Your Location:Home >Products >Functional intermediates >7065-92-1

Product Details
InChI:InChI=1/C17H19N3O4S/c1-13(21)14-3-2-4-15(11-14)19-17-6-5-16(12-18-17)25(22,23)20-7-9-24-10-8-20/h2-6,11-12H,7-10H2,1H3,(H,18,19)
Quinoxaline is one of the privileged heterocyclic fragments for drug molecules. Quinoxaline anticancer drug candidates XK469 and CQS exhibit antiproliferative and proapoptotic properties against various cancers. Based on their chemical structures, we therefore synthesized a series of quinoxaline-1,3,4-oxadiazole hybrids and assessed their anticancer potential on human leukemia HL-60 cells. Although these hybrids exerted significant inhibition of HL-60 cell proliferation, they showed high cytotoxicity on human normal cells (WI-38). Utilizing information from molecular modelling of the hybrids to the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein, we added substructures including phenyl, piperazine, piperidine, and morpholine rings to their frameworks. The designed quinoxaline-1,3,4-oxadiazole hybrid derivatives successfully induced apoptotic response on HL-60 cells with low toxicity on WI-38 cells. Furthermore, RT-PCR analysis demonstrated that these derivatives predominantly inhibit Bcl-2 expression. Our findings highlight the great potential for the development of synthetic quinoxaline-1,3,4-oxadiazole hybrid derivatives as proapoptotic anticancer agents.
The invention discloses an organic electroluminescent compound. The structural general formula of the organic electroluminescent compound is shown in the specification, and the preparation method of the organic electroluminescent compound comprises the following steps: step 1, adding raw materials A and B into a mixed solvent of THF and deionized water, adding alkali and a palladium catalyst underthe protection of inert gas, and fully reacting at 90-100 DEG C to prepare an intermediate C; and 2, adding the intermediate C and a raw material D into DMSO, adding alkali and a catalyst DMAP underthe protection of inert gas, and fully reacting at 90-100 DEG C to obtain the product. The invention further discloses an organic light-emitting device containing the organic light-emitting compound,the organic light-emitting device comprises a first electrode, a second electrode and one or more organic matter layers arranged between the first electrode and the second electrode, and the organic matter layers contain the organic light-emitting compound. After the organic electroluminescent compound is applied to an organic electroluminescent device, the efficiency of the device can be improved, and the service life of the device can be prolonged.
The present invention relates to a novel compound, capable of improving efficiency, and low driving voltage and/or lifespan characteristics in an organic light emitting device, and to an organic light emitting device including the same. The novel compound
Described here are tandem photoelectrocyclization and [1,5]-hydride shift reactions of heteroaryl-containing bis-aryl cyclohexenone derivatives that give heteroaryl-substituted dihydrophenanthrenes. This Letter demonstrates that electrocyclization intermediates can be trapped with acid when the [1,5]-hydride shift is relatively slow. From a practical perspective, the observation that the acid-mediated reaction gives a divergent stereochemical outcome when compared with the reaction run under neutral conditions makes these transformations powerful.
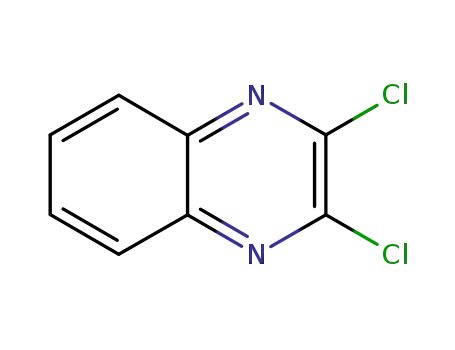
2,3-dichloroquinoxaline
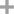
phenylboronic acid

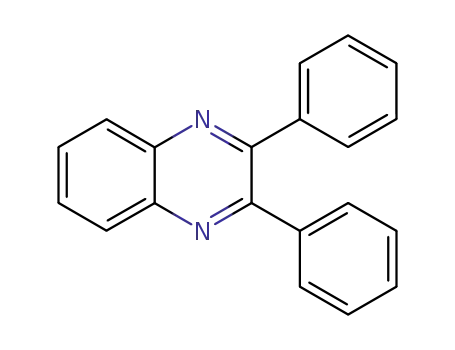
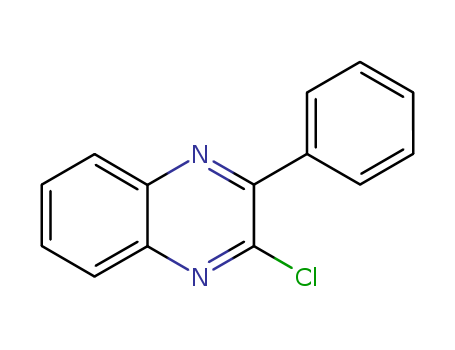
2,3-diphenylquinoxaline

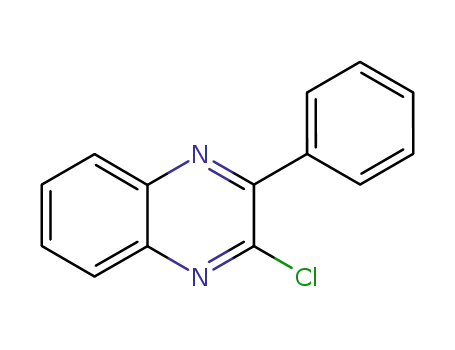
2-chloro-3-phenylquinoxaline
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
caesium carbonate;
(1-adamantylisonitrile)2PdCl2;
In
1,4-dioxane;
Further Variations:;
variation of stoichiometry of reaction partner;
Product distribution;
Heating;
|

