Your Location:Home >Products >Organic phosphines >CyclohexyI phosphines >787618-22-8
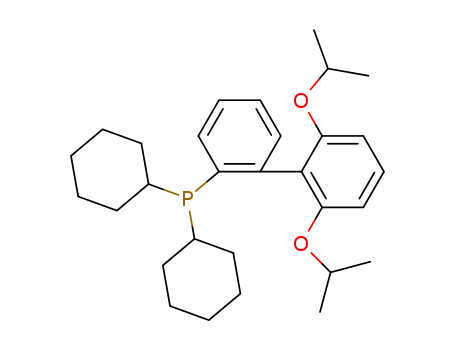

Product Details
Reaction
Versatile Ligand for the Pd-catalyzed coupling of secondary arylamines and alkylamines. Ligand used for the Pd-catalyzed Negishi cross-coupling reaction of (hetero)arylchlorides. Synthesis of ladder-type π-conjugated heteroacenes via palladium-catalyzed double N-arylation and intramolecular O-arylation. A palladium-catalyzed regiospecific synthesis of N-aryl benzimidazoles, Versatile ligand used for the Pd-catalyzed C-N coupling reaction of secondary aryl- and alkyl-amines at low temperature with the Pd precatalyst. Ligand used for the Pd-catalyzed Suzuki-Miyaura coupling of aryl chloride and NHC-boranes. Ligand for the palladium-catalyzed trifluoromethylation of hindered aryl chlorides. Ligand used for the palladium-catalyzed coupling of alkyl boronates.
Uses
suzuki reaction
Uses
2-Dicyclohexylphosphino-2',6'-diisopropoxybiphenyl is the ligand used for the palladium-catalyzed coupling of alkyl boronates.
Uses
Bulky phosphine ligand used in a palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling of aminoethyltrifluoroborate?s with electron-poor aryl bromides.
The Pd-catalyzed α-arylation of cycloheptapyridyl ketone is a key complexity-building step in the synthesis of BMS-846372, a CGRP antagonist. A first-generation process utilized Pd(OAc)2/PtBu 3·HBF4 catalyst system with a strong base NaO tBu. Although this process was demonstrated on multi-kilo scale, the harsh conditions led to non-selective metal catalyzed processes, which generated several operational, quality, and throughput issues. By acquiring detailed knowledge around several important process parameters, we were able to design an efficient and scalable second-generation α-arylation process using a Pd(OAc)2/RuPhos catalyst system with the weaker base, K 3PO4 in tert-amyl alcohol. This new weak base process was high yielding, efficient, and superior in several respects compared to the strong base process. The strategy behind the reaction and isolation development and the process considerations important to scaling a catalytic reaction from laboratory to manufacturing scale will be discussed.
A new catalyst system for the Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling of organozinc reagents with aryl halides (Negishi coupling) has been developed. This system permits efficient preparation of hindered biaryls (triand tetra-ortho- substituted), functions effectively at low levels of catalyst, and tolerates a wide range of functional groups and heterocyclic substrates. A systematic study of ligand structure was performed and was correlated with catalyst activity.
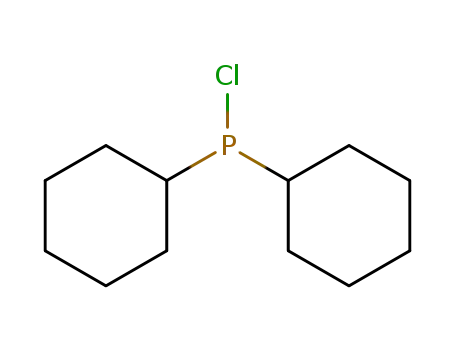
chlorodicyclohexylphosphane
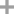
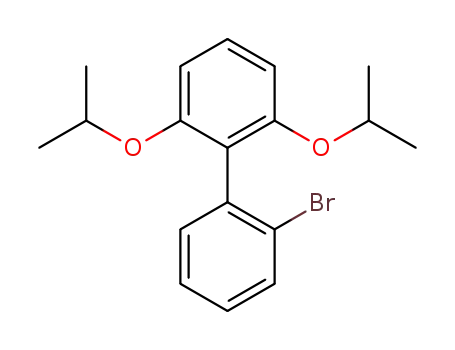
2-(2-bromophenyl)-1,3-diisopropyloxybenzene

