Your Location:Home >Products >OLED intermediates >Thiophenes >1081-34-1

Product Details
Chemical Properties
YELLOW TO YELLOW-BROWN POWDER
Uses
α-Terthienyl was first recognized as a nematicidal constituent of marigolds, but in the presence of light, it is also highly toxic to larvae of several insect species, including mosquitoes. This electron donor thiophenederivative phototoxin is biosynthesized from polyacetylene precursors and appears to function as a photosensitizer catalyzing the formation of reactive oxygen species at the target site (25).
Uses
2,2'':5'',2''''-Terthiophene is a thiophene compound isolated from the roots of Echinops transiliensis, and was studied for its larvicidal activity against Aedes aegypti. 2,2'':5'',2''''-Terthiophene also showed inhibitory effects on dispersal ability of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus when used synergistically with certain antibiotics.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Synthetic Communications, 19, p. 307, 1989 DOI: 10.1080/00397918908050983Synthesis, p. 462, 1991 DOI: 10.1055/s-1991-26494
General Description
2,2′:5′,2′′-Terthiophene (TTh) may be prepared by nickel catalysed coupling reaction of grignard′s reagent derived from 2-bromothiophene and magnesium. It generates singlet oxygen. In nature, it is found in the floral extract of Tagetes minuta and Echinops grijisii. It is known to be toxic to mosquitoes. It also exihibits antifungal activity.
Metabolic pathway
When 14C-a-terthienyl is administered orally to rats in a single dose, two metabolites [1,4-di(2'-thienyl)]-1,4- butadione and 2-2' -bithiophene-5-carboxylic acid are identified in the urine.
Purification Methods
Possible impurities are bithienyl and polythienyls. Suspend it in H2O and steam distil it to remove bithienyl. The residue is cooled and extracted with CHCl3, dried (MgSO4), filtered, evaporated and the residue chromatographed on Al2O3 using pet ether/3% Me2CO as eluent. The terphenyl zone is then eluted from the Al2O3 with Et2O, the extract is evaporated and the residue is recrystallised from MeOH (40mL per g). The platelets are washed with cold MeOH and dried in air. [UV: Sease & Zechmeister J Am Chem Soc 69 270 1947; Uhlenbroek & Bijloo Recl Trav Chim Pays-Bas 79 1181 1960.] It has also been recrystallised from MeOH, *C6H6, pet ether or AcOH. [UV: Zechmeister & Sease J Am Chem Soc 69 273 1947, Steinkopf et al. Justus Liebigs Ann Chem 546 180 1941.] It is a phototoxic nematocide [Cooper & Nitsche Bioorg Chem 13 36 1985, Chan et al. Phytochem 14 2295 1975]. [Beilstein 19 III/IV 4763, 19/9 V 226.]
Cyclization-modified terthiophene displays the change of emission behavior from locally excited (LE) to the intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) state. The rectangular bisterthiophenesiloxanes (DSiTh) was successfully prepared by π–π-stacking-aided hydrogen-bonding interactions. Cyclization-induced ICT in DSiTh could be observed, which was confirmed by absorption spectra, fluorescence spectra, and quantum chemistry analysis. The cyclization produces a strong intramolecular electron redistribution of a highly packed π-conjugated terthiophene. Thus, a distinctive variation of the dipole moment and a through-space ICT happen.
To develop novel oligothiophene-based liquid crystals involving hydrogen bonding, new terthiophene derivatives containing a stearylamide group, N,N′-distearyl-5,5″-dicyano-2,2′:5′,2″- terthiophene-4,4″-dicarboxamide (DNC18DCN 3T) and N,N′-distearyl-5,5′-dipropyl-2,2′:5′, 2′-terthiophene-4,4″-dicarboxamide (DNC18 DP3T), were designed and synthesized, and their thermal behavior examined. Although DNC 18DP3T did not exhibit liquid crystallinity, DNC18DCN3T was found to form smectic A phase. Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.
