Your Location:Home >Products >Organic phosphines >Phenyl phosphines >739-58-2
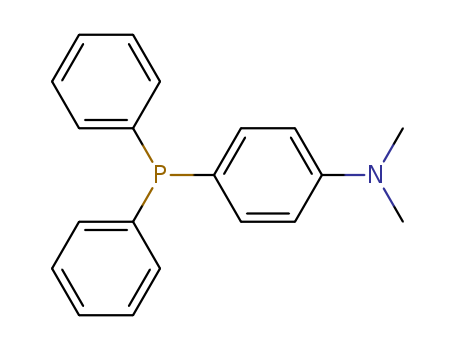

Product Details
Uses
Catalyst for:Preparation of dicyano(aryl)cyclohexenecarboxylic acid esters via regioselective annulationDiastereoselective cycloaddition of styrenyl allenoatesInterfacial carbonylation of methylbenzyl bromideHydroformylation of octeneReducing agent for selectivity of disulfide-internally linked peptide-nucleic acid cleavage
InChI:InChI=1/C20H20NP/c1-21(2)17-13-15-20(16-14-17)22(18-9-5-3-6-10-18)19-11-7-4-8-12-19/h3-16H,1-2H3
The title compound [4-(N,N-dimethylamino)phenyl]diphenylphosphine oxide (1) has been synthesized and its single-crystal X-ray structure determined. The structures of two 'partial' oxides of the parent compound, (2) and (3) (50% and 25% oxidized), isolated from the intermediate phosphine reaction product have also been determined, yielding an unusual isomorphous crystal series. An apparent P-O bond shortening with increasing oxidation is also observed across the series (1)-(3) (1.480(4), 1.351(4), 1.280(4) A respectively) and is considered an artifact of the structure refinement. The packing in the crystals shows primary one-dimensional chains with weak head-to-tail associations between the oxide oxygen (three-centre) and two hydrogen atoms from separate methyl groups of the N-substituted amine (range C-H...O 3.115(4)-3.356(8) A), extended into a sheet structure by peripheral inter-chain C-H (aromatic)...O (oxide) associations.
Reduction of phosphine oxides into the corresponding phosphines using PhSiH3 as a reducing agent and Ph3C+[B(C6F5)4]? as an initiator is described. The process is highly efficient, reducing a broad range of secondary and tertiary alkyl and arylphosphines, bearing various functional groups in generally good yields. The reaction is believed to proceed through the generation of a silyl cation, which reaction with the phosphine oxide provides a phosphonium salt, further reduced by the silane to afford the desired phosphine along with siloxanes. (Figure presented.).
Reduction of phosphine oxides to the corresponding phosphines represents the most straightforward method to prepare these valuable reagents. However, existing methods to reduce phosphine oxides suffer from inadequate chemoselectivity due to the strength of the P=O bond and/or poor atom economy. Herein, we report the discovery of the most powerful chemoselective reductant for this transformation to date, 1,3-diphenyl-disiloxane (DPDS). Additive-free DPDS selectively reduces both secondary and tertiary phosphine oxides with retention of configuration even in the presence of aldehyde, nitro, ester, α,β-unsaturated carbonyls, azocarboxylates, and cyano functional groups. Arrhenius analysis indicates that the activation barrier for reduction by DPDS is significantly lower than any previously calculated silane reduction system. Inclusion of a catalytic Br?nsted acid further reduced the activation barrier and led to the first silane-mediated reduction of acyclic phosphine oxides at room temperature.
The invention relates to a method for preparing phosphine benzene apperception compound, the bromine compound is made with the magnesium reaction of Grignard reagent, then using four (triphenylphosphine) palladium-catalyzed bromophenylacetic compound phosphine chlorination reaction with the Grignard reagent. The specific method is, under the protection of inert gas, the bromo compound is made with the magnesium chips and organic solvent Grignard reagent, reflux 2 the [...] 10 hours; joined four at room temperature (triphenylphosphine) palladium, stirring 10 minutes to 3 hours, chlorinated room temperature instillment phosphine composition, reflux reaction the 1 [...] 10 hours; in the ice water bath in the fluid adds by drops full and weak acid to the reaction under weak alkali salt-water solution, liquid, organic phase exsolution, alcohol solvent crystallization, filtering to obtain compound phosphine benzene. The preparation method of this invention not only greatly improves manufacturing yield, and after treatment is simple, the process of repeated washing with ammonia water, the manufacturing process is simplified, is beneficial for large-scale industrial production. (by machine translation)
Nickel-catalysed P-H/C-CN cross coupling reactions take place efficiently under mild reaction conditions affording the corresponding sp2C-P bonds. This transformation provides a convenient method for the preparation of arylphosphines and arylphosphine oxides from the readily available P-H compounds and arylnitriles. This journal is
![[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]diphenylphosphane oxide](/upload/2023/2/e73275ab-257d-481c-bc69-b5e930b84a7e.png)
[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]diphenylphosphane oxide

