Your Location:Home >Products >OLED intermediates >Thiophenes >97511-05-2

Product Details
Chemical Properties
Light yellow powder
The invention discloses an S,S-dioxo-dibenzothiophene and phenanthroimidazole based small molecule and application thereof in electroluminescent devices. Phenanthroimidazole is used as a donor unit, S,S-dioxo-dibenzothiophene is used as an acceptor unit, and a novel donor-acceptor type blue fluorescent molecule is constructed. The molecule has the characteristics of S,S-dioxo-dibenzothiophene suchas wide band gap, high fluorescence quantum yield, strong electron affinity, high electron mobility, and also has the characteristics of phenanthroimidazole such as large conjugate rigid structure, bipolar transmission, and the like. The molecule has an asymmetric structure, and can inhibit molecular aggregation and reduce exciton quenching. In addition, the emission spectrum can be adjusted by changing the connection sites of the two units. The small molecule can be used for preparing high-efficiency blue light organic electroluminescent devices with different emission wavelengths.
Provided are a compound represented by Formula 1, and an organic electric element comprising a first electrode, a second electrode, and an organic material layer formed between the first electrode and the second electrode, wherein the organic material layer comprised the compound represented by Formula 1, and the driving voltage of an organic electronic device can be lowered, and the luminous efficiency, color purity and life time of an organic electronic device can be improved by comprising the compound represented by Formula 1 in the organic material layer.
A novel deep-blue emitter PhImPOTD based on phenathroimidazole was synthesized, which is incorporated by an electron-donating dibenzothiophene unit and electron-withdrawing phenanthroimidazole and diphenylphosphine oxide moieties. Furthermore, the weak π–π stacking and intermolecular aggregation render the photoluminescence quantum yield is as high as 0.34 in the solid state. Non-doped organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs) based on PhImPOTD emitter exhibits a low turn-on voltage of 3.6?V, a favorable efficiency of 1.13?cd A?1 and a deep blue emission with Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage (CIE) coordinates of (0.15, 0.08). The CIE is very close to the NTSC (National Television Standards Committe) blue standard (CIE: 0.14, 0.08). PhImPOTD is also utilized as blue emitter and the host for a yellow emitter (PO-01) to fabricate white organic light-emitting diodes (WOLEDs). This gives a forward-viewing maximum CE of 4.83?cd A?1 and CIE coordinates of (0.32, 0.32) at the luminance of 1000?cd?m?2. Moreover, the single-carrier devices unambiguously demonstrate that typical bipolar-dominant characteristics of PhImPOTD. This work demonstrates not only that the phenanthroimidazole unit is an excellent building block to construct deep blue emission materials, but also the introduction of a diphenylphosphine oxide deprotonation substituent is an efficient tactic for harvesting deep-blue emitting devices.
Provided is a compound which is represented by chemical formula 1. Also, provided is an organic electrical device which comprises: a first electrode; a second electrode; and an organic material layer between the first electrode and the second electrode. The organic material layer includes the compound represented by chemical formula 1. When the compound represented by chemical formula 1 is contained in the organic material layer of the organic electrical device, driving voltage decreases, while luminous efficiency, color purity, and lifespan increase.COPYRIGHT KIPO 2017
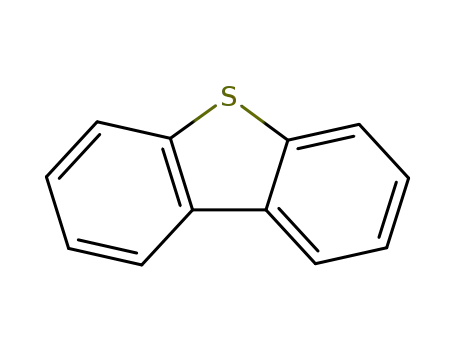
dibenzothiophene