The facile synthesis of poorly soluble unsubstituted and modified α-quinque- and sexithiophenes under microwave irradiation in the liquid phase is described. The use of microwave irradiation allowed these compounds to be prepared in a few minutes and at high yields by means of the Suzuki cross-coupling reaction. Unsubstituted sexithiophene was obtained in 10 min via the one-pot borylation/Suzuki reaction, purified according to a very simple procedure, and isolated in 84% yield. The efficient synthesis of two new methylated quinque- and sexithiophenes displaying liquid crystalline properties is reported. A new microwave-assisted methodology for the conversion of aldehyde-terminated quinque- and sexithiophenes into the corresponding cyano derivatives is also described. The use of microwaves was extended to the Sonogashira coupling reaction and found to be very effective in the preparation of a quinquethiophene containing acetylenic spacers. The electronic and optical characterization of this compound is reported and discussed in relation to that of unsubstituted quinquethiophene.
In the presence of PdCl42- in alcohol/water solution, thiophene oligomerized to form α,α-coupled bithiophene while 2,2'-bithiophene oligomerized to form α,α-coupled tetrathiophene as the major products.In the case of thiophene, two unstable intermediates were isolated and characterized by 1H NMR as η1,C-bonded and η5,?-bonded thiophene-palladium(II) complexes.The mechanism of Α,α-coupling of is thus proposed.
A facile base-promoted sulfur-centered radical generation mode and a single-step protocol for the synthesis of thiophene derivatives using 1,3-diynes via the interaction between elemental sulfur and NaOtBu has been reported. EPR experiments revealed that the trisulfur radical anion acts as a key intermediate of this process. A plausible mechanism has been proposed.
A new oligothiophene-based sensor 3 TH for monitoring Hg2+ has been designed and synthesized based on the intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) mechanism. The 3 TH shows the significant specificity toward Hg2+ through “naked-eye” colorimetric detection as well as via ratiometric fluorescence enhancement response with low detection limit of 62 nM. In addition, sensor 3 TH shows high selectivity and sensitivity for Hg2+ with fast response in a suitable pH range. Moreover, the 3 TH-based test strips was used to conveniently detect Hg2+ ions in water. Furthermore, considering its good ‘‘turn-on’’ fluorescent sensing behavior and low cell cytotoxicity, 3 TH was successfully applied to detect and image Hg2+ in real water samples and living cells, which shows great potentials for application in environmental and biological systems.
To understand the relationship between molecular orientation in organic thin films and organic photovoltaic properties the donor-acceptor type oligothiophene derivatives 5,5″-dicyano-2,2′:5′,2″- terthiophene and 5,5?-dicyano-2,2′:5′,2″:5″, 2?-quaterthiophene were synthesized. Polarizing optical microscopy showed that the oligothiophene derivatives had liquid crystalline properties. The crystalline phases of the oligothiophene derivatives showed molecular orientation. Atomic force microscopy also showed that the vacuum-evaporated oligothiophene derivative thin films had molecular orientation. Using the oligothiophene derivative thin films as donor materials and a 3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic dianhydride thin film as the acceptor material organic photovoltaic devices were fabricated. The structure of these devices is glass-indium tin oxide/donor materials/acceptor material/aluminum. The molecular orientation of the vacuum-evaporated oligothiophene derivative thin films was found to improve the organic photovoltaic performance of these devices.
-
A novel oligothiophene and its fullerene derivative were synthesized and their film morphologies were investigated. AFM images revealed that the oligothiophene formed well-aligned fiber-like nanostructures in the film after being thermally annealed at its liquid-crystalline temperature. In the oligothiophene-fullerene dyad film, fibers were already formed in the as-cast film. Thermal annealing further enhanced the structural order and a long, partially aligned fibrous nanostructure with a width of around 10 nm and a length of as long as 200 nm was observed. Combined with the results of X-ray analysis, these features were ascribed to supramolecular self-assembly via π-π interaction of the oligothiophene groups. Photovoltaic properties of the molecules were also investigated. The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Two series of new oligothiophene-pentacene hybrid compounds were successfully synthesized and characterized, which consist of pentacene and anthradithiophene skeletons modified by different oligothienyl groups at 6,13 sites or 5,11 sites, respectively. Th
The synthesis of RITA and a variety of five-membered heterocyclic triads by the cyclocondensation of 1,4-bis(5-substituted-2-thienyl or 2-furyl)-1,3-butadiynes with water or Na2S·9H2O in the presence of KOH in DMSO is described. The study on the antiproliferative activities against K562, MCF-7, A549, and HCT116 tumor cells has revealed that some of the heterocyclic triads show higher antiproliferative activities than RITA, depending on the structures of substituents, the property of heteroatoms as well as their numbers.
