Your Location:Home >Products >Functional intermediates >577-19-5
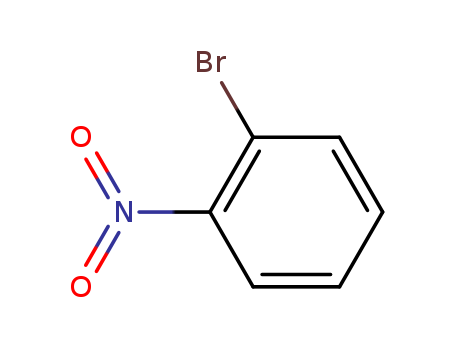

Product Details
Chemical Properties
white to light yellow crystal powder
Uses
1-Bromo-2-nitrobenzene is used in organic synthesis. It also can react with 2-methylamino-benzoic acid to get N-methyl-N-(2-nitro-phenyl)-anthranilic acid. And it is also used in the preparation of 4-methoxy-2?-nitrodiphenyl ether, 1-methoxy-3,5-bis-(2-nitro-phenoxy)benzene.
Uses
1-Bromo-2-nitrobenzene may be used in the preparation of: 4-methoxy-2′-nitrodiphenyl ether1-methoxy-3,5-bis-(2-nitro-phenoxy)benzene5-hydroxy-3-methoxy-2′-nitrodiphenyl ether
General Description
1-Bromo-2-nitrobenzene undergoes palladium[0]-mediated Ullmann cross-coupling reaction with a range of β-halo-enals, -enones or -esters to afford the corresponding β-aryl derivatives. Palladium[0]-mediated Ullmann cross-coupling reaction of 1-bromo-2-nitrobenzene with β-bromo-α,β-unsaturated aldehydes is reported.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it twice from pet ether, using charcoal before the first crystallisation. [Beilstein 5 III 618, 5 IV 728.]
InChI:InChI=1/C6H4BrNO2/c7-5-3-1-2-4-6(5)8(9)10/h1-4H
A variety of deactivated arenes were nitrated to their corresponding nitro derivatives in excellent yields under high-speed ball milling condition using Fe(NO3)3·9H2O/P2O5 as nitrating reagent. A radical involved mechanism was proposed for this facial, eco-friendly, safe, and effective nitration reaction.
Regardless of the sustainable development path, today, there are highly demanded chemical productions still operating that bear environmental and technological risks inherited from the previous century. The fabrication of nitro compounds, and nitroarenes in particular, is traditionally associated with acidic wastes formed in nitration reactions exploiting mixed acids. However, nitroarenes are indispensable for industrial and military applications. We faced the challenge and developed a greener, safer, and yet effective method for the production of nitroaromatics. The proposed approach comprises the application of an eco-friendly nitrating agent, namely dinitrogen pentoxide (DNP), in the medium of liquefied 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane (TFE) - one of the most non-hazardous Freons. Importantly, the used TFE is not emitted into the atmosphere but is effortlessly recondensed and returned into the process. DNP is obtainedviathe oxidation of dinitrogen tetroxide with ozone. The elaborated method is characterized by high yields of the targeted nitro arenes, mild reaction conditions, and minimal amount of easy-to-utilize wastes.
In this work, we developed a low-temperature and efficient approach for the highly selective preparation of valuable p-nitrochlorobenzene from the liquid-phase catalytic nitration of chlorobenzene with NO2 in O2-Ac2O-Hβ composite system. The results demonstrated that the introduction of molecular oxygen remarkably enhanced the chlorobenzene conversion and the cooperation catalysis of Hβ zeolite and Ac2O envidently improved the selectivity to para-nitro product. Under the optimized reaction conditions, 93.6 % of the selectivity to p-nitrochlorobenzene with 84.0 % of chlorobenzene conversion was obtained, and the ratio of p-nitrochlorobenzene to o-nitrochlorobenzene could reach up to 20.3. Furthermore, the selectivity distribution of nitration products was reasonably explained by the density functional theory (DFT) calculation. Finally, the possible nitration reaction pathway of chlorobenzene with NO2 was suggested in O2-Ac2O-Hβ composite catalytic system. The present work affords a new and mild nitration approach for highly selective preparation of valuable para-nitro products, and has potential industrial application prospects.
The electrochemical generation of aryldiazonium salts from nitroarenes in a two-phase system (ethyl acetate/water) was reported for the first time. Some compounds including azo, azosulfone, and arylazides were prepared in good yields with good purity. Cathodically generated aryldiazoniums and anodically produced copper(Ι) ions were used to perform Sandmeyer reactions. To improve the method, an H-type self-driving cell equipped with a Zn rod as an anode was introduced and used for two-phase aryldiazonium production.
C14H10Br2F3IO4S

