Your Location:Home >Products >OLED intermediates >Fluorenes >20302-14-1

Product Details
InChI:InChI=1/C25H18/c1-3-11-19(12-4-1)25(20-13-5-2-6-14-20)23-17-9-7-15-21(23)22-16-8-10-18-24(22)25/h1-18H
A superacid-promoted method for the synthesis of 9,9-diarylfluorenes is described. The chemistry involves cyclizations and arylations with biphenyl-substituted heterocyclic ketones and a mechanism is proposed involving superelectrophilic intermediates. The key reactive intermediates-dicationic and trication fluorenyl cations have been observed by low-temperature NMR and the mechanism has been further studied using DFT calculations.
While 10,10-diphenyl-9-(10H)-phenanthrenone (1) is inert under conventional irradiation conditions, it undergoes decarbonylation under high-intensity argon laser-jet conditions to form 9,9-diphenylfluorene (3) and the cycloheptatriene 4.Molecular modeling studies indicate that 3 arises from collapse of the singlet carbene 15 and the triene 4 from the triplet carbene 35.
The present invention relates to a compound constituting a hole transport layer and an electron transport layer of an organic light emitting diode, or a method for manufacturing the same. According to the present invention, it is possible to provide a plurality of compounds having excellent yields and excellent purity constituting the hole transport layer and the electron transport layer. An object of the present invention is to provide the compound constituting the hole transport layer and the electron transport layer of the organic light emitting diode, or the method for manufacturing the same.(AA) HPLC analysis result of a final productCOPYRIGHT KIPO 2020
Treatment of dibenzothiophene dioxides with cyclic diarylmethanes in the presence of KN(SiMe3)2 results in the formation of fluorene-based spirocyclic tetraarylmethanes in a single operation. The transformation would proceed via an intermolecular SNAr reaction of the dioxides with cyclic diarylmethylpotassium followed by intramolecular SNAr cyclization. This straightforward strategy provides a wide range of spirocyclic diarylfluorenes including unusual ones that are otherwise difficult to synthesize.
In the presence of a catalytic system comprised of palladium(II) acetate and tricyclohexylphosphine, the reaction of fluorene with haloarenes generated 9-arylfluorenes in good to excellent yields. The scope and limitations of the coupling reaction were investigated. This synthetic protocol is more efficient than conventional methods. A wide range of functional groups, including alkyl, alkoxy, ester, and nitrile, can tolerate the reaction conditions herein. Sterically congested haloarenes also gave satisfactory results. Furthermore, this synthetic method is utilized to prepare 9,9-diarylfluorenes and tetraarylindenofluorene. Depending on the reaction conditions, the arylation of bowl-shaped sumanene gave monoarylated sumanene either as the sole product or with another diaryl-substituted product. Copyright
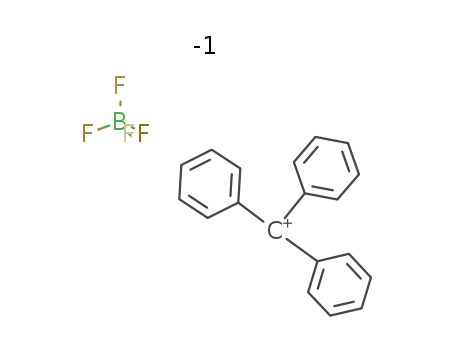
trityl tetrafluoroborate
benzene

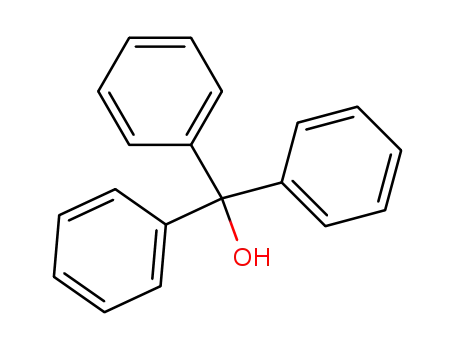
triphenylmethyl alcohol

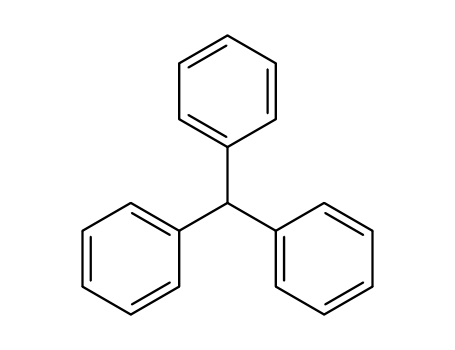
triphenylmethane

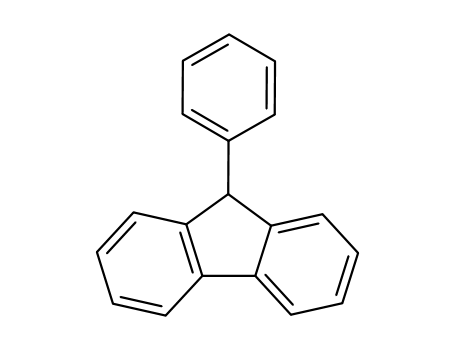
9-Phenylfluorene

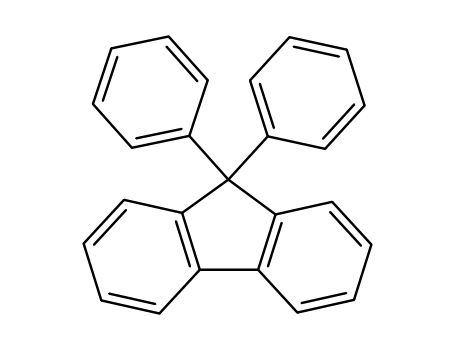
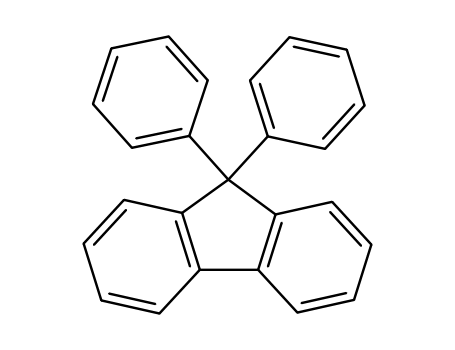
9,9-diphenylfluorene
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
at 80 ℃;
for 6h;
|
0.5% 1% 3% 52% |