4-(N,N-Dimethylamino)triphenylphosphine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
1,3-diphenyl-disiloxane;
In
toluene;
at 110 ℃;
chemoselective reaction;
Sealed tube;
|
89% |
|
[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]diphenylphosphane oxide;
With
trityl tetrakis(pentafluorophenyl)borate;
In
(2)H8-toluene;
at 20 ℃;
Glovebox;
Inert atmosphere;
With
phenylsilane;
In
(2)H8-toluene;
at 80 ℃;
for 3.5h;
Glovebox;
Inert atmosphere;
Sealed tube;
|
80% |
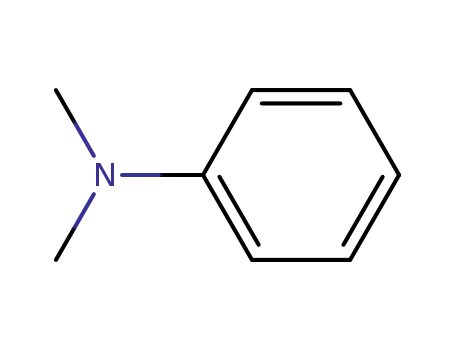
N,N-dimethyl-aniline
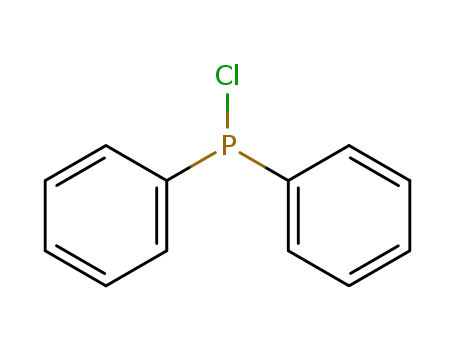
chloro-diphenylphosphine


4-(N,N-Dimethylamino)triphenylphosphine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
pyridine; aluminium trichloride;
In
benzene;
|
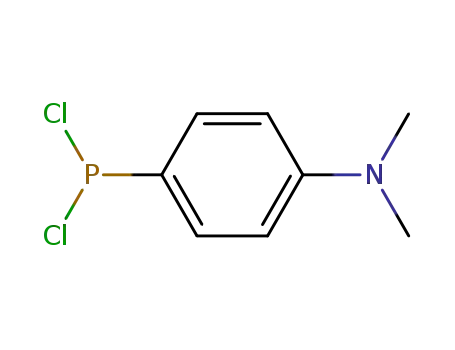
(4-dimethylamino-phenyl)-phosphonous acid dichloride

N,N-dimethyl-aniline

chloro-diphenylphosphine
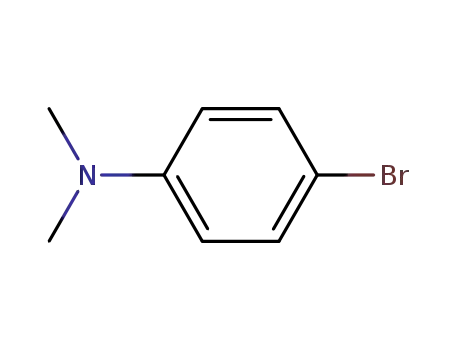
4-bromo-N,N-dimethylaniline
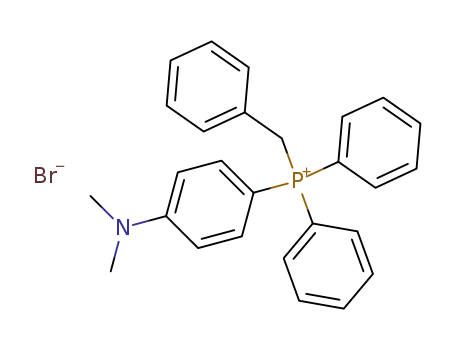
Diphenyl-benzyl-<4-dimethylaminophenyl>-phosphoniumbromid
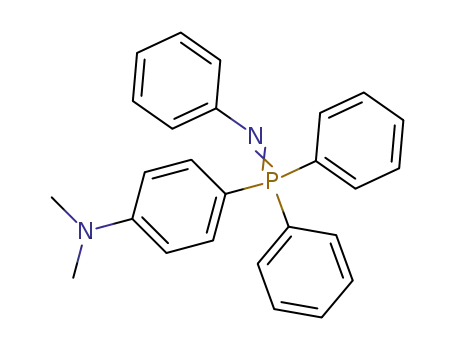
N-
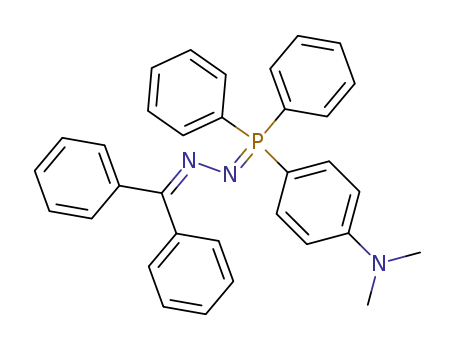
Benzophenon-p-dimethylaminophenyl-diphenyl-phosphazin
CAS:161265-03-8
Molecular Formula:C39H32OP2
Molecular Weight:578.6
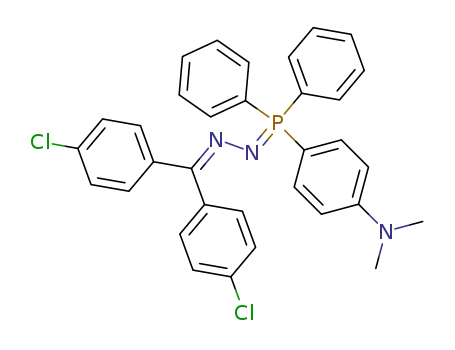
CAS:1762-84-1
CAS:37943-90-1