Your Location:Home >Products >Acid Anhydrides >716-39-2

Product Details
Appearance
2,3-NAPHTHALENEDICARBOXYLIC ANHYDRIDE is a pale Beige Solid.
Description
A few years ago, the product was still synthesized from the corresponding diacid, but in recent years, it has been difficult to find the shadow of the diacid in the market, and the sales of this product have been repeatedly restricted, resulting in high prices.
Uses
2,3-Naphthalic anhydride is used as a reagent to synthesize analogues of Thalidomide (T338850), an inhibitor of tumour necrosis factor that was once abandoned because it caused birth defects, but is currently used as an inhibitor of angiogenesis in patients with multiple myeloma.
InChI:InChI=1/C12H6O3/c13-11-9-5-7-3-1-2-4-8(7)6-10(9)12(14)15-11/h1-6H
The synthesis of chiral C2-symmetric substituted bisoxazoline ligands containing naphthalene group were investigated. Ethyl 2,3-naphthylene-dicarboxylate reacted with amino alcohols and the resulting amides were treated with SOCl2 and then reacted with Et3N in toluene to afford the desired bisoxazolines. 2,3-Naphthylenedicarbonitrile reacted with amino alcohol give N-(1′-phenyl-2′-hydroxyethyl)-2,3naphthylenedicarboximide 1. The 2,3-naphthylenedicarboxylic acid reacted with thionyl chloride give the 2,3-Naphthalenedicarboxylic acid cyclic anhydride rather than corresponding 2,3-naphthalenedicarboxylic acid dichloride, the former reacted with amino alcohol also give compound 1. The later two strategies cannot give the target bisoxazoline.
We have developed a simple picomole (low nanogram) scale HPLC scheme which can separate all eight isomers of sphingosine and dihydrosphingosine thus leading to the identification of their relative and absolute configurations. The amino group of the sample is derivatized to its fluorescent N-naphthimide which is analyzed by normal and chiral phase HPLC, coupled with fluorescence peak detection. If necessary, the results of this HPLC method can be further corroborated by measurements of circular dichroic (CD) spectra of the N-naphthimido-derivatives and/or N,O-chromophoric derivatives.
A transition-metal-free oxidative cross-dehydrogenative coupling reaction has been developed for the preparation of symmetrical carboxylic anhydrides through self-coupling dual C-O bond formations of aryl methanols. In the presence of a catalytic amount of tetrabutylphosphonium bromide (TBPB) as transfer agent and aqueous tert -butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP) as oxidant and reactant, methylene groups of aryl methanols were efficiently oxidized to C=O and coupled with the peroxide oxygen from TBHP to form a diverse array of symmetrical carboxylic anhydride derivatives.
The invention discloses a preparation method of 2,3-naphthalic acid, belonging to the technical field of preparation of organic compounds used as medical and liquid crystal intermediates. According to the preparation method, o-phthalaldehyde is used as a raw material, and through performing acetalation reaction, reducing reaction, hydrolysis reaction, cycloaddition reaction, dehydration reaction and hydrolysis reaction in sequence, finally the 2,3-naphthalic acid is prepared. The preparation method optimizes the reaction steps and conditions and has the advantages of reasonable synthetic route, high purity and yield of product, low production cost, low pollution, easy industrialization and the like.
Acenes comprise an important class of organic semiconducting materials. As graphene nanoribbons of ultimate width, they are valuable atom-precise model systems for studying the properties of this form of nanoscale carbon materials. Heptacene is the smallest member of the acene series that could only be studied under matrix isolation conditions. Its existence in bulk had never been positively confirmed, despite efforts dating back more than 70 years. We report that the reduction of 7,16-heptacenequinone produces a mixture of two diheptacene molecules. The diheptacenes undergo thermal cleavage to heptacene at high temperatures in the solid state. Monitoring this cycloreversion by solid state 13C cross-polarized magic angle spinning NMR reveals that solid heptacene has a half-life time of several weeks at room temperature. The diheptacenes are valuable precursors for generating films of heptacene by vapor phase deposition that can be studied below or at room temperature.
A method for producing a carboxylic acid anhydride includes heating a composition containing a specific compound in a solvent to yield the carboxylic acid anhydride. The solvent is an aprotic polar solvent having a boiling point of 50° C. or more.
1,3-dihydronaphtho<2,3-c>furan

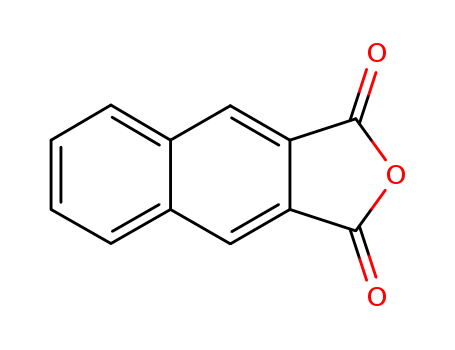
2,3-Naphthalenedicarboxylic anhydride
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
tert.-butylhydroperoxide; tetrabutyl phosphonium bromide;
In
water; chlorobenzene;
at 80 ℃;
for 3.5h;
Sealed tube;
|
65% |
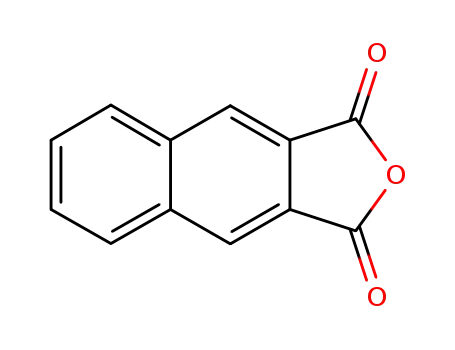
C12H8O4