trityl tetrafluoroborate


triphenylmethyl alcohol


triphenylmethane


9-Phenylfluorene


9,9-diphenylfluorene
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
Product distribution;
Mechanism;
effect of the amount of acid;
|
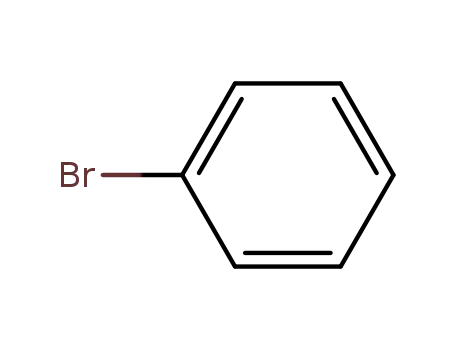
bromobenzene
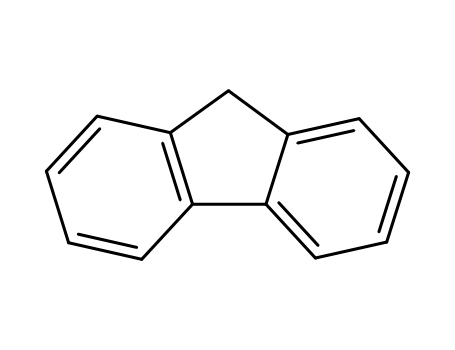
9H-fluorene
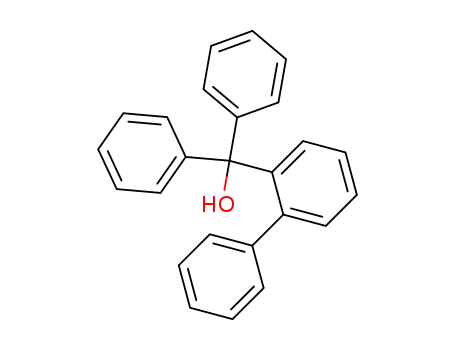
(biphenyl-2-yl)(diphenyl)methanol
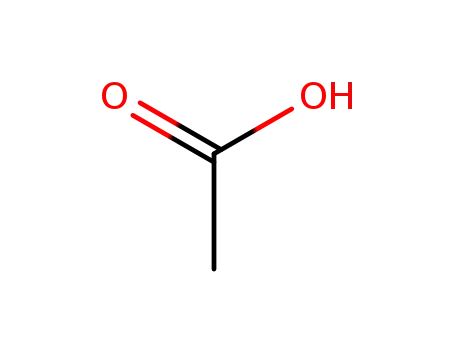
acetic acid
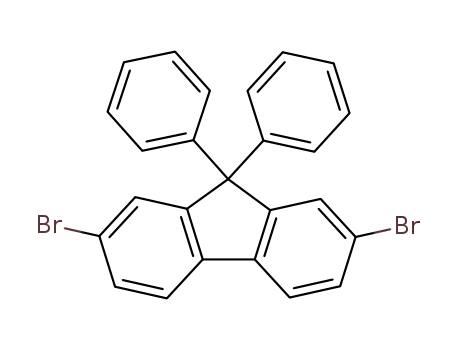
2,7-dibromo-9,9-diphenyl-9H-fluorene
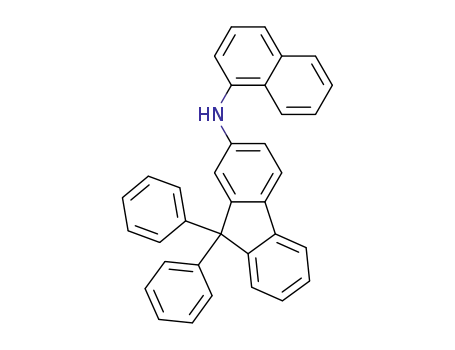
N-(naphthalen-1-yl)-9,9-diphenyl-9H-fluoren-2-amine
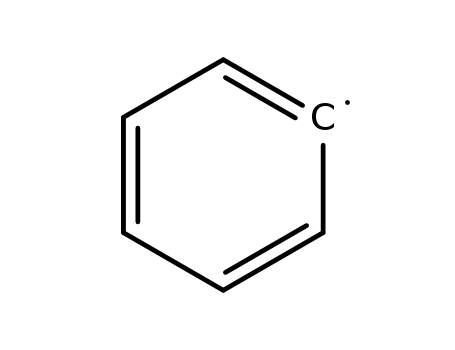
phenyl radical
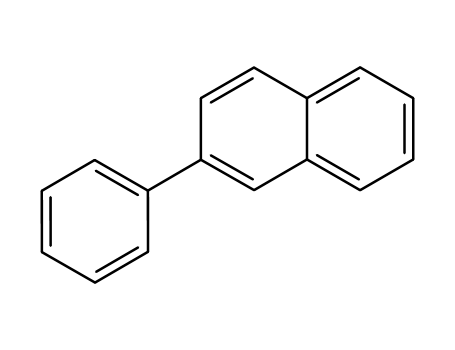
2-phenylnaphthalene
CAS:500717-23-7
Molecular Formula:C30H27N
Molecular Weight:401.5
CAS:1189047-28-6
CAS:189367-54-2