-acceptor as subunit. The band gap Eg was measured using UV-vis spectroscopy and compared with that obtained by cyclic voltammetry (CV). Due to intramolecular electron transfer from Cbz-donor to 1,8-napthalimide-acceptor, the fluorescence quenching was observed. When the spectro-electrochemical and electrochromic properties of polymer film were investigated, various tones of green color were obtained on the polymeric film. In the positive regime, the polymer film obtained thereby is dark green resulting from the association of carbazolylium cation radicals at oxidized state and then it can be bleached by electrochemical reduction. Besides, in the negative regime, yellowish green color of film converted to blue attributed to reduction of the 1,8-napthalimide moiety. Finally, the polymeric electrochromic exhibits multi-electrochromic behavior, high redox stability, high coloration efficiency and reasonable response time.
By conjugating 10-phenyl-10H-phenothiazine-5,5-dioxide (2PTO) with aromatic amine substituents (PhCz and DMACMN), three novel host materials namely 10-(9-phenyl-9H-carbazol-3-yl)-10H-phenothiazine 5,5-dioxide (3CzNPTO), (10-(4-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)phenyl)-10H-phenothiazine 5,5-dioxide (9CzNPTO) and 10-(4-(9,9-dimethylacridin-10(9H)-yl)-2,5-dimethylphenyl)-10H-phenothiazine 5,5-dioxide (DMACMNPTO) were designed and synthesized. DMACMNPTO with thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) properties exhibited bipolar characteristics resulting from the completely separated HOMO/LUMO distribution. Using DMACMNPTO as a host for TADF emitters, devices showed a maximum external quantum efficiency (EQEmax), current efficiency (CEmax) and power efficiency (PEmax) of 18.3%, 33.3 cd A-1 and 37.4 lm W-1 in blue-emitting diodes, 18.6%, 49.1 cd A-1 and 47.2 lm W-1 in green-emitting diodes, and 19.1%, 59.2 cd A-1 and 66.0 lm W-1 in yellow-emitting diodes, respectively. These results corroborated the potential of phenothiazine dioxide-containing derivatives as host materials in a sequence of color TADF-OLEDs.
[Figure not available: see fulltext.] New fluorinated tetraketone derivatives of N-substituted carbazoles were synthesized and tested as ligands for fluorescence immunoassay. The spectral properties of the obtained heterocyclic tetraketones and their Eu(III) complexes were studied. The complexes showed longwave absorption at 360–380 nm, high extinction coefficient values, long lifetime of excited states, and intense luminescence, allowing to consider the use of such lanthanide complexes in immunofluorescence analysis.
A simple carbazole based nanoprobe prepared by reprecipitation method shows selective sensing behavior for Fe3?+ ion in aqueous medium. The prepared SDS capped 9-phenyl carbazole nanoparticles (9-PCzNPs) has narrower particle size distribution with an average diameter 35?nm and zeta potential of ??34.3?mV predicted a good stability with negative surface charge over the nanoparticles. The Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM) image showed cubic shape morphology of nanoparticles. The aqueous suspension of SDS capped 9-phenyl carbazole nanoparticles exhibited aggregation induced enhanced red shifted intense emission in comparison with the emission arising from dilute solution of 9-phenyl carbazole in DCM. The cation recognition test based on fluorescence change shows Fe3?+ ion induce significant fluorescence quenching, however remaining cations responds negligibly. The obtained quenching data fit into Stern–Volmer relation in the concentration range of 0.0–1.0?μg·mL??1 of Fe3?+ ion solution and the detection limit is 0.0811?μg·mL??1. The probable mechanism of fluorescence quenching of SDS capped 9-PCzNPs is because of adsorption of Fe3?+ ion over the negatively charged surface of NPs through electrostatic interaction. Thus the proposed method was successfully applied for the detection of Fe3?+ ion in environmental water sample.
The syntheses of novel well-defined star-shaped carbazole-functionalized triazatruxenes, which consist of six carbazole arms linked with a central triazatruxene core consisting of three carbazoles with one phenyl, are presented. Both 9-hexylcarbazole and 9-phenylcarbazole as arms gave high yields. Their chemical formulas were confirmed by means of 1H NMR, MALDI-TOF mass spectroscopy, and elementary analysis. The fluorescent spectra showed that these compounds exhibit good blue fluorescence. The maximum fluorescence emission wavelengths were between 420 and 430 nm.
A continuous flow UV light reactor has been constructed using commercially available equipment, and its efficiency was demonstrated by performing a photocyclodehydrogenation reaction to prepare carbazole derivatives of the drug carprofen.
