Your Location:Home >Products >Organic phosphines >Phenyl phosphines >69227-47-0
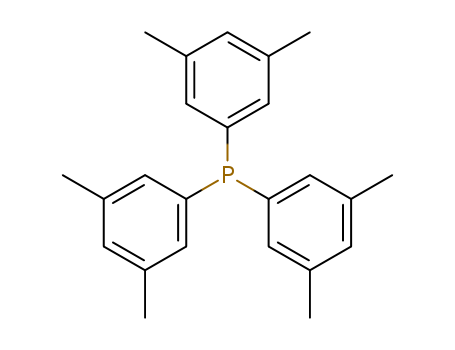

Product Details
Chemical Properties
white to light yellow crystal powde
Uses
Catalyst for:Cu / diphosphine-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation of heteroaromatic ketones and enonesHighly selective rhodium-catalyzed hydrogenation reactionsClassical versus kinetic resolution in preparation of privileged silicon-stereogenic silanaphthalenesUsed for kinetic resolution of donor-functionalized secondary alcohols via Cu-H-catalyzed stereoselective silylation by dehydrogenative Si-O coupling with Si-stereogenic silanesUsed for comparative studies of conformational rigidity of silicon-stereogenic silanes in asymmetric catalysis
InChI:InChI=1/C24H27P/c1-16-7-17(2)11-22(10-16)25(23-12-18(3)8-19(4)13-23)24-14-20(5)9-21(6)15-24/h7-15H,1-6H3
The metal-free reduction of phosphane oxides with molecular hydrogen (H2) using oxalyl chloride as activating agent was achieved. Quantum-mechanical investigations support the heterolytic splitting of H2 by the in situ formed electrophilic phosphonium cation (EPC) and phosphane oxide and subsequent barrierless conversion to the phosphane and HCl. The reaction can also be catalyzed by the frustrated Lewis pair (FLP) consisting of B(2,6-F2C6H3)3 and 2,6-lutidine or phosphane oxide as Lewis base. This novel reduction was demonstrated for triaryl and diaryl phosphane oxides providing access to phosphanes in good to excellent yields (51–93 %).
Chiral diphosphine ligands analogous to bdpp have been synthesized and tested in order to study the effect of the electronic nature of the ligands in Rh-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation of some prochiral olefins. The results are compared with those obtained with the analogous unsubstituted ligand (bdpp). The rhodium-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation of olefins was influenced by ligand-based electronic effects, as well as substrate based ones. Excellent ee's (up to 98.3%) have been obtained in the rhodium-catalyzed hydrogenation of (Z)-α-acetamidocinnamic acids and esters.
A concise synthesis of a symmetrical biaryl diphosphine ligand bearing 3,5-dimethylphenyl substituents at phosphorus is described. The ruthenium catalysts [diphosphine RuCl2 diamine] containing the new ligand Xyl-TetraPHEMP were found to be as active and as selective as the state-of-the-art catalysts for homogeneous asymmetric ketone hydrogenation.
A large number of triarylphosphines exhibiting different steric hindrance has been prepared.The pyramidalization angle α of these compounds was calculated with use of the MM2 force field and was shown to depend almost exclusively on the number of ortho substituents on the phenyl rings.In a series of isosteric (same α) phosphines, the oxidation potential correlates with the sum of the ?+ Hammett parameters of the phenyl substituents.In the absence of oxygen, anodic oxidation of all the triarylphosphines bearing two o-methyl substituents on each phenyl ring is reversible and yields very persistent phosphoniumyl radicals.These radicals are easly detected by ESR in liquid solution and were shown to retain a pyramidal geometry that is significantly flattened compared to that of the parent phosphine.
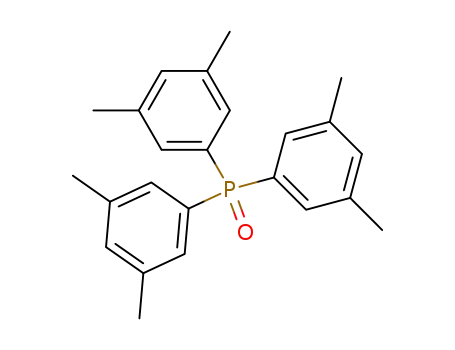
tris(3,5-dimethylphenyl)phosphine oxide

