Your Location:Home >Products >Organic phosphines >Tert-butyl phosphines >224311-51-7

Product Details
Reactions
Ligand used in the palladium-catalyzed synthesis of aromatic amines from aryl chlorides, bromides and triflates. Ligand employed in a very active and general catalyst for Suzuki coupling reactions using aryl chlorides, bromides and triflates. Ligand used in palladium-catalyzed synthesis of oxindoles from α-chloroacetanilides. Effective ligand used in palladium-catalyzed arylation of thiazoles. Used in the formation of 2-benzylindolines via sequential palladium-catalyzed N-arylation/cyclization/C-arylation. Selective in the palladium-catalyzed arylation of silyl enol ethers formed from copper-catalyzed reduction of enones.
Chemical Properties
white to light yellow crystal powde
Uses
suzuki reaction
Uses
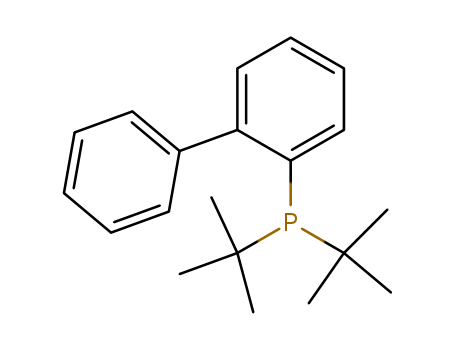
2-(Di-tert-butylphosphino)biphenyl (also known as JohnPhos) is a Buchwald ligand that is highly efficient in palladium-catalyzed reactions.
General Description
JohnPhos is a Buchwald′s sterically bulky biaryl phosphine ligand. It is a reactive dialkylbiaryl phosphine ligand which catalyzes the carbon-nitrogen bond-forming reactions. Coordination chemistry of gold catalysts bearing JohnPhos as ligand has been investigated by NMR spectroscopy.
InChI:InChI=1/C20H27P/c1-19(2,3)21(20(4,5)6)18-15-11-10-14-17(18)16-12-8-7-9-13-16/h7-15H,1-6H3
The kinetics of quinuclidine displacement of BH3 from a wide range of Lewis base borane adducts have been measured. Parameterization of these rates has enabled the development of a nucleofugality scale (NFB), shown to quantify and predict the leaving group ability of a range of other Lewis bases. Additivity observed across a number of series R′3-nRnX (X = P, N; R′ = aryl, alkyl) has allowed the formulation of related substituent parameters (nfPB, nfAB), providing a means of calculating NFB values for a range of Lewis bases that extends far beyond those experimentally derived. The utility of the nucleofugality parameter is explored by the correlation of the substituent parameter nfPB with the hydrolyses rates of a series of alkyl and aryl MIDA boronates under neutral conditions. This has allowed the identification of MIDA boronates with heteroatoms proximal to the reacting center, showing unusual kinetic lability or stability to hydrolysis.
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing tert-[...] biphenyl compounds, which belongs to the field of organic synthesis. In the oxygen free atmosphere, in order to di-tert-butylphenol [...] as raw material, under the action of the palladium catalyst, with the O-bromophenylacetic reaction, then the obtained by coupling with aryl boric acid di-tert-butylphenol [...] biphenyl compound. Compared with the prior art the invention less reaction steps, the operation is simple, high yield, is more suitable for industrial production. (by machine translation)
The invention relates to a method for preparing phosphine benzene apperception compound, the bromine compound is made with the magnesium reaction of Grignard reagent, then using four (triphenylphosphine) palladium-catalyzed bromophenylacetic compound phosphine chlorination reaction with the Grignard reagent. The specific method is, under the protection of inert gas, the bromo compound is made with the magnesium chips and organic solvent Grignard reagent, reflux 2 the [...] 10 hours; joined four at room temperature (triphenylphosphine) palladium, stirring 10 minutes to 3 hours, chlorinated room temperature instillment phosphine composition, reflux reaction the 1 [...] 10 hours; in the ice water bath in the fluid adds by drops full and weak acid to the reaction under weak alkali salt-water solution, liquid, organic phase exsolution, alcohol solvent crystallization, filtering to obtain compound phosphine benzene. The preparation method of this invention not only greatly improves manufacturing yield, and after treatment is simple, the process of repeated washing with ammonia water, the manufacturing process is simplified, is beneficial for large-scale industrial production. (by machine translation)
Palladium-catalyzed arylation of (diisopropylphosphoryl)biphenyl skeleton derivatives by the P(O)R2 directed C-H functionalization was reported. The related products were obtained in high regioselectivity and good functional group tolerance was observed. This reaction provided a new and efficient pathway for the synthesis of polyaromatic monophosphorus ligands. The Royal Society of Chemistry.
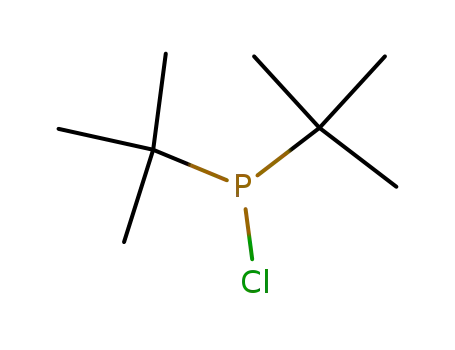
di(tert-butyl)chlorophosphine
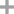
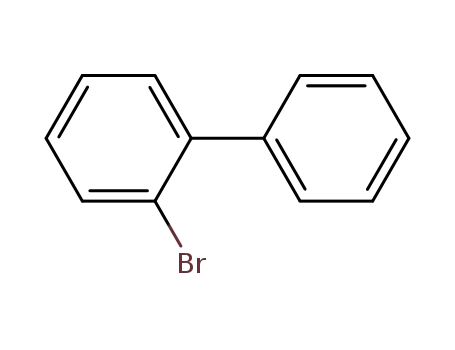
2-Bromobiphenyl

