Your Location:Home >Products >Organic phosphines >CyclohexyI phosphines >213697-53-1
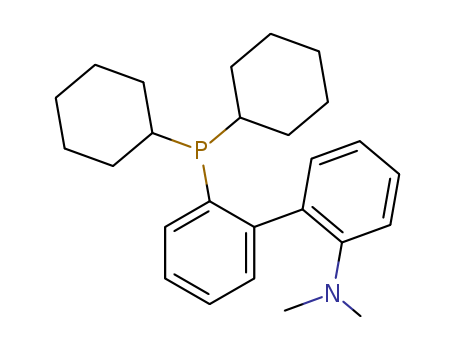
Product Details
Reaction
Ligand used in the Pd-catalyzed Suzuki coupling and animation of unactivated aryl chlorides. The reactions generally occur at room temperature and give high yields of product. Ligand used in Pd-catalyzed C-N bond formation. A general synthesis of N6-aryl-2'deoxyadenosine analogues. Ligand used in Pd-catalyzed N-arylation of indoles. Ligand used in Pd-catalyzed synthesis of aryl-tert-butyl ethers. Effective ligand in the Pd-catalyzed arylation of ester enolates. Ligand employed in arylation of ketone enolates using ortho-halo nitrobenezenes. Ligand employed in the amination of aryl nonaflates using Pd catalysts. Ligand used for cascade alkenyl amination/Heck reaction for the synthesis of indoles. Ligand used in Pd-catalyzed Kumada-Corriu cross coupling at low temperatures. Ligand used in Rh-catalyzed intramolecular hydroamination of unactivated terminal and internal alkenes with primary and secondary amines. Ligand used in Au-catalyzed cycloisomerization of allenes.
Chemical Properties
white to light yellow crystals or
Uses
suzuki reaction
Uses
Effective ligand in the Pd-catalyzed arylation of ester enolates
Uses
2-Dicyclohexylphosphino-2'-(N,N-dimethylamino)biphenyl can act as ligand used in the palladium-catalyzed Suzuki coupling and amination of unactivated aryl chlorides.
The metal-free reduction of a range of phosphine(V) oxides employing oxalyl chloride as an activating agent and hexachlorodisilane as reducing reagent has been achieved under mild reaction conditions. The method was successfully applied to the reduction of industrial waste byproduct triphenylphosphine(V) oxide, closing the phosphorus cycle to cleanly regenerate triphenylphosphine(III). Mechanistic studies and quantum chemical calculations support the attack of the dissociated chloride anion of intermediated phosphonium salt at the silicon of the disilane as the rate-limiting step for deprotection. The exquisite purity of the resultant phosphine(III) ligands after the simple removal of volatiles under reduced pressure circumvents laborious purification prior to metalation and has permitted the facile formation of important transition metal catalysts.
The palladium-catalyzed coupling of amines and aryl halides or aryl alcohol derivatives has matured from an exotic small-scale transformation into a very general, efficient and robust reaction during the last ten years. This article reports several applications of this method from an industrial vantage point, including ligand synthesis, synthesis of arylpiperazines, arylhydrazines and diarylamines. Much emphasis in placed on issues of scale-up and safety to underline the potential of C-N couplings as solutions for industrial-scale synthetic problems.
One aspect of the present invention relates to ligands for transition metals. A second aspect of the present invention relates to the use of catalysts comprising these ligands in transition metal-catalyzed carbon-heteroatom and carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions. The subject methods provide improvements in many features of the transition metal-catalyzed reactions, including the range of suitable substrates, reaction conditions, and efficiency.
Biphenyl-based phosphine ligands can be prepared on a significantly larger scale than previously possible as a result of the following discoveries and improvements to the original experimental procedure: the finding that CuCl catalyzes the coupling of hindered dialkylchlorophosphines with Grignard reagents; the development of conditions that permit ClPCy2 to be prepared and utilized in situ; the development of a more reliable large-scale preparation of 2-dimethylaminophenylmagnesium halide.
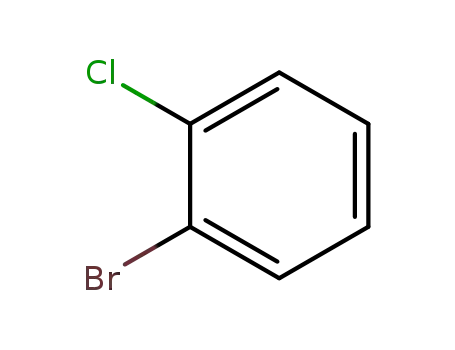
2-bromo-1-chlorobenzene
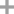
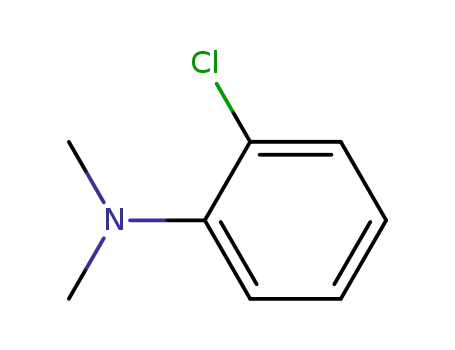
1-chloro-2-(dimethylamino)benzene

