Your Location:Home >Products >Organic phosphines >Phenyl phosphines >19845-69-3
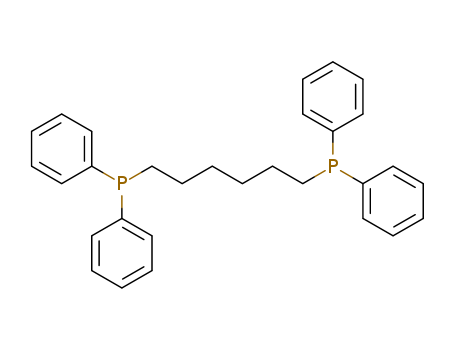

Product Details
Uses
suzuki reaction
InChI:InChI=1/C30H32P2/c1(15-25-31(27-17-7-3-8-18-27)28-19-9-4-10-20-28)2-16-26-32(29-21-11-5-12-22-29)30-23-13-6-14-24-30/h3-14,17-24H,1-2,15-16,25-26H2
A mild and efficient method for the synthesis of ditertiary phosphines has been developed. In the presence of cesium hydroxide, molecular sieves, and DMF, various dihalides were coupled with diphenylphosphine at room temperature, and the results have demonstrated that this methodology offers a general synthetic procedure producing a variety of ditertiary phosphines in high yields.
A mild and efficient method for the synthesis of tertiary phosphines and ditertiary phosphines has been developed. In the presence of cesium hydroxide, molecular sieves and DMF at room temperature, various secondary phosphines and alkyl bromides were examined, and the results have demonstrated that this methodology offers a general synthetic procedure to produce tertiary phosphines in moderate to high yields. Optically active tertiary phosphine synthesis is also described.
When oganohalosilanes are prepared by charging a reactor with a contact mass containing a metallic silicon powder and a copper catalyst, and introducing an organohalide-containing gas into the reactor to effect the direct reaction, a poly(organo)phosphino compound is added to the contact mass. The invention is successful in producing organohalosilanes at a significantly improved production rate without reducing the selectivity of useful silane.
A matrix ESR study on radiogenic radical cations of Ph2P-R-PPh2 derivatives with various linkers (R) is presented.The experiments show that in a frozen dichloromethane solution the radical cations can adopt localized (Ph2PR*+), cyclic , and dimeric (Ph2RP*-PRPh2+) configurations, depending on the nature of the linker.The cyclic and dimeric products are formed in the reaction of a localized cation with a second free-electron pair, resulting in an intra- or intermolecular three-electron P-P ?* bond, respectively.The formation of the cyclic structure, with a strongly bent P-P ?* bond, requires a specific proximate position of the two phosphine moieties in the precursor molecule.The mutual orientation of the two free-electron pairs of the precursors is assessed by NMR via the nJPP spin-spin coupling constant.Ab initio UHF quantum chemical calculations at the 3-21G*/SCF level support the assignments.
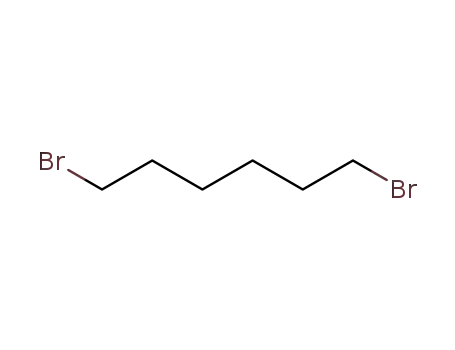
1 ,6-dibromohexane
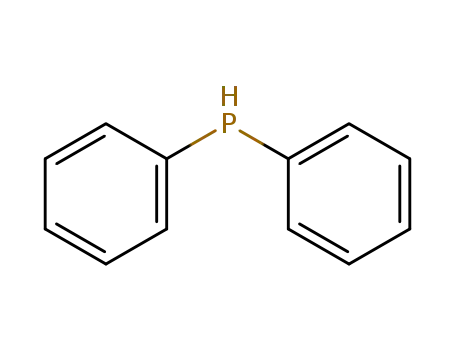
diphenylphosphane

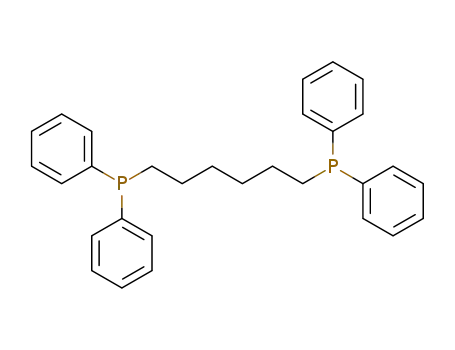
1,6-bis(diphenylphosphino)hexane
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
cesium hydroxide; 4 Angstroem MS;
In
N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
at 23 ℃;
for 72h;
|
69% |
|
With
cesium hydroxide; 4 A molecular sieve;
In
N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
at 23 ℃;
for 72h;
|
69% |

1,6-bis(diphenylphosphino)hexane

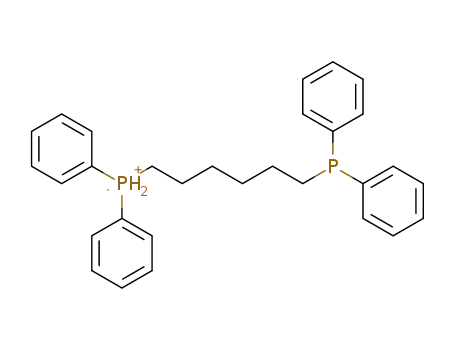
1,6-bis(diphenylphosphino)hexane radical cation
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In
dichloromethane;
at -196.1 ℃;
for 4h;
Irradiation;
|

1 ,6-dibromohexane

diphenylphosphane
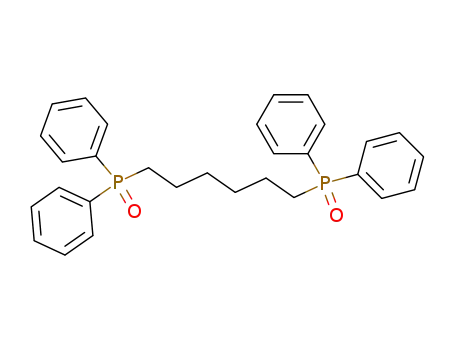
Tetra-P-phenyl-P,P'-hexanediyl-bis-phosphine oxide

C40H50P2(2+)*2Cl(1-)
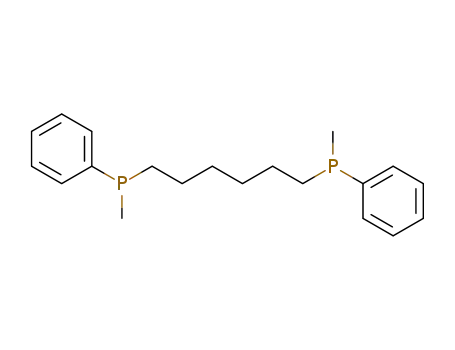
Hexamethylen-bis-
((C2H5O)2PSN(C6H5)2P)2(CH2)6
CAS:787618-22-8
CAS:19999-87-2
CAS:27721-02-4
CAS:12150-46-8