Your Location:Home >Products >Acid Anhydrides >85-42-7
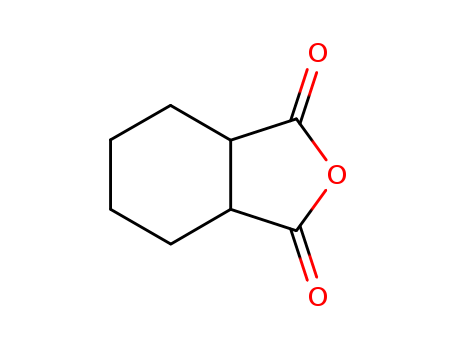

Product Details
|
Application |
Predominantly cis 1,2-cyclohexanedicarboxylic anhydride (HHPA) is a cyclic anhydride that can be used for a variety of applications such as: plasticizer, rust inhibitor, and a curing agent for epoxy based resins.HPPA, in combination with triethaylamine (TEA), can be used as a polymerization initiator in the preparation of polyester based resins. It can also be used as a hardener to cure 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether which can be used as an epoxy based system for electronic devices. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A cyclic dicarboxylic anhydride that is the cyclic anhydride of hexahydrophthalic acid. |
|
General Description |
Predominantly cis 1,2-cyclohexanedicarboxylic anhydride (HHPA) is a cyclic anhydride that can be used for a variety of applications such as: plasticizer, rust inhibitor, and a curing agent for epoxy based resins. |
|
Hazard |
Toxic by inhalation, strong irritant to eyes and skin. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Nonflammable |
|
Synthesis |
Hexahydrophthalic anhydride is obtained by reacting ciscyclohexane-1, 2-dicarboxylic acid with oxalyl chloride.Combine ciscyclohexane-1, 2-dicarboxylic acid (1 mmol, 172 mg) and oxalyl chloride (1.2 mmol, 152 mg, 0.103 ml) in dry toluene (5 mL) and add a drop of freshly distilled DMF. Purge the reaction vessel with argon and heat the reaction under stirring for 3 h. Stop the stirring, decant the toluene solution and filter. Evaporate the volatiles. Transform into crystalline form by trituration with diethyl ether. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 3.18 - 3.12 (m, 2H 2CH) 1.96 - 1.83 (m, 4H 2CH2) 1.57 - 1.49 (m, 4H 2CH2). HRMS (ESI), calcd for C8H10NaO3 [M+Na]+ 175.0522, found 175.0527; calcd for C9H14NaO4 [M+CH3 OH+Na]+ 209.0784, found 209.0788.Fig The synthetic method of Hexahydrophthalic anhydride. |
InChI:InChI=1/C8H10O3/c9-7-5-3-1-2-4-6(5)8(10)11-7/h5-6H,1-4H2/t5-,6+
The invention provides a synthesis metho...
The invention discloses a class of new p...
Hydrogenation of aromatic dicarboxylic a...
The active conformation of a family of m...
benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid

2-methyl-1-cyclohexanecarboxylic acid

cyclohexane-1,2-dicarboxylic acid

1,2-Cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid-anhydride
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With 5% active carbon-supported ruthenium; hydrogen; In 1,4-dioxane; at 179.84 ℃; for 12h; under 51680.2 Torr;
|
benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid

phthalic anhydride

2-methyl-1-cyclohexanecarboxylic acid

1,2-Cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid-anhydride
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With 5%-palladium/activated carbon; hydrogen; In 1,4-dioxane; at 219.84 ℃; for 12h; under 51680.2 Torr;
|
3,4,5,6-Tetrahydrophthalic anhydride
(1R,2S)-cyclohexane-1,2-dicarboxylic acid
cyclohexane-1,2-dicarboxylic acid
phthalic anhydride
2-(2-diethylamino-ethyl)-(3ar,7ac)-hexahydro-isoindole-1,3-dione
cis-2-allylhexahydroisoindole-1,3-dione
9,10-phenanthrenequinone
6β-((1Ξ)-ξ-2-carboxy-cyclohexanecarbonylamino)-penicillanic acid
CAS:120-74-1
Molecular Formula:C<sub>8</sub>H<sub>10</sub>O<sub>2</sub>
Molecular Weight:138.16
CAS:85-43-8
Molecular Formula:C<sub>8</sub>H<sub>8</sub>O<sub>3</sub>
Molecular Weight:152.15
CAS:26590-20-5
Molecular Formula:C<sub>9</sub>H<sub>10</sub>O<sub>3</sub>