A new synthetic route to mononitrated oligothiophenes is described, as well as the preparation of halogenated derivatives (Br, I) thereof. An unusual deep red colour is observed and explained, with the aid of DFT calculations, as arising from a significant quinoidal contribution to the molecular structure. The crystal structures of two compounds, H(C4H2S) 3NO2 and Br(C4H2S) 3NO2, are presented. Both compounds have planar sheets held together by intermolecular short contacts (hydrogen bonds and, for the latter, NO2...Br interactions); the sheets do not directly superimpose, so the effect of the π-stacking is not maximized. Solid-state fluorescence and extended-Hueckel band-structure calculations are also presented for these materials.
Oligomers containing from 2 to 6 thiophene units attached by their 2 and 5 positions were synthesized unambiguously by iodine oxidation of a suitable ate complex obtained by stepwise reactions of 9-BBN with methanol, a 2-lithiothiophene, boron trifluoride etherate, and a second 2-lithiothiophene.This is a one-pot procedure, carried out under nitrogen between -80 deg C and 0 deg C.
The copper-based metal-organic framework (MOF) HKUST-1 adsorbs organic molecules into its pores. When loaded with electron-rich oligothiophenes, the resulting system reacts under heat to initiate oxidative polymerization without the use of any other oxidant or catalyst. This reaction is not observed in the non-redox-active MOF MIL-100(Al). We have characterized the composites by optical and nanoscale microscopy, vibrational and UV-vis spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, N2 sorption analysis, and thermogravimetric analysis/residual gas analysis. Unsubstituted oligothiophenes polymerize within MOF pores, while 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene forms a coating on the MOF surface. MOF composites with conjugated polymer dopants trapped inside their pores undergo profound shifts in the composite electronic structure. Reasoning from time-dependent density functional theory calculations of an HKUST-1 model system bound to monomers, we rationalize the observed reactivity and propose an initiation mechanism based on a ligand-to-metal charge-transfer state.
A series of α-terthiophene derivatives were prepared and their protein kinase C inhibitory activity were evaluated. The aldehyde derivatives were most potent inhibitors (IC50 1 μM). 2a-Terthiophene monoaldehyde was inactive in the inhibitions of protein kinase A, mitogen activated protein kinase and protein tyrosine kinase.
A preliminary account of the synthesis and liquid crystal properties of representative members of an homologous series of 5-alkanoyl-5″-alkyl-2,2′:5′,2″-terthienyls and the analogous 5,5″-di-alkyl-2,2′:5′,2″-terthienyls is given. The disposition of the three thiophene rings renders the molecular geometry sufficiently anisotropic that suitably substituted compounds are mesomorphic, and the liquid crystal transition temperatures of corresponding members of the two series are compared. The related 5,5′-disubstituted 2,2′-bithienyl derivatives are not mesomorphic.
Lanthanide ion (LnIII) complexes, [Ln(3Tcbx)2]3+ (LnIII=YbIII, NdIII, ErIII) are isolated with a new pyridine-bis(carboxamide)-based ligand with a 2,2′:5′,2′′-terthiophene pendant (3TCbx), and their resulting photophysical properties are explored. Upon excitation of the complexes at 490 nm, only LnIII emission is observed with efficiencies of 0.29 % at 976 nm for LnIII=YbIII and 0.16 % at 1053 nm for LnIII=NdIII. ErIII emission is observed but weak. Upon excitation at 400 nm, concurrent 1O2 formation is seen, with efficiencies of 11 % for the YbIII and NdIII complexes and 13 % for the ErIII complex. Owing to the concurrent generation of 1O2, as expected, the efficiency of metal-centered emission decreases to 0.02 % for YbIII and 0.05 % for NdIII. The ability to control 1O2 generation through the excitation wavelength indicates that the incorporation of 2,2′:5′,2′′-terthiophene results in access to multiple sensitization pathways. These energy pathways are unraveled through transient absorption spectroscopy.
Different methods for the coupling of 2-(4-pyridyl)thiophene to α-dibrominated thiophene oligomers and their efficiency to produce a homologous series of extended di(4-pyridyl)thiophene oligomers have been studied. The coupling was found to be most efficient with the organozinc derivative of 2-(4-pyridyl)thiophene, using a Pd(dppf) complex as the catalyst in the coupling reaction. The resulting compounds are promising new models for trans-membrane molecular conductors.
