Your Location:Home >Products >Organic phosphines >Tert-butyl phosphines >6002-34-2


Product Details
Uses
New family of Ph2(t-Bu)P phosphines for efficient Silyl-Heck transformations.
Uses
Catalyst for:Nickel/Lewis acid-catalyzed carbocyanation of alkynes with acetonitrile or substituted acetonitrilesPalladium catalyzed hydrocarboxylation of acetylene with carbon monoxide to acrylic acid under mild conditionsPalladium to form a catalyst for methoxycarbonylation reactionsRu-catalyzed transfer hydrogenation in reductive coupling of disubstituted allenes with aldehydesStereoselective silylation by dehydrogenative Si-O coupling with Si-stereogenic silanesPhosphine ligand in nickel-catalyzed carbocyanation of alkynesMonodentate P-Donor Ligands (LKB-P)
InChI:InChI=1/C16H19P/c1-16(2,3)17(14-10-6-4-7-11-14)15-12-8-5-9-13-15/h4-13H,1-3H3
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a tert-butyl diphenylphosphine compound, and belongs to the field of organic synthesis. The method comprises the following step: in an anhydrous and oxygen-free atmosphere, tert-butyl alcohol is taken as a raw material and reacts with diphenylphosphine under the action of a catalyst to generate tert-butyl diphenylphosphine. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, simple operation, high yield, simple and easily available raw materials and reduced production cost, and is suitable for industrial production.
The kinetics of quinuclidine displacement of BH3 from a wide range of Lewis base borane adducts have been measured. Parameterization of these rates has enabled the development of a nucleofugality scale (NFB), shown to quantify and predict the leaving group ability of a range of other Lewis bases. Additivity observed across a number of series R′3-nRnX (X = P, N; R′ = aryl, alkyl) has allowed the formulation of related substituent parameters (nfPB, nfAB), providing a means of calculating NFB values for a range of Lewis bases that extends far beyond those experimentally derived. The utility of the nucleofugality parameter is explored by the correlation of the substituent parameter nfPB with the hydrolyses rates of a series of alkyl and aryl MIDA boronates under neutral conditions. This has allowed the identification of MIDA boronates with heteroatoms proximal to the reacting center, showing unusual kinetic lability or stability to hydrolysis.
Asymmetrically substituted tertiary phosphines and quaternary phosphonium salts are used extensively in applications throughout industry and academia. Despite their significance, classical methods to synthesize such compounds often demand either harsh reaction conditions, prefunctionalization of starting materials, highly sensitive organometallic reagents, or expensive transition-metal catalysts. Mild, practical methods thus remain elusive, despite being of great current interest. Herein, we describe a visible-light-driven method to form these products from secondary and primary phosphines. Using an inexpensive organic photocatalyst and blue-light irradiation, arylphosphines can be both alkylated and arylated using commercially available organohalides. In addition, the same organocatalyst can be used to transform white phosphorus (P4) directly into symmetrical aryl phosphines and phosphonium salts in a single reaction step, which has previously only been possible using precious metal catalysis.
Using rational ligand design, we have developed of a second-generation ligand, bis(3,5-di-tert-butylphenyl)(tert-butyl)phosphine, for the preparation of allylsilanes using the palladium-catalyzed silyl-Heck reaction. This new ligand provides nearly complete suppression of starting material alkene isomerization that was observed with our first-generation catalyst, providing vastly improved yields of allylsilanes from simple alkene starting materials. The studies quantifying the electronic and steric properties of the new ligand are described. Finally, we report an X-ray crystal structure of a palladium complex resulting from the oxidative addition of Me3SiI using an analogous ligand that provides significant insight into the nature of the catalytic system.
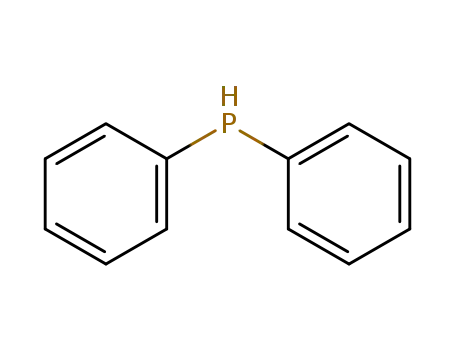
diphenylphosphane

tert-butyl alcohol


tert-butyldiphenylphosphine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
silica gel;
In
toluene;
at 100 ℃;
for 6h;
Temperature;
Reagent/catalyst;
Inert atmosphere;
|
92% |
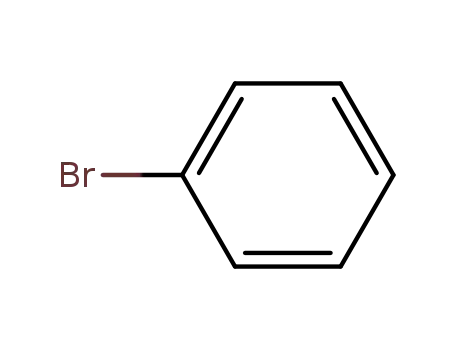
bromobenzene