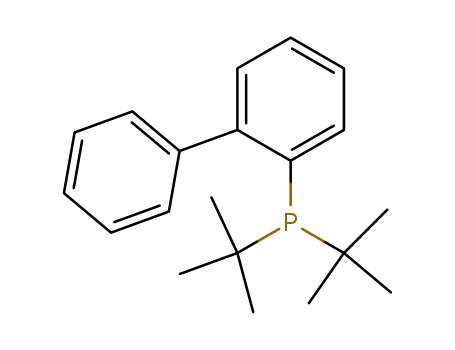
johnphos
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
2-Bromobiphenyl;
With
magnesium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
for 2h;
Inert atmosphere;
Reflux;
di(tert-butyl)chlorophosphine;
With
tetrakis(triphenylphosphine) palladium(0);
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 20 ℃;
for 2h;
Reagent/catalyst;
Reflux;
Inert atmosphere;
|
95.7% |
|
2-Bromobiphenyl;
With
iodine; magnesium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
for 2h;
Heating;
di(tert-butyl)chlorophosphine;
With
copper(l) chloride;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
for 8h;
Heating;
|
67% |
|
With
iodine; magnesium; copper(l) chloride;
Yield given;
Multistep reaction;
1.) THF, reflux, 2 h, 2.) THF, reflux, 8 h;
|

di(tert-butyl)chlorophosphine

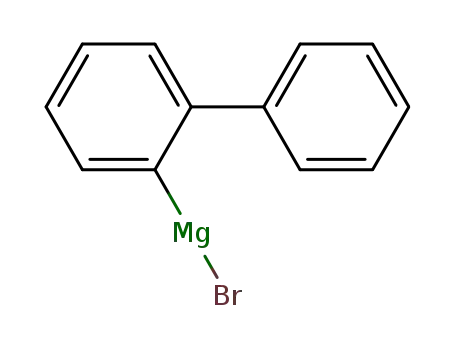
2-biphenylmagnesium bromide


johnphos
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
copper(I) bromide;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 30 - 35 ℃;
for 4h;
Heating / reflux;
|
87.5% |

