Your Location:Home >Products >OLED intermediates >Fluorenes >1347758-80-8
Product Details
The invention provides a compound shown as a general formula (I), which can be used for a hole transport material. The compound has a parent structure of difluorene substituted arylamine, is high in bond energy between atoms, has good thermal stability, is beneficial to intermolecular solid accumulation, is strong in hole transition capability, and can effectively reduce device voltage and prolongthe service life of the material when being used as a hole transport material. The invention further provides an organic light-emitting device and a display device containing the compound shown in the general formula (I).
The invention discloses a triarylamine derivative and an organic electroluminescent device thereof, and relates to the technical field of organic photoelectric materials. The technical problem to be solved by the invention is that the existing hole transport material is poor in film-forming property and poor in organic electroluminescent device performance. The triarylamine derivative disclosed bythe invention contains a special substituent group, namely spirobifluorenofluorene. The spirobifluorenofluorene substituent group in the triarylamine derivative represented by formula I has a high spatial three-dimensional effect, and has good electron blocking performance, hole mobility and stability. The organic electroluminescent device comprises an anode, a hole transport region and a cathode, the hole transport region is located between the anode and the cathode, the hole transport region comprises a hole transport layer, and the hole transport layer comprises the triarylamine derivative. The organic electroluminescent device provided by the invention has high light-emitting efficiency and long service life.
The present invention relates to an organic electroluminescent compound applied to a hole transfer material, which is characterized by being presented by chemical formula 1-1 and chemical formula 1-2. The organic electroluminescent compound according to the present invention can manufacture an organic electroluminescent device having improved light emitting efficiency and life properties, when applied to a hole transfer layer of the organic electroluminescent device.
An amine-based compound and an organic light-emitting diode including the same are provided.
![biphenyl-4-yl-(9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluoren-2-yl)-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-[1,3,2]dioxaborolan-2-yl)phenylamine](/upload/2023/2/01746a55-bd5b-4023-9ad6-ce945354b338.png)
biphenyl-4-yl-(9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluoren-2-yl)-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-[1,3,2]dioxaborolan-2-yl)phenylamine
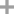
bis(pinacol)diborane

![(N-[1,1‘-biphenyl]-4-yl)-9,9-dimethyl-N-(4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane-2-yl)phenyl)-9H-fluorene-2-amine](/upload/2023/2/61a8a42c-8bd3-475c-9971-d2c85a201989.png)
(N-[1,1‘-biphenyl]-4-yl)-9,9-dimethyl-N-(4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane-2-yl)phenyl)-9H-fluorene-2-amine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
(1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium(II) dichloride; potassium acetate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 85 ℃;
for 12h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
90% |
|
With
palladium bis[bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene] dichloride; potassium acetate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 85 ℃;
for 12h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
84% |
|
With
(1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium(II) dichloride; potassium acetate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 85 ℃;
for 12h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
84% |
|
With
(1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium(II) dichloride; potassium acetate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
for 12h;
Inert atmosphere;
Reflux;
|
78% |
|
With
(1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium(II) dichloride; potassium acetate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
for 12h;
Inert atmosphere;
Reflux;
|
78% |
|
With
(1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium(II) dichloride; potassium acetate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
for 12h;
Inert atmosphere;
Reflux;
|
78% |
|
With
(1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium(II) dichloride; potassium acetate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
for 12h;
Reflux;
Inert atmosphere;
|
78% |
|
With
(1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium(II) dichloride; potassium acetate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 95 ℃;
for 24h;
|
71% |
|
With
(1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium(II) dichloride; potassium acetate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 95 ℃;
for 24h;
|
71% |
|
With
(1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium(II) dichloride; potassium acetate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 95 ℃;
for 24h;
|
71% |
|
With
(1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium(II) dichloride; potassium acetate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 95 ℃;
for 24h;
|
71% |
|
With
palladium bis[bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene] dichloride; potassium acetate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 20 - 80 ℃;
for 24.3333h;
|
70% |
|
With
dicyclohexyl-(2',6'-dimethoxybiphenyl-2-yl)-phosphane; potassium acetate; palladium diacetate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 105 ℃;
for 18h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
57% |
|
With
(1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium(II) dichloride; potassium acetate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 85 ℃;
for 12h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
40% |
|
With
(1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium(II) dichloride; potassium acetate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 100 ℃;
for 12h;
|