2,3-dichloroquinoxaline


phenylboronic acid


2-chloro-3-phenylquinoxaline
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
tetrakis(triphenylphosphine) palladium(0); potassium carbonate;
In
tetrahydrofuran; water;
at 60 ℃;
for 3h;
|
90% |
|
With
caesium carbonate; tricyclohexylphosphine;
tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium (0);
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 85 ℃;
for 24h;
|
69% |
|
With
caesium carbonate; triphenylphosphine; bis(dibenzylideneacetone)-palladium(0);
at 75 ℃;
for 24h;
|
60% |
|
With
tetrakis(triphenylphosphine) palladium(0); potassium carbonate;
In
tetrahydrofuran; water;
at 90 - 100 ℃;
for 21h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
55.4% |
|
With
tetrakis(triphenylphosphine) palladium(0); potassium carbonate;
In
ethanol; water; toluene;
for 4h;
Reflux;
|
25 g |
|
With
tetrakis(triphenylphosphine) palladium(0); potassium carbonate;
In
1,4-dioxane; water;
Reflux;
Inert atmosphere;
|
907 mg |

2,3-dichloroquinoxaline

phenylboronic acid
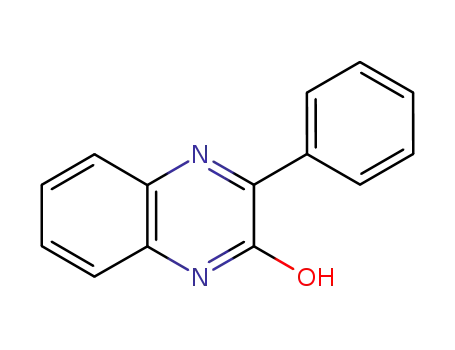
2-hydroxy-3-phenylquinoxaline
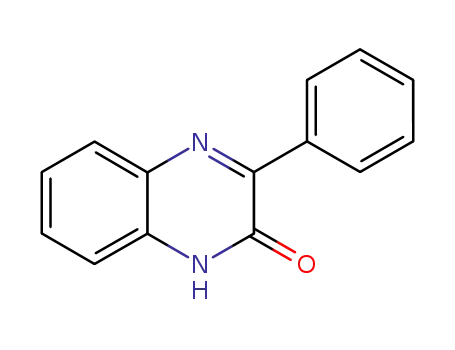
3-phenylquinoxaline-2(1H)-one
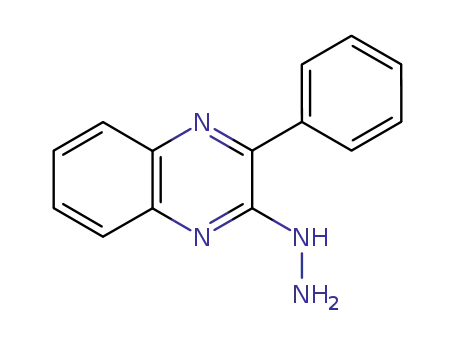
2-hydrazino-3-phenylquinoxaline
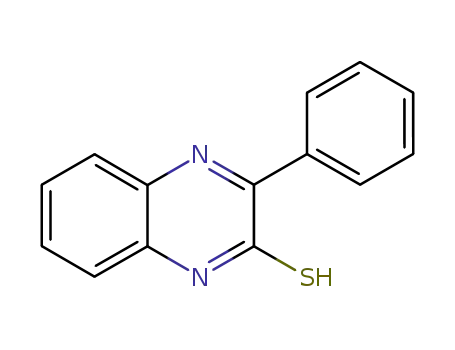
3-phenyl-1,4-quinoxalin-2(1H)-thiol
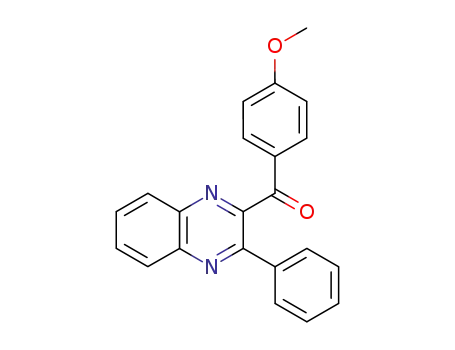
(4-methoxyphenyl)(3-phenylquinoxalin-2-yl)methanone
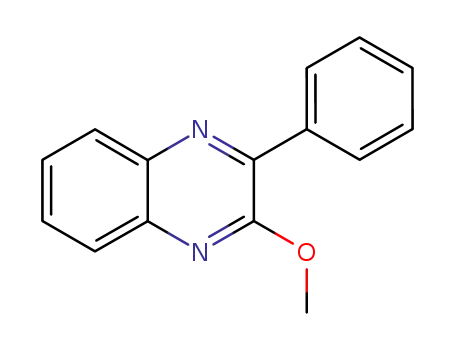
2-methoxy-3-phenylquinoxaline
CAS:159-62-6
CAS:864377-33-3
Molecular Formula:C18H14BNO2
Molecular Weight:287.1
CAS:3741-77-3
CAS:1606981-69-4