In order to develop novel oligothiophene-based liquid crystals capable of hydrogen bonding, new terthiophene derivatives containing an alkylamide group, N,N′-dialkyl-5,5″-dichloro-2,2′:5′,2″- terthiophene-4,4″-dicarboxamide (DNCnDCl3T, n=8, 18)
The purpose of this study was to obtain a rapid, efficient, and environmentally friendly methodology for the synthesis of highly pure thiophene oligomers. The solvent-free, microwave-assisted coupling of thienyl boronic acids and esters with thienyl bromides, using aluminum oxide as the solid support, allowed us to rapidly check the reaction trends on changing times, temperature, catalyst, and base and easily optimize the experimental conditions to obtain the targeted product in fair amounts. This procedure offers a novel, general, and very rapid route to the preparation of soluble thiophene oligomers. Thus, for example, quaterthiophene was obtained in 6 min by reaction of 2-bromo-2,2′-bithiophene with bis(pinacolato)diboron (isolated yield 65%), whereas quinquethiophene was obtained in 11 min by reaction of dibremoterthiophene with thienylboronic acid (isolated yield 74%). The synthesis of new chiral 2,2′-bithiophenes is reported. The detailed analysis of the byproducts of some reactions allowed us to elucidate a few aspects of reaction mechanisms. While the use of microwaves proved to be very convenient for the coupling between conventional thienyl moieties, the same was not true for the coupling of thienyl rings to thienyl-S,S-dioxide moieties. Indeed, in this case, the targeted product was obtained in low yields because of the competitive, accelerated, Diels-Alder reaction that affords a variety of condensation products.
A new simple oligothiophene-indenedione-based sensor 3TI has been synthesized for the highly reactive and selective detection of cyanide anion (CN?) in 70% aqueous media. The sensor 3TI displays distinct colorimetric and fluorometric detection of CN? due to the addition of CN? to the electron-deficient indenedione-vinyl group of 3TI, which hampers intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) efficiencies. The recognition mechanism of 3TI for CN? was confirmed by the optical measurements, 1H NMR titration, FTIR spectra, HRMS analysis, and TD-DFT calculations. The sensor 3TI for CN? shows the outstanding advantages of high fluorescence brightness, fast response time (30 s), low detection limit (31.3 nM), minimal pH dependence in the physiologically relevant range, and excellent selectivity in presence of other competitive anions. Encouraged by these desirable sensing properties, the 3TI has been successfully used for determination of CN? in real water and food samples, silica-based sensing kits and fluorescence imaging in living cells with satisfactory results.
A series of high coplanar alternative linear small molecules with acceptor-donor-acceptor (A-D-A) structure containing electron-accepting tetrazine (Tz) moiety and electron-donating oligothiophenes (OTs) moiety, alkylated thiophene attached to both sides of the Tz moiety were designed and synthesized. The influences of varied oligothiophene length on small molecules' optical and electrochemical properties, crystallization, self assembling morphology in blend film with (6,6)-phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester (PC61BM), and photovoltaic properties for the application as donor materials in organic solar cells (OSCs) were studied. The optical and electrochemical properties of small molecules showed that the HOMO and LUMO energy levels were determined by the number of OTs moiety and electron-accepting ability of Tz in the alternative small molecules, respectively. Meanwhile, the varied OT moieties can significantly affect the hierarchical structures when mixed with PC61BM. The molecule with intermediate conjugate moity length showed the highest ordering in its crystalline state, as revealed by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and X-ray diffraction experiments, and best photovoltaic properties when blended together with PC61BM or (6,6)-phenyl-C71-butyric acid methyl ester (PC71BM) as active layer in photovoltaic devices. The results indicate that hierarchical structures controlled by adjusting the conjugate moity length of small molecules is an effective way to improve the performance of OSCs. The photovoltaic device based on TT(HTTzHT)2:PC71BM with 1% DIO additives showed the best performance, with a Jsc of 7.87 mA/cm2 and a PCE of 3.24%.
