Your Location:Home >Products >Organic phosphines >Phenyl phosphines >240417-00-9
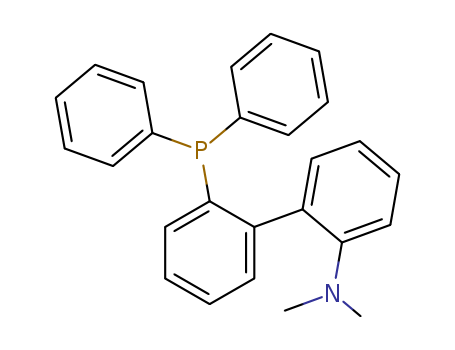

Product Details
Reaction
Useful ligand for sterically hindered substrates in the Pd-catalyzed amination reactions of aryl bromides. Ligand used for the Cu-catalyzed phosphorylation of alcohols. Ligand for Pd-catalyzed C-H benzylation. Ligand for palladium-catalyzed [4 + 2] benzannulation reaction.
Chemical Properties
white to yellow powder, crystals, crystalline
Uses
suzuki reaction
Readily available air- and moisture-stable dimeric chloro-bridged CN-, CS- and CP-cyclopalladated complexes with the (sp2)C-Pd bond react with 4.5 equiv. of KPPh2 in THF to give the corresponding P,N-, P,S- and P,P-bidentate ligands
(Chemical Equation Presented) The reduction of tertiary phosphine oxides (TPOs) and sulfides with diisobutylaluminum hydride (DIBAL-II) has been studied in detail. An extensive solvent screen has revealed that hindered aliphatic ethers, such as MTBE, are optimum for this reaction at ambient temperature. Many TPOs undergo considerable reduction at ambient temperature and then stall due to inhibition. 31P and 13C NMR studies using isotopically labeled substrates as well as competition studies have revealed that the source of this inhibition is tetraisobutyldialuminoxane (TIBAO), which builds up as the reaction proceeds. TIBAO selectively coordinates the TPO starting material, preventing further reduction. Several strategies have been found to circumvent this inhibition and obtain full conversion with this extremely inexpensive reducing agent for the first time. Practical reduction protocols for these critical targets have been developed.
Monodentate, biphenyl-type phosphines have emerged as a powerful class of ligands in homogeneous catalysis. Synthetic methods for these ligands are limited, however. We report that the palladium-catalysed Suzuki coupling of OPR2(o-C6H4X) (R=Ph, t-Bu; X=Br, I) with arylboronic acids affords a variety of biaryl phosphine oxides including those that contain heterocycles. The corresponding phosphines are readily obtained by treatment with HSiCl3. The methodology provides an easy entry to monodentate biaryl and heterobiaryl Poverlapping logical AND signX (X=N, O, S) phosphines with diverse steric and electronic properties.
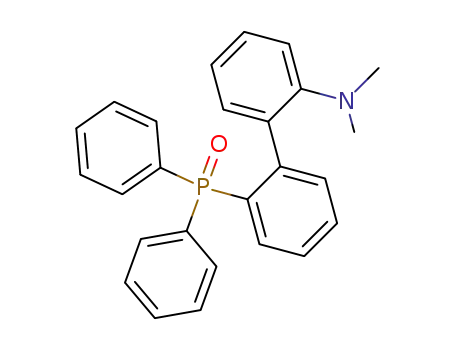
(2'-(dimethylamino)biphenyl-2-yl)diphenylphosphine oxide


2′-(diphenylphosphino)-N,N′-dimethyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-2-amine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
diisobutylaluminium hydride;
In
various solvent(s);
at 125 ℃;
for 15h;
|
98% |
|
With
trichlorosilane; triethylamine;
In
toluene;
at 120 ℃;
|
72% |
![di-μ-chlorobis-[2′-(2-N,N-dimethylamino)biphenyl-C,N]dipalladium(II)](/upload/2023/2/856486db-4ee5-441d-a3ad-44b87a0029f8.png)
di-μ-chlorobis-[2′-(2-N,N-dimethylamino)biphenyl-C,N]dipalladium(II)
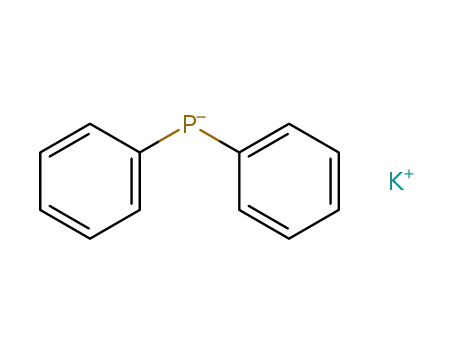
potassium diphenylphosphine


2′-(diphenylphosphino)-N,N′-dimethyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-2-amine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 20 ℃;
for 18h;
Inert atmosphere;
Schlenk technique;
|
47% |

(2'-(dimethylamino)biphenyl-2-yl)diphenylphosphine oxide
1-Bromo-2-iodobenzene
(2-bromophenyl)diphenylphosphine oxide
Diphenylphosphine oxide
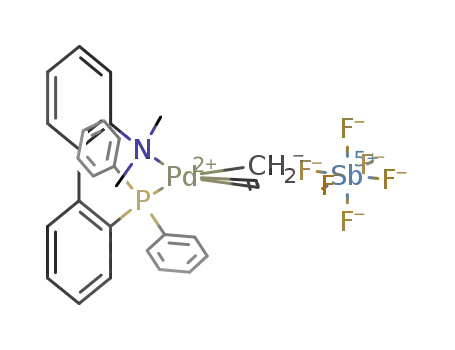
[(η3-allyl)Pd(2-(diphenylphosphino)-2'-(dimethylamino)biphenyl)]SbF6
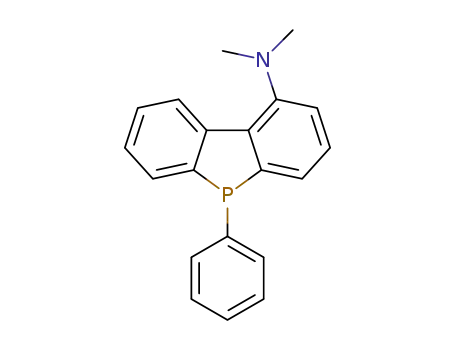
1-N,N-dimethylamino-5-phenyl-5H-dibenzophosphole
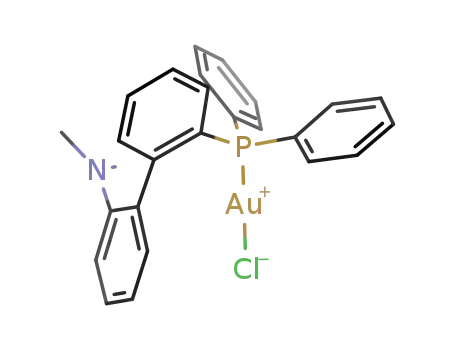
2'-(diphenylphosphinyl)-N,N-dimethylbiphenyl-2-aminegold(I) chloride
CAS:610-09-3
Molecular Formula:C<sub>8</sub>H<sub>12</sub>O<sub>4</sub>
Molecular Weight:172.18
CAS:5525-40-6
CAS:1038-95-5