Your Location:Home >Products >Organic phosphines >Other organic phosphines >5518-52-5
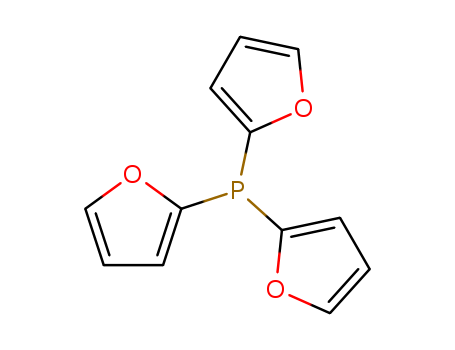

Product Details
Reaction
Useful ligand for C-C coupling reactions. Ligand used for the alkynylation of thioesters. Ligand used for enol ester formation. Ligand for palladium-catalyzed 3-Component coupling. Ligand for palladium-catalyzed C-C coupling reaction. Ligand for trans-olefin formation. Olefin formation from N-tosylhydrazones and benzyl halides. C-H arylation/alkenylation of 1-substituted tetrazoles.
Chemical Properties
TRI(2-FURYL)PHOSPHINE is white to light yellow crystal powde
Uses
TRI(2-FURYL)PHOSPHINE is a phopshine ligand used in transition-metal mediated organic synthesis, in particular in wittig reactions to improved (Z) selectivity.
Uses
suzuki reaction
Uses
A phopshine ligand used in transition-metal mediated organic synthesis, in particular in wittig reactions to improved (Z) selectivity.
InChI:InChI=1/C12H9O3P/c1-4-10(13-7-1)16(11-5-2-8-14-11)12-6-3-9-15-12/h1-9H
Pentacarbonyl iron reacts with this(2-furyl)phosphine (or tris(2-benzofuryl)phosphine) in the presence of sodium borohydride in refluxing n-butanol to give the title compounds.The crystal and molecular structure of pentacarbonylbis(μ-bis(2-furyl)phosphido>diiron(0) were determined by X-ray crystallography. Keywords: Iron; Dinuclear; Carbonyls; X-ray structure; Benzoferrylphosphine complex
The kinetics of quinuclidine displacement of BH3 from a wide range of Lewis base borane adducts have been measured. Parameterization of these rates has enabled the development of a nucleofugality scale (NFB), shown to quantify and predict the leaving group ability of a range of other Lewis bases. Additivity observed across a number of series R′3-nRnX (X = P, N; R′ = aryl, alkyl) has allowed the formulation of related substituent parameters (nfPB, nfAB), providing a means of calculating NFB values for a range of Lewis bases that extends far beyond those experimentally derived. The utility of the nucleofugality parameter is explored by the correlation of the substituent parameter nfPB with the hydrolyses rates of a series of alkyl and aryl MIDA boronates under neutral conditions. This has allowed the identification of MIDA boronates with heteroatoms proximal to the reacting center, showing unusual kinetic lability or stability to hydrolysis.
Reduction of phosphine oxides into the corresponding phosphines using PhSiH3 as a reducing agent and Ph3C+[B(C6F5)4]? as an initiator is described. The process is highly efficient, reducing a broad range of secondary and tertiary alkyl and arylphosphines, bearing various functional groups in generally good yields. The reaction is believed to proceed through the generation of a silyl cation, which reaction with the phosphine oxide provides a phosphonium salt, further reduced by the silane to afford the desired phosphine along with siloxanes. (Figure presented.).
Disclosed is a process for producing a phosphine derivative from a phosphine oxide derivative, which comprises the following steps: (I) mixing a phosphine oxide derivative represented by formula (1) with a chlorinating agent in a polar organic solvent to cause the reaction between these components; and (II-1) adding a salt of a metal having an ionization tendency equal to or lower than that of aluminum to the reaction mixture and carrying out the reductive reaction in the presence of aluminum or (II-2) subjecting the reaction mixture to electrolytic reduction, thereby producing a phosphine derivative represented by formula (2). ArnR3-nP═O (1) ArnR3-nP (2) In formulae (1) and (2), Ar represents an aryl group such as a phenyl group, a phenyl group having a substituent, a heteroaromatic ring group, and a heteroaromatic ring group having a substituent; R represents an aliphatic hydrocarbon group or an aliphatic hydrocarbon group having a substituent; and n represents an integer of 0 to 3.
Catalyst-free alcoholytic deprotection of borane-protected phosphorus compounds offers a smooth, efficient, and clean alternative to existing deprotection methods. In this paper we report our results on the general applicability of deprotecting phosphane-
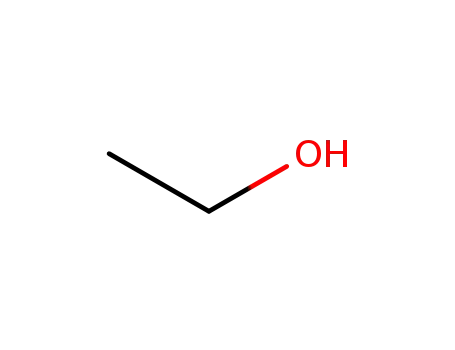
ethanol
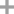
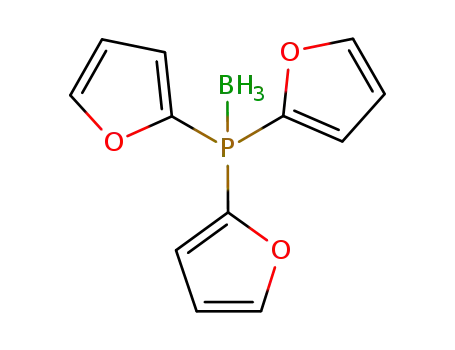
tris(2-furyl)phosphane-borane(1:1)