In the present work, we have developed a rapid, one step, calcination-free protocol for the synthesis of uniform spherical Cu/Cu2O nano/microparticles (NMPs). The synthesis of Cu/Cu2O NMPs was achieved by microwave irradiation of copper acetate as a precursor and 1,4-butanediol as a solvent in a few minutes. The prepared Cu/Cu2O NMPs gave 100% yield of uniform spherical morphology. 1,4-Butanediol plays a crucial role in reactions such as a solvent, reactant, stabilizer and capping agent which control the crystal morphology. The resultant product was characterized with the help of different techniques such as XRD, FEG-SEM, EDS, TEM, FT-IR, TPR, DSC-TGA, XPS and BET surface area analysis. The results confirm that the Cu/Cu2O NMPs had good crystallinity and were essentially pure. This is a simple, faster, inexpensive and additive-free protocol for synthesis of nanocrystalline Cu/Cu2O compared to the conventional method. These Cu/Cu2O NMPs showed excellent catalytic activity in the Buchwald-Hartwig amination coupling reaction. Notably the reaction does not require any ligand source, and requires low catalyst loading, and low temperature with catalyst recyclability. the Partner Organisations 2014.
Phosphine ligands embodying a carbazolyl motif have been found to be successful in many palladium-catalyzed biaryl syntheses and direct C-H bond arylation processes. Here, a practical scaled-up synthesis of a series of carbazolyl-derived phosphine ligands, the PhenCarPhos series, is described. The original protocol for accessing the target ligand skeleton via aromatic C-N bond formation is limited by the use of a substoichiometric amount of copper salt and diamine catalysts, which both add cost and generate purification problems (significant amounts of side products and copper residues). In order to develop a more attractive and scalable synthetic pathway, a simple nucleophilic substitution method was attempted involving simple heating of 1-bromo-2-fluorobenzene, a carbazole derivative, and KOH in DMF without inert atmosphere protection. This route enables the large-scale synthesis of the desired ligand skeletons and minimizes the association of inseparable reduction side products. Particular examples of the use of these ligands in Pd-catalyzed sterically hindered arylation processes are also shown.
Simple N-phenylcarbazole (NPC) could readily form brightly mechanofluorescent crystals with mechanically touch-sensitive response, regardless of crystallization methods. NPC with roomerature photophosphorescence did not exhibit mechano-phosphorescence, signifying that the excitation modes could play an important role in affecting light-emitting processes.
Functionalized nanocellulose was prepared and employed for immobilization of phenanthroline-copper(I) complex to afford cellulose nanofibril grafted heterogeneous copper catalyst [CNF-phen-Cu(I)]. This nanocatalyst was well characterized using FT-IR, NMR, XRD, CHNS, AAS, TGA, EDX and SEM. The activities of the synthesized catalyst were examined in the synthesis of diaryl ethers via C-O cross-coupling of phenols and aryl iodides, as well as, the preparation of N-aryl amides and N-aryl heterocycles through C-N cross-coupling of amides and N-H heterocycle compounds with aryl halides. In this trend, various substrates containing electron-donating and electron-withdrawing groups were exploited to evaluate the generality of this catalytic protocol. Accordingly, the catalyst demonstrated remarkable catalytic efficiency for both C-N and C-O cross-coupling reactions, thereby resulting in good to excellent yields of the desired products. Furthermore, the recoverability experiments of the catalyst showed that it can be readily retrieved by simple filtration and successfully reused several times with negligible loss of its catalytic activity.
The photoreactivity of triphenylamine in homogeneous media has been investigated by means of laser flash photolysis spectroscopy and preparative experiments. The goal of this study consists in the evaluation of the photophysical and photochemical behavior of transient N-phenyl-4a,4b-dihydrocarbazole (DHC0) under polar and non-polar solvents which was not performed yet. The kinetic parameters of such a key intermediate including lifetime (τd, τR and τox) and rate constants (kd, kR and kox) have been measured and the intermediacy of DHC0 in the co-oxidation of nucleophilic substrates such as sulfides and phosphines was investigated by a combined time-resolved and steady-state approach. Two distinctly oxidizing intermediates, a hydroperoxy radical and a hydroperoxide derivative were formed from transient DHC0 in the presence of molecular oxygen. Radical I oxidizes triarylphosphines, whereas intermediate II converts sulfides into the corresponding sulfoxides.
In this work, three novel bipolar host materials TPA-SA, 3CBZ-SA and 4CBZ-SA have been designed and synthesized by incorporating triphenyl amine and carbazole as donor and benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide as an acceptor. These molecules exhibit moderately high triplet energies and bipolar carrier transport characteristics (ambipolarity) which is useful for the exothermic energy transfer to the dopants and also for the balanced carrier injection/transport in the emissive layers. These materials exhibited good performances in PhOLEDs and furnished external quantum efficiency in the range of 10.0–15.0%. Notably, a red phosphorescent device using TPA-SA as the host doped with Ir(pq)2(acac) exhibited a maximum EQE, power efficiency and current efficiency of 15.0%, 16.0 lm/W, and 25.3 cd A?1, respectively.
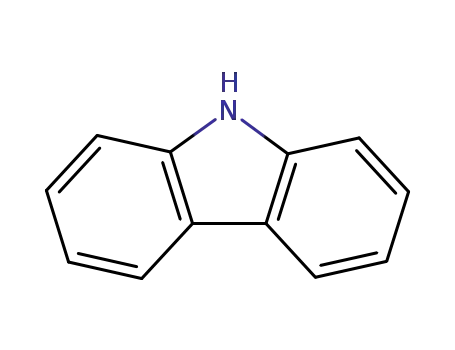
9H-carbazole
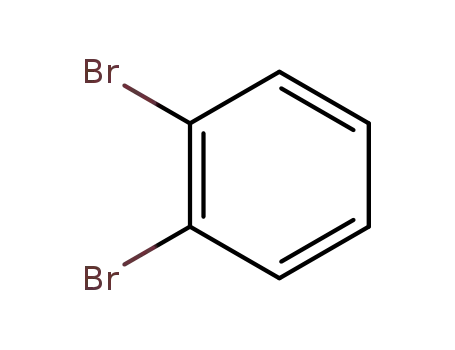
2,3-dibromobenzene