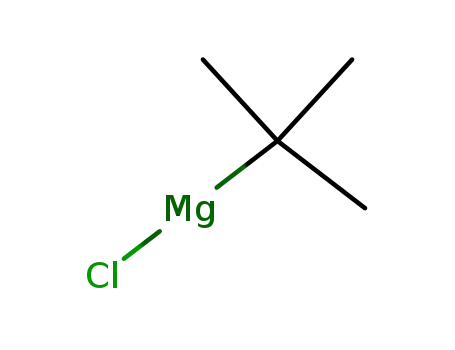
tert-butylmagnesium chloride

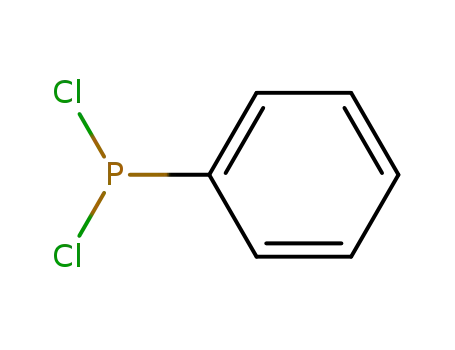
Dichlorophenylphosphine

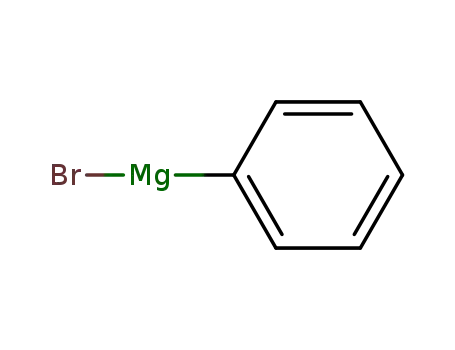
phenylmagnesium bromide


tert-butyldiphenylphosphine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
hydrogenchloride; magnesium;
In
water;
|
46% |
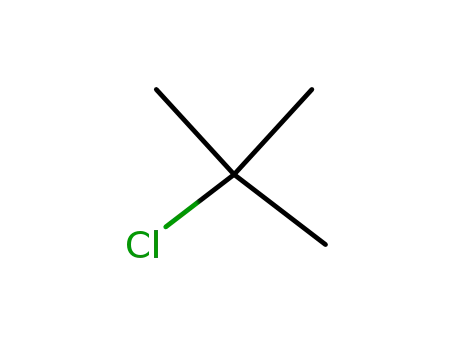
tertiary butyl chloride

Dichlorophenylphosphine
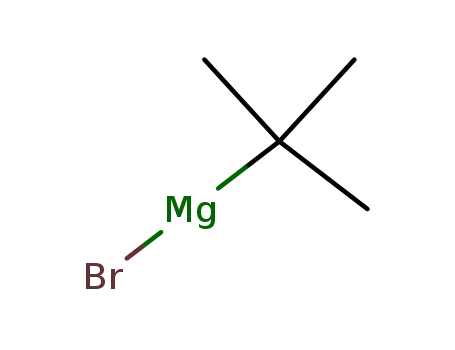
tert-butylmagnesium bromide
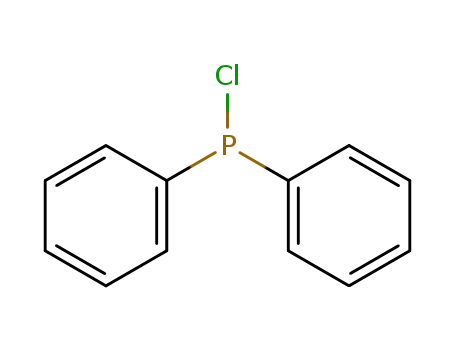
chloro-diphenylphosphine
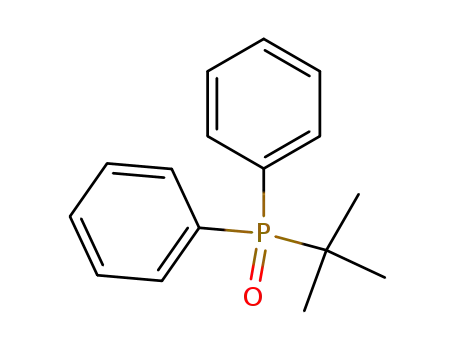
diphenyl(tert-butyl)phosphine oxide
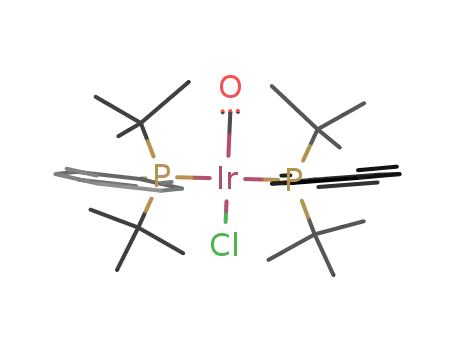
trans-carbonylchlorobis(phenyldi-t-butylphosphine)iridium(I)
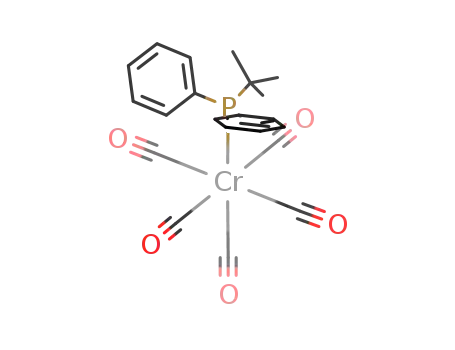
(CO)5CrP(C6H5)2{C(CH3)3}
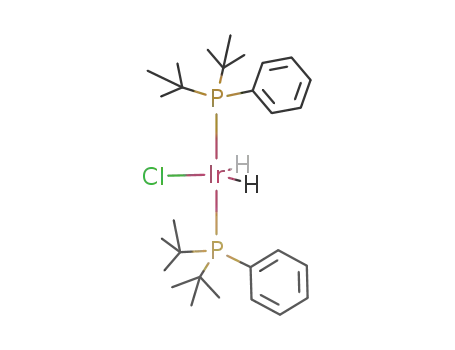
chlorodihydridobis(phenyldi-t-butylphosphine)iridium(III)
CAS:22082-99-1
CAS:819-19-2
CAS:32673-25-9
CAS:932710-63-9
Molecular Formula:C16H28NP
Molecular Weight:265.37