Your Location:Home >Products >Organic phosphines >Phenyl phosphines >6224-63-1

Product Details
Chemical Properties
white to light yellow crystal powde
Uses
suzuki reaction
Uses
Tri-m-tolylphosphine acts as a reagent for the preparation, crystal structure, multinuclear NMR, antitumor activity, photolysis of silver methylxanthate complexes against human adrenocarcinoma breast cancer cells.
InChI:InChI=1/C21H21P/c1-16-7-4-10-19(13-16)22(20-11-5-8-17(2)14-20)21-12-6-9-18(3)15-21/h4-15H,1-3H3
Chlorobenzenes are important starting materials for the preparation of commercially valuable triarylphosphines and tetraarylphosphonium salts, but their use for the direct arylation of elemental phosphorus has been elusive. Here we describe a simple photochemical route toward such products. UV-LED irradiation (365 nm) of chlorobenzenes, white phosphorus (P4) and the organic superphotoreductant tetrakis(dimethylamino)ethylene (TDAE) affords the desired arylphosphorus compounds in a single reaction step.
The invention aims to provide an aryl phosphine oxide compound as a raw material, wherein P=O keys are activated by an acid anhydride and alkali is continued. The preparation of the phosphine (III) compound is carried out under the action of a crown ether and a reducing agent. The method has the advantages of cheap and easily available raw materials, simple operation, high atomic economy and the like. Compared with a traditional reduction mode, the method is ingenious in design, waste emission is reduced, separation of intermediate products is omitted, and related reagents such as silicon hydrogen, aluminum, boron and the like with higher price can be avoided. And the reaction suitability is extensive.
The kinetics of quinuclidine displacement of BH3 from a wide range of Lewis base borane adducts have been measured. Parameterization of these rates has enabled the development of a nucleofugality scale (NFB), shown to quantify and predict the leaving group ability of a range of other Lewis bases. Additivity observed across a number of series R′3-nRnX (X = P, N; R′ = aryl, alkyl) has allowed the formulation of related substituent parameters (nfPB, nfAB), providing a means of calculating NFB values for a range of Lewis bases that extends far beyond those experimentally derived. The utility of the nucleofugality parameter is explored by the correlation of the substituent parameter nfPB with the hydrolyses rates of a series of alkyl and aryl MIDA boronates under neutral conditions. This has allowed the identification of MIDA boronates with heteroatoms proximal to the reacting center, showing unusual kinetic lability or stability to hydrolysis.
Detailed 31P{1H} NMR spectroscopic investigations provide deeper insight into the complex, multi-step mechanisms involved in the recently reported photocatalytic arylation of white phosphorus (P4). Specifically, these studies have identified a number of previously unrecognized side products, which arise from an unexpected non-innocent behavior of the commonly employed terminal reductant Et3N. The different rate of formation of these products explains discrepancies in the performance of the two most effective catalysts, [Ir(dtbbpy)(ppy)2][PF6] (dtbbpy=4,4′-di-tert-butyl-2,2′-bipyridine) and 3DPAFIPN. Inspired by the observation of PH3 as a minor intermediate, we have developed the first catalytic procedure for the arylation of this key industrial compound. Similar to P4 arylation, this method affords valuable triarylphosphines or tetraarylphosphonium salts depending on the steric profile of the aryl substituents.
tri(m-tolyl)phosphine oxide

tri(m-tolyl)phosphine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
oxalyl dichloride; hydrogen;
In
chloroform-d1;
at 130 ℃;
for 18h;
under 60006 Torr;
Reagent/catalyst;
|
93% |
|
With
chloro-trimethyl-silane; tetrabutylammomium bromide; copper; zinc;
In
acetonitrile;
at 45 ℃;
Electrochemical reaction;
Inert atmosphere;
|
92% |
|
With
chloro-trimethyl-silane; magnesium;
at 20 ℃;
for 6h;
|
84% |
|
tri(m-tolyl)phosphine oxide;
With
trifluoroacetic anhydride;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 20 ℃;
for 0.5h;
Inert atmosphere;
With
15-crown-5; sodium hydride; sodium hydrogencarbonate;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 150 ℃;
for 24h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
80% |
|
Multi-step reaction with 2 steps
1.1: oxalyl dichloride; tetrabutylammonium trifluoromethylsulfonate / acetonitrile / 0.17 h / 20 °C / Inert atmosphere
2.1: tetrabutylammonium trifluoromethylsulfonate / acetonitrile / 8 h / 20 °C / Electrochemical reaction; Undivided electrochemical cell with aluminum anode/platinum cathode; Inert atmosphere
2.2: Inert atmosphere
With
oxalyl dichloride; tetrabutylammonium trifluoromethylsulfonate;
In
acetonitrile;
|
m-tolylmagnesium bromide


tri(m-tolyl)phosphine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
phosphorus trichloride;
In
diethyl ether;
|
75% |
|
With
diethyl ether; hydrogen; phosphorus trichloride;
|
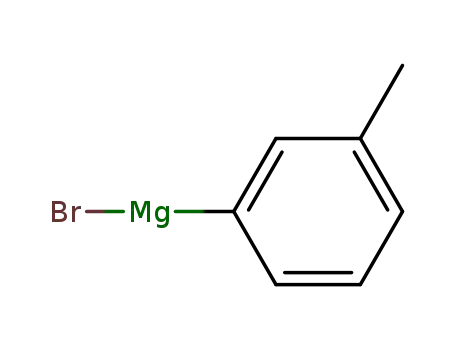
m-tolylmagnesium bromide
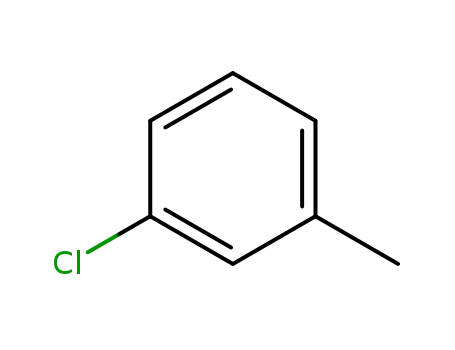
1-chloro-3-methylbenzene
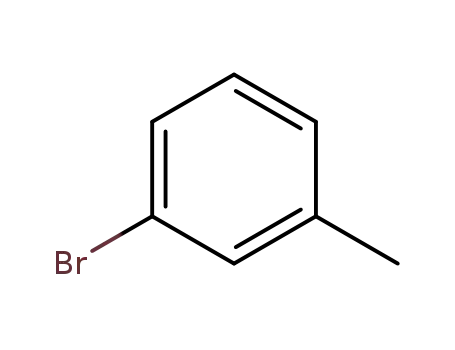
meta-bromotoluene
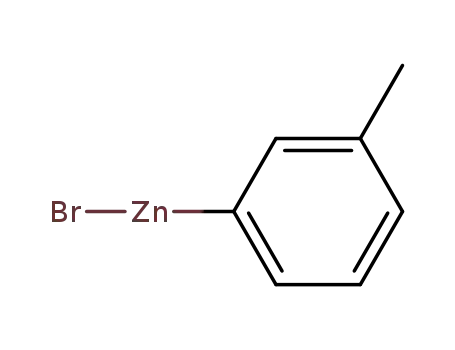
m-tolylzinc(II) bromide

tri(m-tolyl)phosphine oxide
4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2,2,2-tri-m-tolyl-2λ5-[1,3,2]dioxaphospholane

tri(3-methylphenyl)phosphine sulfide
diphenyldisulfane
CAS:18794-77-9
CAS:855-38-9