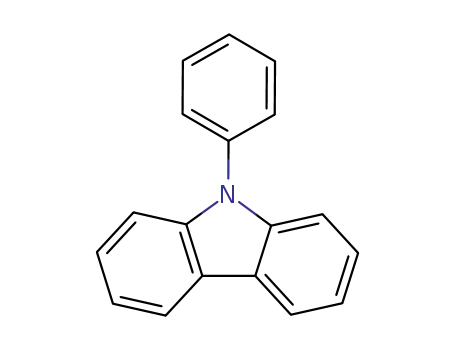
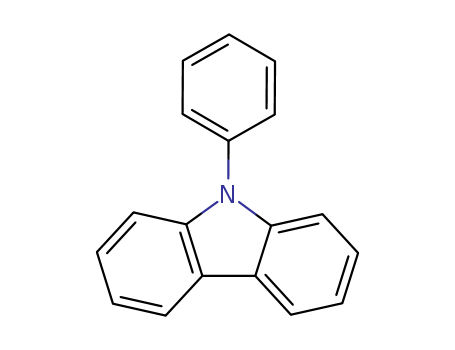
N-phenylcarbazole

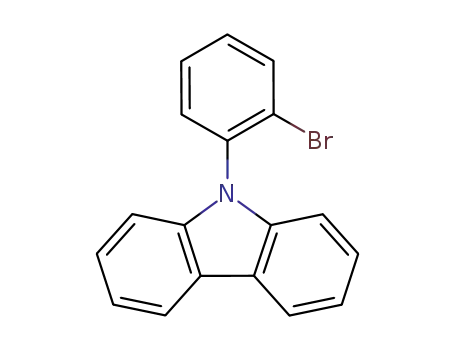
9-(2-bromophenyl)-9H-carbazole
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
copper(I) oxide; potassium phosphate; N,N`-dimethylethylenediamine;
In
5,5-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene;
at 170 ℃;
for 24h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
60% 13.8% |