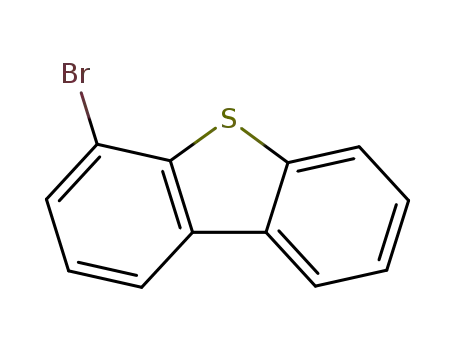
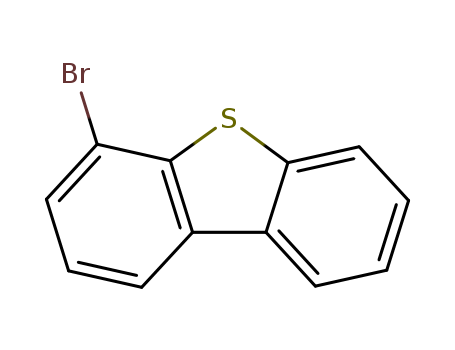
4-bromodibenzothiophene
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
dibenzothiophene;
With
n-butyllithium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at -40 - 0 ℃;
for 7h;
With
ethylene dibromide;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at -78 - 20 ℃;
for 12h;
|
95% |
|
dibenzothiophene;
With
n-butyllithium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at -40 - 0 ℃;
for 6h;
With
ethylene dibromide;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at -78 - 20 ℃;
for 14h;
|
71% |
|
dibenzothiophene;
With
n-butyllithium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at -78 - 0 ℃;
With
ethylene dibromide;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at -78 - 20 ℃;
for 12h;
|
60% |
|
dibenzothiophene;
With
n-butyllithium;
In
tetrahydrofuran; hexane;
at -30 - 20 ℃;
for 4h;
Inert atmosphere;
With
ethylene dibromide;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at -60 - 20 ℃;
for 16h;
|
48% |
|
With
n-butyllithium; diethyl ether;
Behandeln der Reaktionsloesung mit Brom-Dampf in Stickstoff-Strom;
|
|
|
With
n-butyllithium; bromocyane;
Yield given. Multistep reaction;
1.) THF, hexane, -78 deg C, then room temperature, 5 h, 2.) -78 deg C to room temperature, then 10-15 h;
|
|
|
With
n-butyllithium; ethylene dibromide;
Yield given. Multistep reaction;
1.) THF, hexane, 0 deg C, 6 h, 2.) THF, room temperature, 14 h;
|
|
|
dibenzothiophene;
With
n-butyllithium;
In
tetrahydrofuran; hexane;
at 20 ℃;
for 4h;
With
ethylene dibromide;
In
tetrahydrofuran; hexane;
at -60 - 20 ℃;
for 1h;
|
|
|
dibenzothiophene;
With
n-butyllithium;
In
tetrahydrofuran; hexane;
at -78 - 0 ℃;
for 6h;
Inert atmosphere;
With
ethylene dibromide;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 20 ℃;
for 10h;
|
|
|
dibenzothiophene;
With
n-butyllithium;
at -78 - 0 ℃;
With
ethylene dibromide;
at -78 - 20 ℃;
|
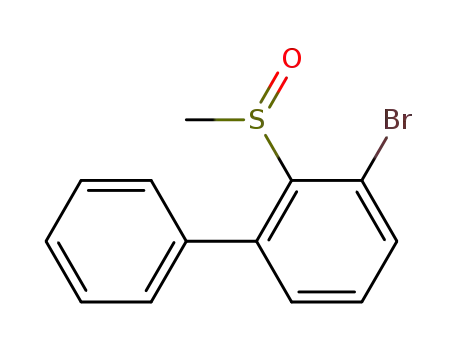
3-bromo-2-(methylsulfinyl)-1,1‘-biphenyl


4-bromodibenzothiophene
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
3-bromo-2-(methylsulfinyl)-1,1‘-biphenyl;
With
trifluoroacetic acid;
at 20 ℃;
for 24h;
With
pyridine;
In
water;
for 0.5h;
Reflux;
|
88% |
|
3-bromo-2-(methylsulfinyl)-1,1‘-biphenyl;
With
trifluorormethanesulfonic acid;
at 20 ℃;
for 24h;
With
pyridine;
In
water;
for 0.5h;
Reflux;
|
81% |
|
3-bromo-2-(methylsulfinyl)-1,1‘-biphenyl;
With
trifluorormethanesulfonic acid;
In
water;
at 20 ℃;
for 24h;
With
pyridine;
In
water;
for 0.5h;
Reflux;
|
81% |

dibenzothiophene
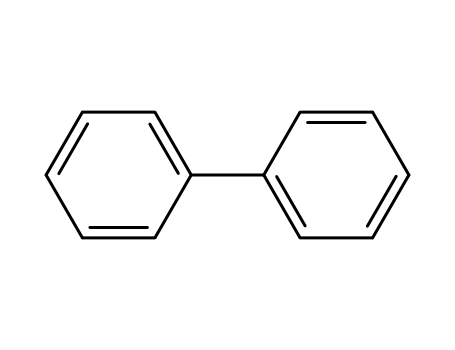
biphenyl
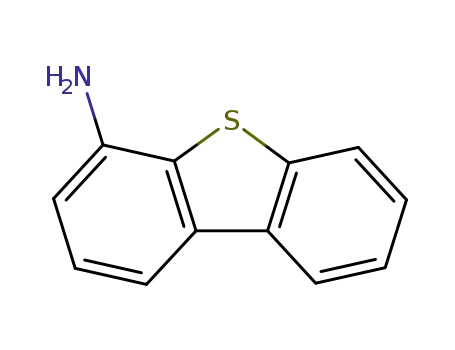
dibenzo[b,d]thiophene-4-amine
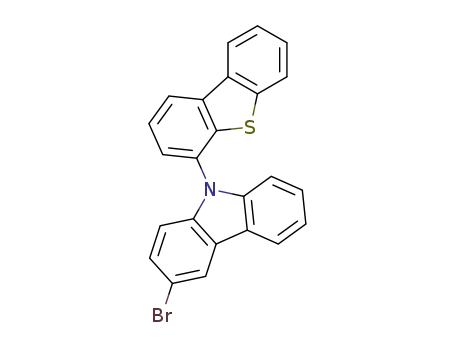
3-bromo-9-(dibenzo[b,d]thiophen-4-yl)-9H-carbazole

9-(dibenzo[b,d]thiophen-4-yl)-9?-phenyl-9H,9'H-3,3?-bicarbazole
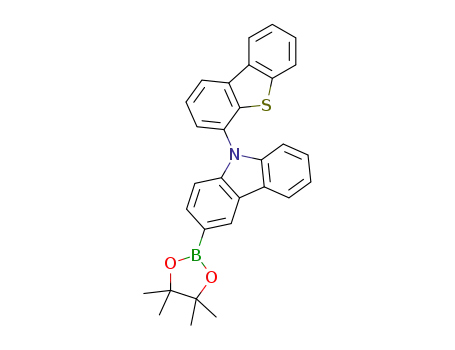
9-(dibenzo thiophen-4-yl)-3-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)-9H-carbazole
CAS:4731-53-7
CAS:10537-08-3
CAS:89827-45-2