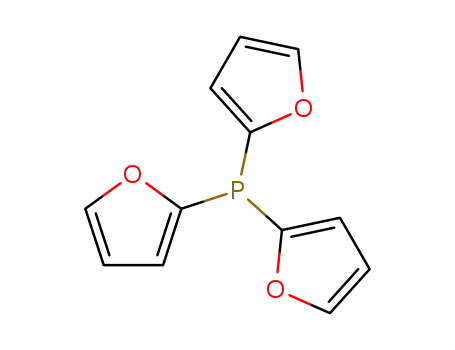
trifuran-2-yl-phosphane

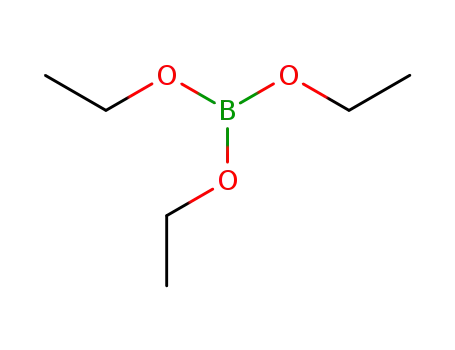
triethyl borate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
Inert atmosphere;
Reflux;
|
100% |
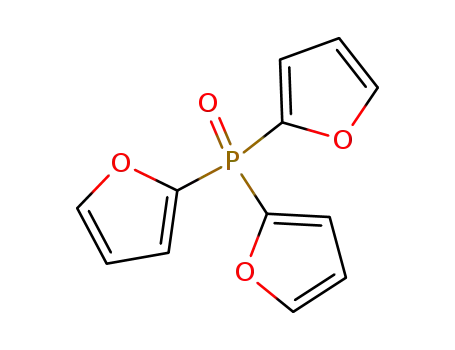
tris(furan-2-yl)phosphine oxide


trifuran-2-yl-phosphane
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
tris(furan-2-yl)phosphine oxide;
With
trityl tetrakis(pentafluorophenyl)borate;
In
(2)H8-toluene;
at 20 ℃;
Glovebox;
Inert atmosphere;
With
phenylsilane;
In
(2)H8-toluene;
at 80 ℃;
for 1.5h;
Glovebox;
Inert atmosphere;
Sealed tube;
|
89% |
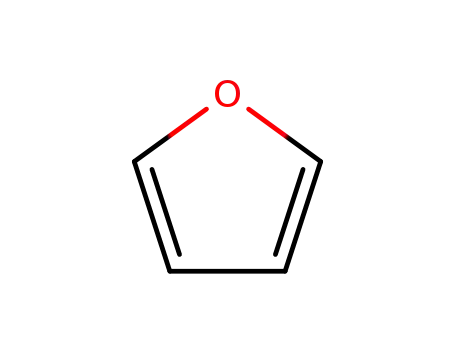
furan
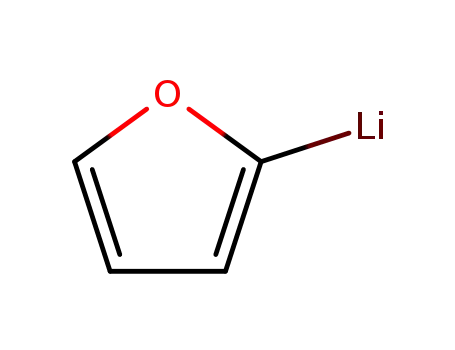
2-lithiofuran
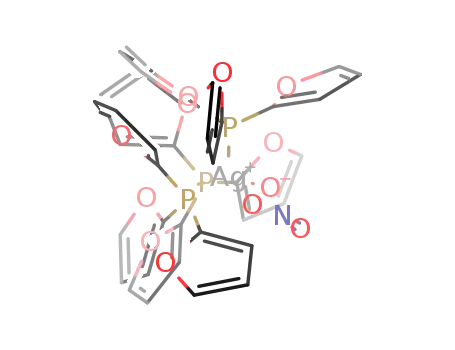
Ag(tris(2-furyl)phosphine)3(ONO2)

ethanol
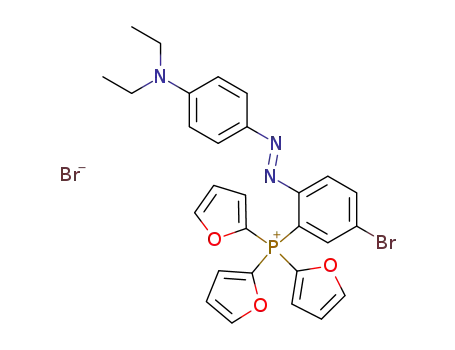
tri-2-furyl<3-bromo-6-(4-diethylaminophenylazo)phenyl>phosphonium bromide
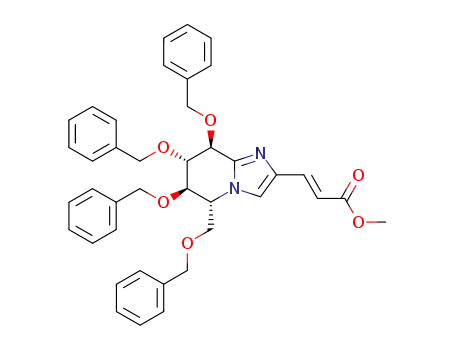
methyl (E-3{(5R,6R,7S,8S)-6,7,8-tris(benzyloxy)-5-[(benzyloxy)methyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydroimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-2-yl}prop-2-enoate)
methyl-tri(2-furyl)phosphonium iodide
CAS:864377-33-3
Molecular Formula:C18H14BNO2
Molecular Weight:287.1
CAS:89827-45-2
CAS:554-70-1
CAS:998-40-3