9H-carbazole


2,3-dibromobenzene


N-phenylcarbazole


9-(2-bromophenyl)-9H-carbazole

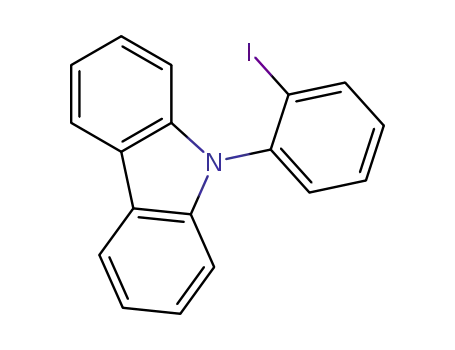
9-(2-iodophenyl)-9H-carbazole
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
copper(l) iodide; potassium carbonate;
In
5,5-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene;
for 168h;
Reagent/catalyst;
Inert atmosphere;
Reflux;
|
60% 10% Ca. 15 %Chromat. |
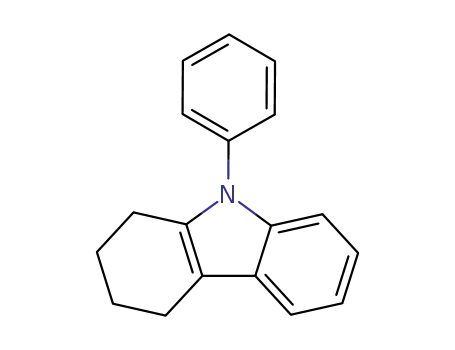
9-phenyl-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-carbazole
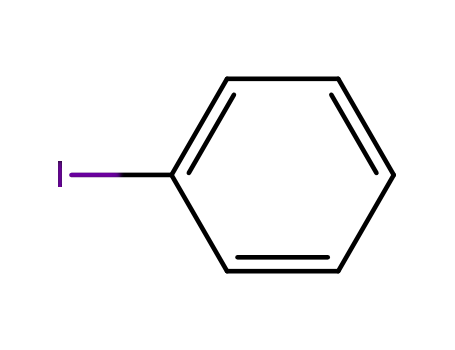
iodobenzene

9H-carbazole
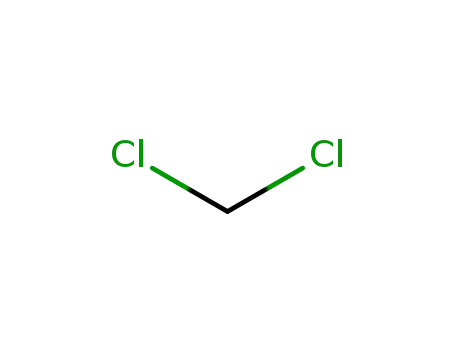
dichloromethane
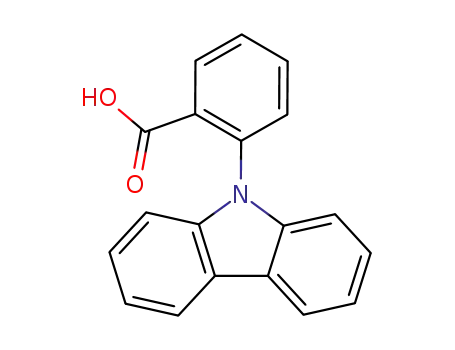
2-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)benzoic acid
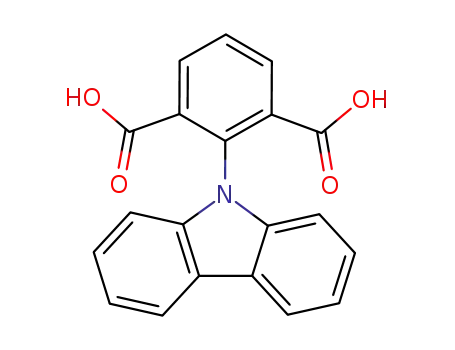
2-carbazol-9-yl-isophthalic acid
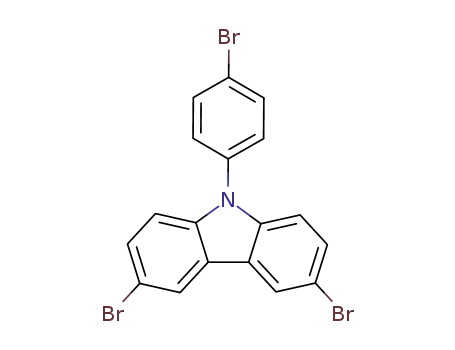
3,6-dibromo-9-(4-bromophenyl)-9H-carbazole
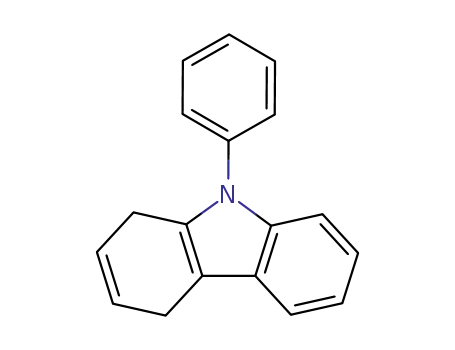
dihydro-1,4 phenyl-9 carbazole
CAS:854952-58-2
CAS:185112-61-2
Molecular Formula:C18H12BrN
Molecular Weight:322.2
CAS:57103-20-5