Novel electron acceptors bearing a heteroquinonoid system, 5,5'-bis(dicyanomethylene)5,5'-dihydro-Δ2,2'-bithiophene, its 3,3'-dichloro, 3,3'-dibromo, and 3,3',4,4'-tetrabromo derivatives, and 5,5''-bis(dicyanomethylene)-5,5''-dihydro-Δ2,2':5',2''-tertiophene were synthesized by the action of tetracyanoethylene oxide or by Pd(0)-catalyzed substitution reactions with sodium dicyanomethanide on the corresponding α,α'-dihalogeno-heteroaromatics.They showed very small on-site Coulomb repulsion as expected, and afforded several highly conductive molecular complexes with electron donors such as hexamethylenetetratellurafulvalene.
On the basis of the principle of combination of active groups, a series of novel N-(4-([2,2′:5′,2″-terthiophen]- 5-yl)-2-methylbut-3-yn-2-yl) benzamide derivatives were designed, synthesized and systematically evaluated for their antiviral activity agains
-
For the purpose of developing novel photovoltaic materials and organic photovoltaic devices with good performance characteristics, 5-cyano-2,2′: 5′,2″-terthiophene (3T-CN) and 5-cyano-2,2′:5′,2″: 5″,2″ ′-tetrathiophene (4T-CN) were synthesized. The 3T-CN and 4T-CN were donor-acceptor oligothiophene derivatives possessing mesogenic properties. The photovoltaic properties of 3T-CN and 4T-CN were studied. The rigid and flexible photovoltaic devices were fabricated using 3T-CN, 4T-CN, and 3,4,9,10-perylenetertracarboxylic dianhydride (PTCDA). The results showed that the -CN group played an important role in increasing short circuit current density (Isc) and power conversion efficiency (PCE). Both rigid device glass-ITO/4T-CN/PTCDA/Al and flexible device PET-ITO (indium tin oxides coated with polyethylene terephthalate)/4T-CN/PTCDA/Al had greater I sc and PCE compared with rigid device glass-ITO/4T/PTCDA/Al. It was possible that the -CN group, with strong electron-withdrawing character, and mesogenic properties of 4T-CN enhanced the efficiency by promoting forward interfacial electron transfer. Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.
-
Efficient synthesis of a series of terminally dicyanovinyl (DCV)-substituted oligothiophenes, DCVnT 1-6, without solubilizing side chains synthesized via a novel convergent approach and their application as electron donors in vacuum-processed m-i-p-type planar and p-i-n-type bulk heterojunction organic solar cells is described. Purification of the products via gradient sublimation yields thermally highly stable organic semiconducting materials in single crystalline quality which allows for X-ray structure analysis. Important insights into the packing features and intermolecular interactions of these promising solar cell materials are provided. Optical absorption spectra and electrochemical properties of the oligomers are investigated and valuable structure-property relationships deduced. Photovoltaic devices incorporating DCVnTs 4-6 showed power conversion efficiencies up to 2.8% for planar and 5.2% for bulk heterojunction organic solar cells under full sun illumination (mismatch corrected simulated AM 1.5G sunlight). The 5.2% efficiency shown here represents one of the highest values ever reported for organic vacuum-deposited single heterojunction solar cells.
Hemagglutinin (HA) which is essential for influenza viral infection and replication has become a target for the design of anti-influenza drugs. A novel series of oligothiophene compounds focused on the target were synthesized as specific inhibitors agains
For the purpose of developing novel photovoltaic materials, 5,5″-biformyl-2,2′:5′,2″-terthiophene (OHC-3T-CHO) and 5,5″-biformyl-2,2′:5′,2″:5″,2?:5?, 2″″-q-uinquethiophene (OHC-5T-CHO) were synthesized. The photovoltaic properties of OHC-3T-CHO and OHC-5T-CHO were studied. We have fabricated two flexible organic photovoltaic devices using OHC-3T-CHO, OHC-5T-CHO, and 3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic dianhydride (PTCDA). The PET-ITO (indium tin oxides coated with polyethylene terephthalate)/OHC-3T-CHO/ PTCDA/Al device has an open circuit voltage (Voc) of 1.12V, and photoelectric conversion efficiency (PCE) of 1.00%, whereas the PET-ITO/OHC-5T-CHO/PTCDA/Al device has a Voc of 1.78V and PCE of 1.08%. Both devices have high Voc (1.12V and 1.78V). It is possible that intermolecular hydrogen bonding between the -CHO group of OHC-nT-CHO and the carboxylic dianhydride of PTCDA enhanced the efficiency by promoting forward interfacial electron transfer.