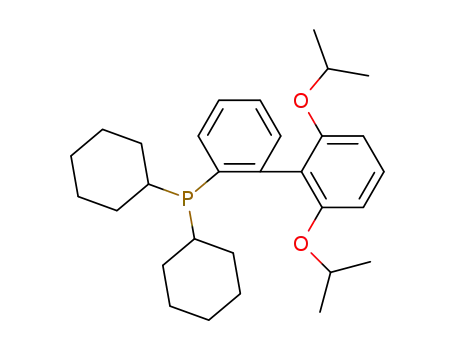
ruphos
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
2-(2-bromophenyl)-1,3-diisopropyloxybenzene;
With
n-butyllithium;
In
tetrahydrofuran; hexane;
at -78 ℃;
for 1h;
chlorodicyclohexylphosphane;
In
tetrahydrofuran; hexane;
at -78 - 20 ℃;
|
2.24% |
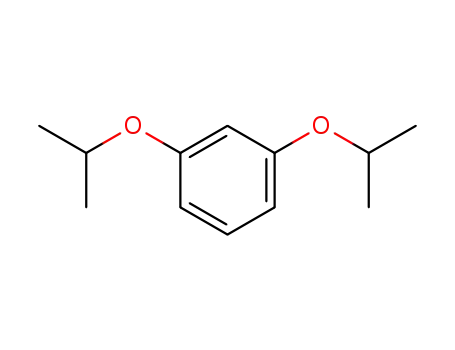
1,3-diisopropoxybenzene


ruphos
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
Multi-step reaction with 2 steps
1.1: n-BuLi / hexane / 2.5 h / Heating
1.2: hexane / 1.83 h / Heating
2.1: n-BuLi / tetrahydrofuran; hexane / 1 h / -78 °C
2.2: 2.24 percent / tetrahydrofuran; hexane / -78 - 20 °C
With
n-butyllithium;
In
tetrahydrofuran; hexane;
|

chlorodicyclohexylphosphane

2-(2-bromophenyl)-1,3-diisopropyloxybenzene

1,3-diisopropoxybenzene
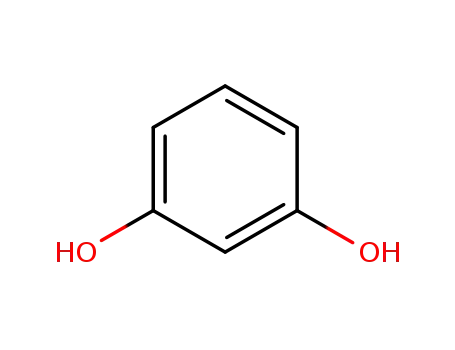
recorcinol
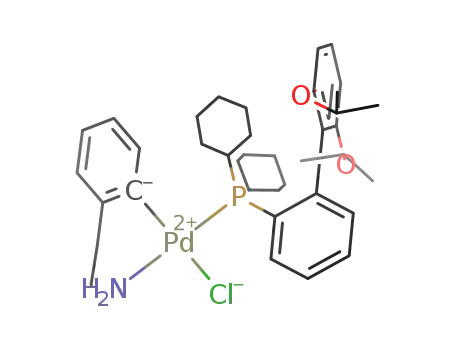
chloro(2-dicyclohexylphosphino-2′,6′-di-i-propoxy-1,1′-biphenyl)(2′-amino-1,1′-biphenyl-2-yl)-palladium(II)
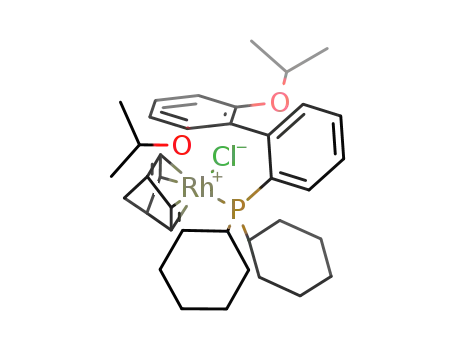
(η4-nornornadiene)Rh(2-(dicyclohexylphosphino)-2',6'-diisopropoxy-1,1'-biphenyl)Cl
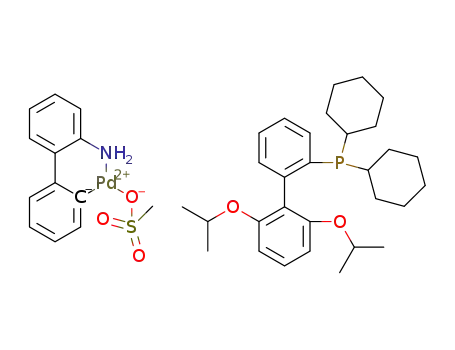
C30H43O2P*C13H13NO3PdS
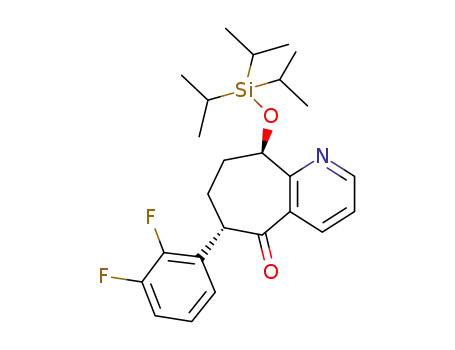
(6S,9R)-6-(2,3-difluorophenyl)-9-((triisopropylsilyl)oxy)-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5Hcyclohepta[b]pyridin-5-one
CAS:104934-52-3
CAS:1002345-50-7
Molecular Formula:C27H52B2F8P2
Molecular Weight:612.3