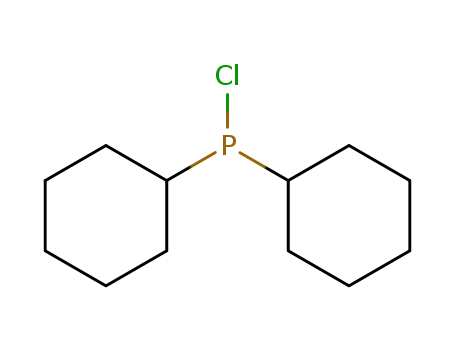
chlorodicyclohexylphosphane

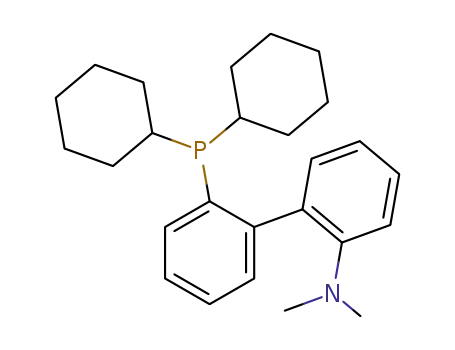
DavePhos
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
1-chloro-2-(dimethylamino)benzene;
With
magnesium; ethylene dibromide;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
for 29.5h;
Heating;
2-bromo-1-chlorobenzene;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 60 ℃;
for 2h;
chlorodicyclohexylphosphane;
With
copper(l) chloride;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 20 ℃;
for 9h;
Further stages.;
|
55% |
|
1-chloro-2-(dimethylamino)benzene;
With
magnesium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
Heating;
2-bromo-1-chlorobenzene;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
chlorodicyclohexylphosphane;
With
copper(l) iodide; lithium bromide;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
|

2-bromo-1-chlorobenzene

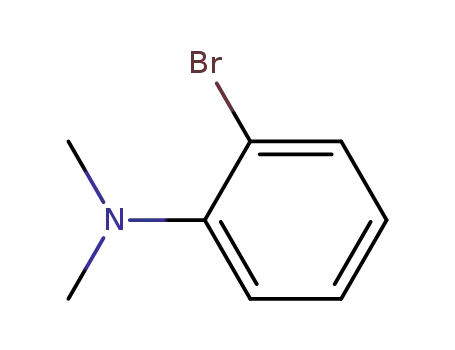
2-bromo-N,N-dimethylaniline


chlorodicyclohexylphosphane


DavePhos
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
2-bromo-N,N-dimethylaniline;
With
magnesium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
Heating;
2-bromo-1-chlorobenzene;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 60 ℃;
for 2.25h;
chlorodicyclohexylphosphane;
With
copper(l) chloride;
In
tetrahydrofuran; diethyl ether;
at 20 ℃;
for 1h;
Further stages.;
|
58% |

2-bromo-1-chlorobenzene
cyclohexyl chloride

1-chloro-2-(dimethylamino)benzene

chlorodicyclohexylphosphane
2-amino-4-p-tolyl-quinoline-3-carbonitrile
5-(4-methoxy-benzyloxy)-2-pyridin-4-yl-[1,7]naphthyridine
benzyl (3R,4S)-3-[(3,6-diethylpyrazin-2-yl)amino]-4-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxylate
1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-6-[4-(2-oxo-1-piperidinyl)phenyl]-1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-7H-pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridin-7-one
CAS:15155-41-6
Molecular Formula:C6H2Br2N2S
Molecular Weight:293.97
CAS:657408-07-6
Molecular Formula:C26H35O2P
Molecular Weight:410.5
CAS:1002345-50-7
Molecular Formula:C27H52B2F8P2
Molecular Weight:612.3