di(tert-butyl)chlorophosphine
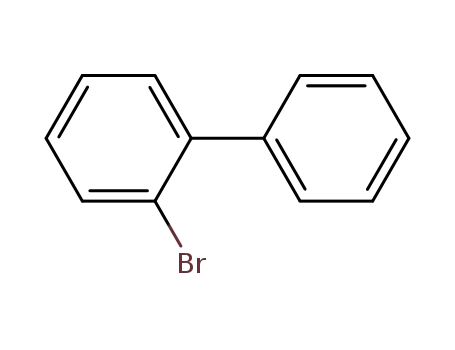
2-Bromobiphenyl
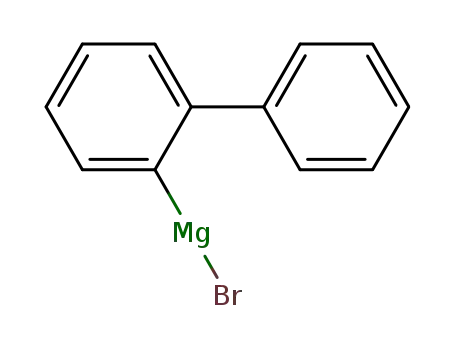
2-biphenylmagnesium bromide
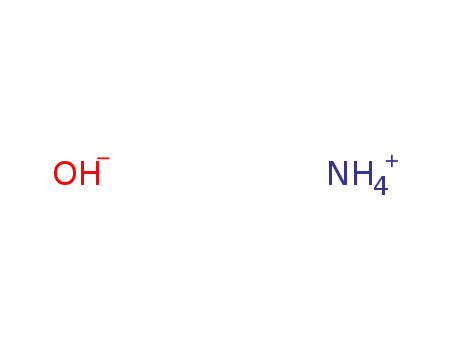
ammonium hydroxide
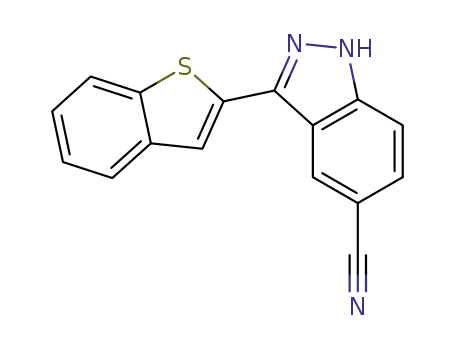
3-benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl-1H-indazole-5-carbonitrile
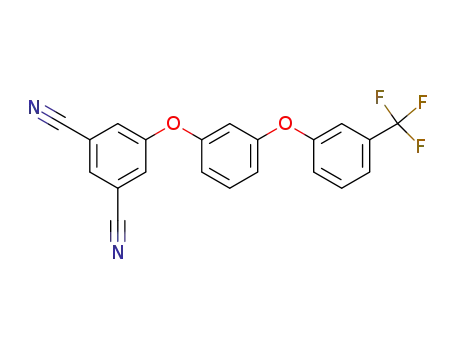
5-[3-(3-trifluoromethylphenoxy)phenoxy]isophthalonitrile
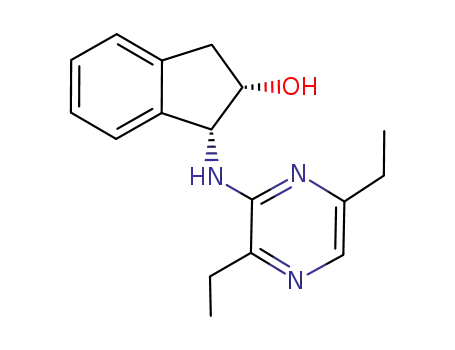
(1R,2S)-1-[ (3,6-diethylpyrazin-2-yl) amino]-2,3-DIHYDRO-1H-INDEN-2-OL
4-(5-bromo-pyridin-3-yl)-piperazine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
CAS:333432-28-3
Molecular Formula:C15H15BO2
Molecular Weight:238.09
CAS:23449-08-3
CAS:932710-63-9
Molecular Formula:C16H28NP
Molecular Weight:265.37
CAS:84680-95-5