2,3-Naphthalenedicarboxylic anhydride
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
sulfuric acid;
at 50 ℃;
for 7h;
Temperature;
Reagent/catalyst;
|
95% |
|
With
sulfuric acid; acetic anhydride;
Yield given. Multistep reaction;
1.) 15 min, 2.) reflux;
|
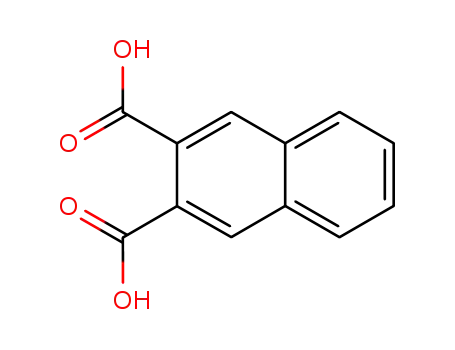
naphthalene-2,3-dicarboxylic acid
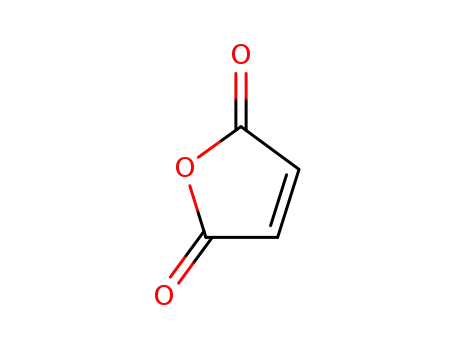
maleic anhydride
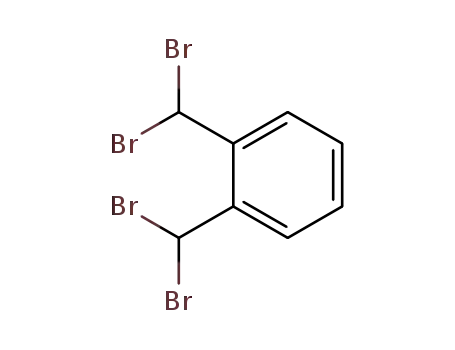
1,2-bis(dibromomethyl)benzene

C12H8O4
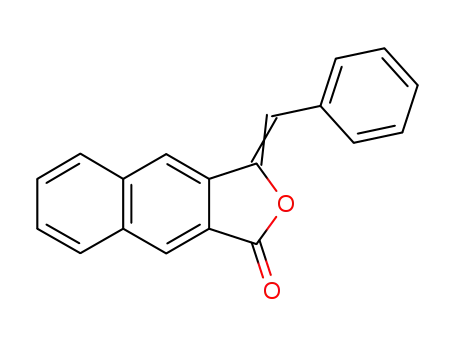
3-((Ξ)-benzylidene)-3H-naphtho[2,3-c]furan-1-one
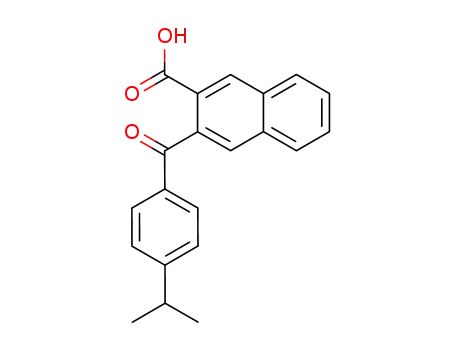
3-(4-isopropyl-benzoyl)-[2]naphthoic acid
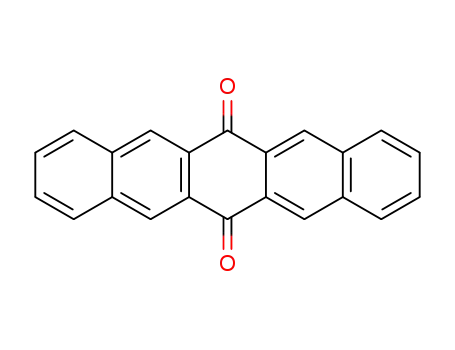
6,13-pentacenequinone
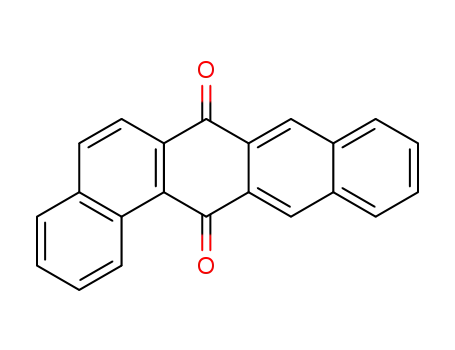
dibenz
CAS:69227-47-0
CAS:1081-34-1
CAS:19438-60-9
Molecular Formula:C9H12O3
Molecular Weight:168.19