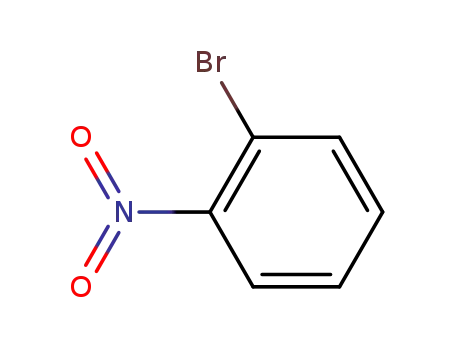
2-nitrophenyl bromide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
sodium nitrite;
In
1,2-dichloro-ethane;
at 20 - 80 ℃;
Schlenk technique;
|
85% |
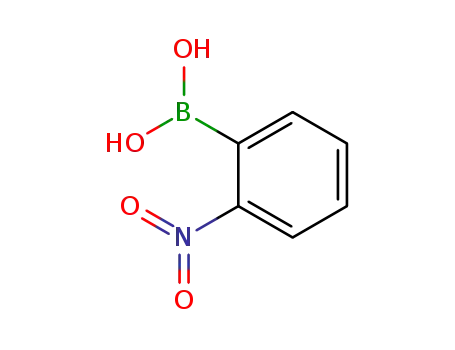
2-nitrophenylboronic acid


2-nitrophenyl bromide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
sodium nitrite;
In
acetonitrile;
at 80 ℃;
for 20h;
Sealed tube;
|
80% |
bromobenzene
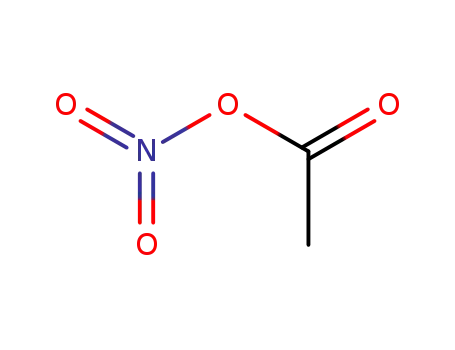
nitro acetate
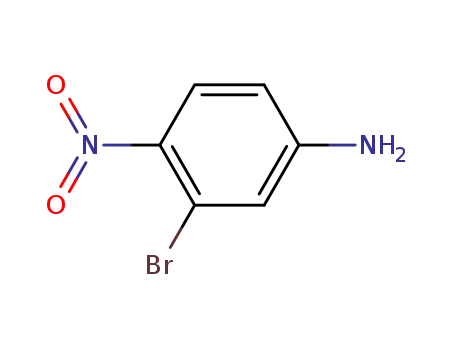
3-bromo-4-nitroaniline
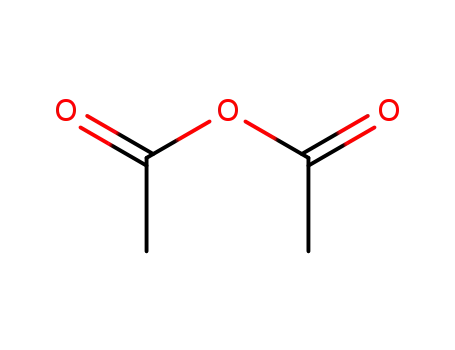
acetic anhydride
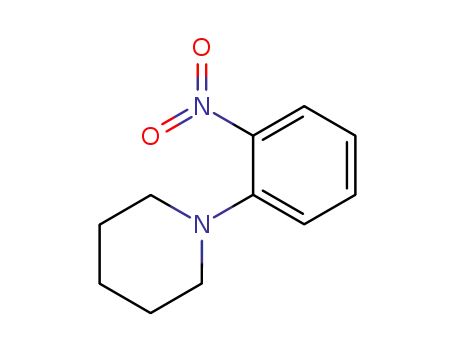
1-(2-nitrophenyl)piperidine
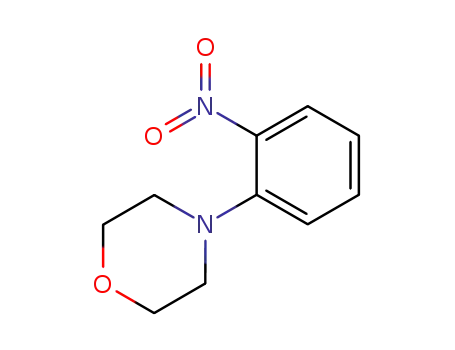
N-(2-nitrophenyl)morpholine
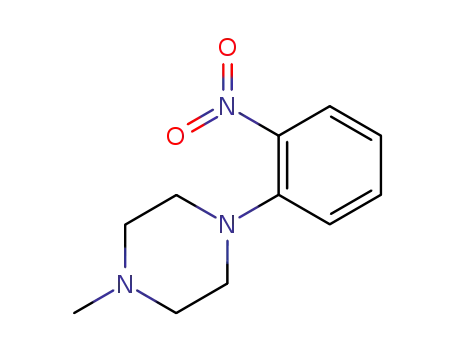
2-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-1-nitrobenzene
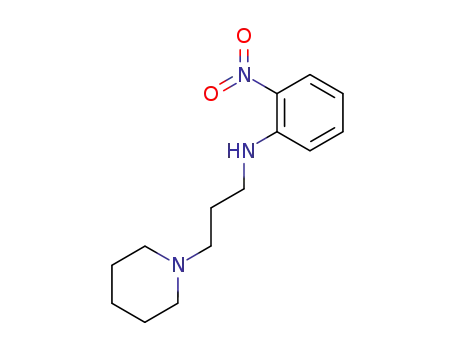
2-nitro-N-(3-piperidino-propyl)-aniline
CAS:166330-10-5
Molecular Formula:C36H28OP2
Molecular Weight:538.6
CAS:400607-04-7
Molecular Formula:C24H15Br
Molecular Weight:383.3
CAS:496-15-1