A series of novel 5-phenyl-3-(2,2′:5′,2′′-terthien- 5-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazolines were synthesized in this report. Their photoactivated cytotoxicities on the Spodoptera litura (SL) cell line were evaluated using the MTT method. It was noticed that the inhibitory activities of all the conjugates was enhanced when irradiated with UV-A light. Compounds 4, 6 and 8 were found to be most effective with inhibition rates of 88.1%, 88.0%, and 90.5%, respectively. For compound 5, the inhibition rate value was only slightly enhanced under the irradiation treatment (78.3%) compared to the dark treatment (74.8%). The relationship analysis between structure and activity showed that the middle thiophene ring played an important role on the inhibitory activities. It was shown that these compounds could be the potential candidates for new photoactivated pesticides.
Trimethylsilyl end-capped bi- and terthiophene carbaldehydes were prepared by reaction of bi- and terthienyl lithium with DMF. Condensation of 5-trimethylsilyl-2,2′-bithiophene-5′-carbaldehyde with dinitrile of malonic acid gave silylbithienyl methylidenedinitrile in good yield, while reaction with hydroxylamine was accompanied by desilylation. The reaction of hydroxylamine with silylbithienyldinitrile leads to the formation of 2-[5-(5′-trimethylsilyl-2,2′-bithienyl)methylidene]malonic acid bisamidoxime. The cytotoxic effect of bi- and terthiophene derivatives was investigated in vitro on two monolayer tumor cell lines: MG-22A (mouse hepatoma) and HT-1080 (human fibrosarcoma). The molecular structure of 5-trimethylsilyl-2,2′-bithiophene-5′-carbaldehyde was studied by X-ray diffraction.
A series of novel soluble donor-acceptor lowbandgap-conjugated polymers consisting of different oligothiophene (OTh) coupled to electron-accepting moiety 2-pyran-4ylidenemalononitrile (PM)-based unit were synthesized by Stille or Suzuki coupling polymerization. The combination of electron-accepting PM building block with varied OThn (the number of thiophene unit increases from 3 to 5) results in enhanced π-π stacking in solid state and intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) transition, which lead to an extension of the absorption spectra of the copolymers. Cyclic voltammetry measurements and molecular orbital distribution calculations indicate that the highest occupied molecular orbitals (HOMO) energy levels could be fine-tuned by changing the number of thiophene units of the copolymers, and the resulting copolymers possessed relatively low HOMO energy levels promising good air stability and high-open circuit voltage (Voc) for photovoltaic application. Bulk heterojunction photovoltaic devices were fabricated by using the copolymers as donors and (6,6)phenyl C61-butyric acid methyl ester as acceptor. It was found that the highest Voc reached 0.94 V, and the short circuit currents (Jsc) were improved from 1.78 to 2.54 mA/cm2, though the power conversion efficiencies of the devices were measured between 0.61 and 0.99% under simulated AM 1.5 solar irradiation of 100 mW/cm 2, which indicated that this series copolymers can be promising candidates for the photovoltaic applications.
A highly efficient cobalt-catalyzed homocoupling of terminal alkynes with di-tert-butyldiaziridinone as the oxidant has been developed. The protocol tolerates a wide array of terminal alkynes, both activated and unactivated alkynes, to afford the corresponding conjugated 1,3-diynes. The mild reaction conditions further allow late-stage homocoupling of alkynes derived from complex natural products.
Pyrene is composed of four benzene rings and has a unique planar melting ring structure. Pyrene is the smallest condensed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and its unique structural properties have been extensively studied. Pyrene has excellent properties such as thermal stability, high fluorescence quantum efficiency and high carrier mobility. This paper mainly used thiophene, EDOT and triphenylamine groups to enhance the pyrene based π-conjugated system and control the molecular accumulation of organic semiconductors, and improve their charge transport performances. Five kinds of polymer were synthesized and correspondingly characterized. The five kinds of pyrene conductive polymer had outstanding properties in terms of solubility, fluorescence intensity and thermal stability, good film-forming properties, stable electrochromic properties and high coloring efficiency. The coloration efficiency (CE) of PPYTP was as high as 277 cm2C?1, and the switching response time was short. The coloring time of PPYEDOT was 1.3 s and the bleaching time was 3.2 s. The lower impedance will also provide the possibility of such polymers being incorporated into electrochromic devices in the future. In short, the synthesized new pyrene conductive polymers will have wide application prospects in the field of electrochromic materials.