N?(biphenyl?4?yl)?9,9?dimethyl?9H?fluorene?2?amine

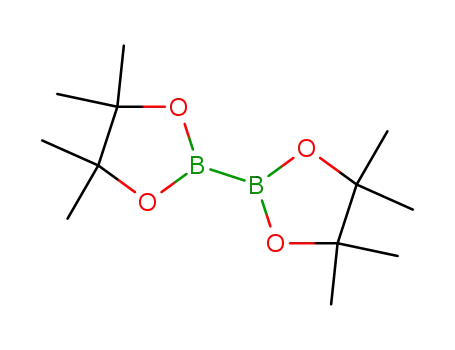
p-bromophenylboronic acid pinacol ester

![(N-[1,1‘-biphenyl]-4-yl)-9,9-dimethyl-N-(4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane-2-yl)phenyl)-9H-fluorene-2-amine](/upload/2023/2/61a8a42c-8bd3-475c-9971-d2c85a201989.png)
(N-[1,1‘-biphenyl]-4-yl)-9,9-dimethyl-N-(4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane-2-yl)phenyl)-9H-fluorene-2-amine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
tris-(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0); sodium t-butanolate; tri tert-butylphosphoniumtetrafluoroborate;
In
toluene;
at 100 ℃;
for 7h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
70% |

biphenyl-4-yl-(9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluoren-2-yl)-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-[1,3,2]dioxaborolan-2-yl)phenylamine

bis(pinacol)diborane

N?(biphenyl?4?yl)?9,9?dimethyl?9H?fluorene?2?amine
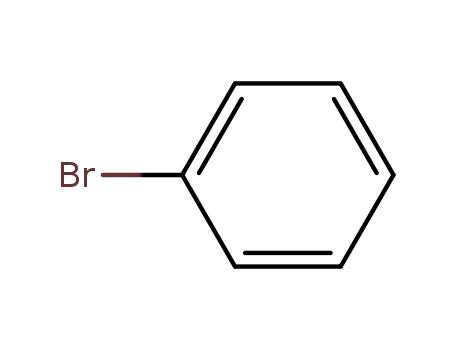
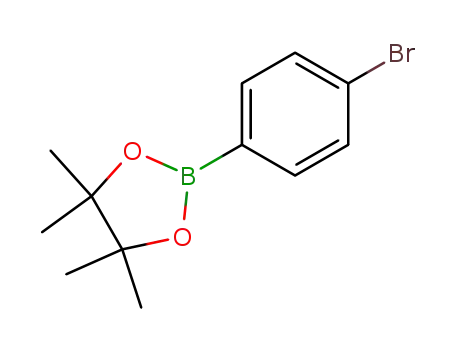
bromobenzene
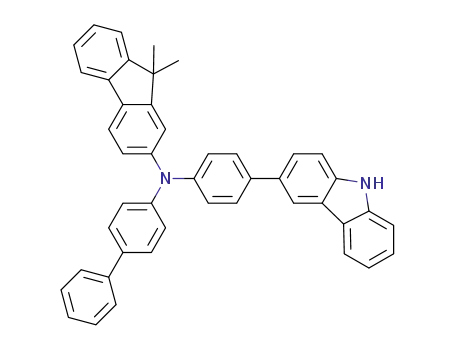
N-(4-(9H-carbazol-3-yl)phenyl)-N-([1,1‘-biphenyl]-4-yl)-9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluoren-2-amine
CAS:6002-34-2
CAS:19261-06-4
CAS:402936-15-6