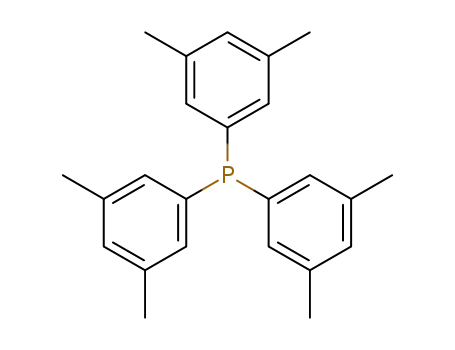
tris(3,5-dimethylphenyl)phosphine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
2,6-dimethylpyridine; oxalyl dichloride; hydrogen; tris(2,6-difluorophenyl)borane triethylphosphine oxide;
In
(2)H8-toluene;
at 130 ℃;
for 2h;
under 3000.3 Torr;
Reagent/catalyst;
|
56% |
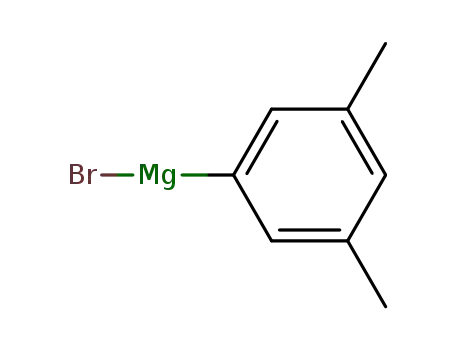
3,5-dimethyphenylmagnesium bromide


tris(3,5-dimethylphenyl)phosphine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
phosphorus trichloride;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
0 deg C then reflux, 2 h;
|
52% |
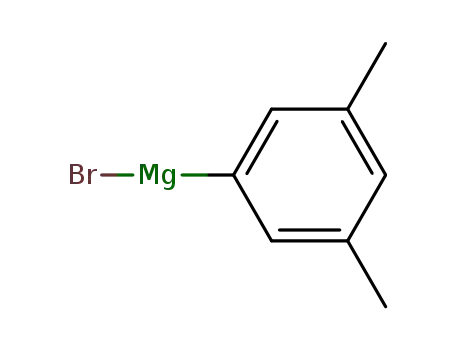
3,5-dimethyphenylmagnesium bromide

5-bromo-1,3-xylene

tris(3,5-dimethylphenyl)phosphine oxide
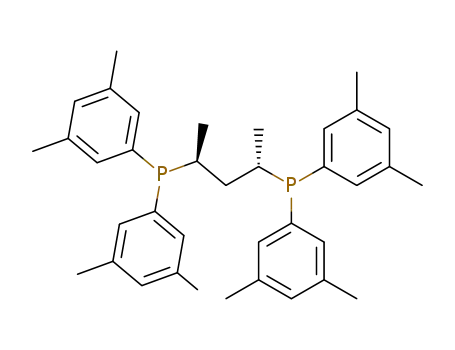
(2S,4S)-2,4-bis[di(3,5-dimethylphenyl)phosphino]pentane
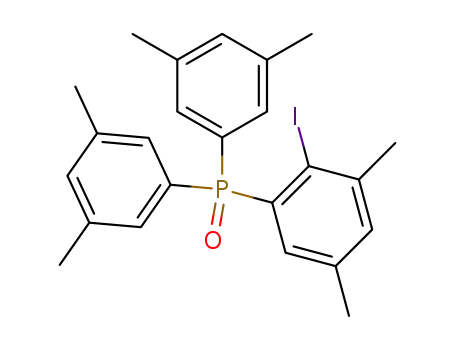
1-[Bis-(3,5-dimethyl-phenyl)-phosphinoyl]-2-iodo-3,5-dimethyl-benzene
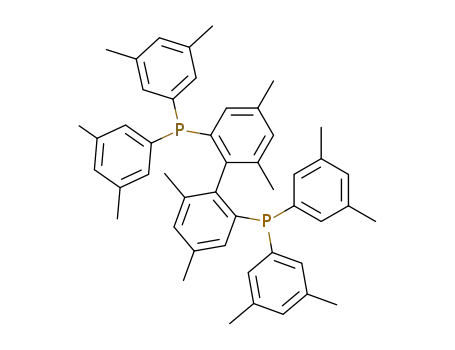
rac-4,4',6,6'-tetramethyl-2,2'-bis[bis(3,5-dimethylphenyl)phosphino]biphenyl
rac-4,4',6,6'-tetramethyl-2,2'-bis[bis(3,5-dimethylphenyl)phosphinoyl]biphenyl
CAS:400607-31-0
CAS:2622-14-2
CAS:5525-40-6