The trithiocarbonate anion (CS32-) was generated in situ from CS2 and KOH in dimethyl sulfoxide by a simple method and used as a novel synthetic equivalent of the S2- synthon for the synthesis of 2,5-disubstituted thiophenes from 1,3-butadiynes. Additionally, this system was employed for the metal-free synthesis of 2-substituted benzo[b]thiophenes from 2-haloalkynyl (hetero)arenes. These compounds were obtained from a cheap and readily available sulfur source in moderate to good yields, with good functional group tolerance.
We report organic photodetectors (OPDs) exhibiting high photocurrent density (Jph), low dark current density (Jd), and broadband external quantum efficiency (EQE) based on three push-pull type D-π-A small molecule donors (H1, H2, and H3) with different π-
2-bromothiophene

2,2':5',2''-terthiophene
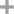
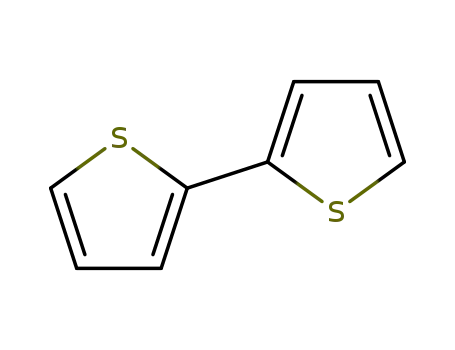
2,2'-Bithiophene
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
[2,2]bipyridinyl; nickel diacetate; sodium tert-pentoxide;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 25 ℃;
for 0.000277778h;
|
25% 70% |
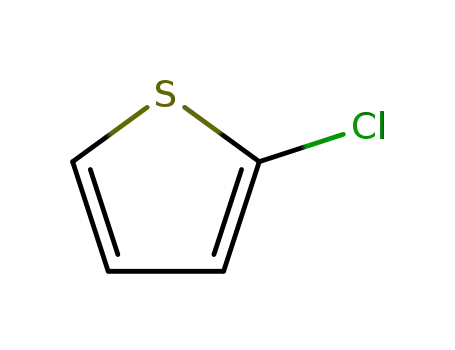
2-thienyl chloride


2,2':5',2''-terthiophene


2,2'-Bithiophene
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
[2,2]bipyridinyl; nickel diacetate; sodium tert-pentoxide;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 25 ℃;
for 0.00472222h;
|
24% 60% |
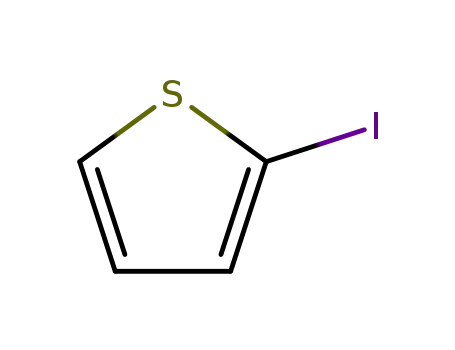
2-Iodothiophene
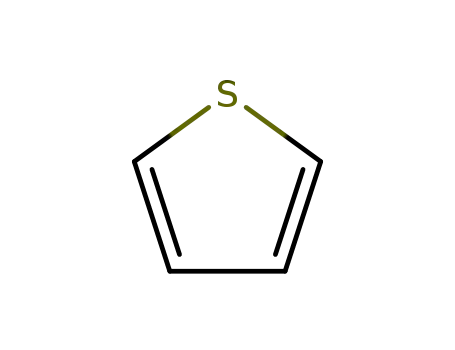
thiophene

2-thienyl chloride

2-bromothiophene
5,5'-dibromo-2,2':5'2''-terthiophene
tetracyanoethylene radical cation
methyl viologen cation radical
2,2':5',2''-terthiophene-5-carboxaldehyde
CAS:139100-06-4
CAS:333432-28-3
Molecular Formula:C15H15BO2
Molecular Weight:238.09
CAS:1693-86-3
CAS:149703-84-4